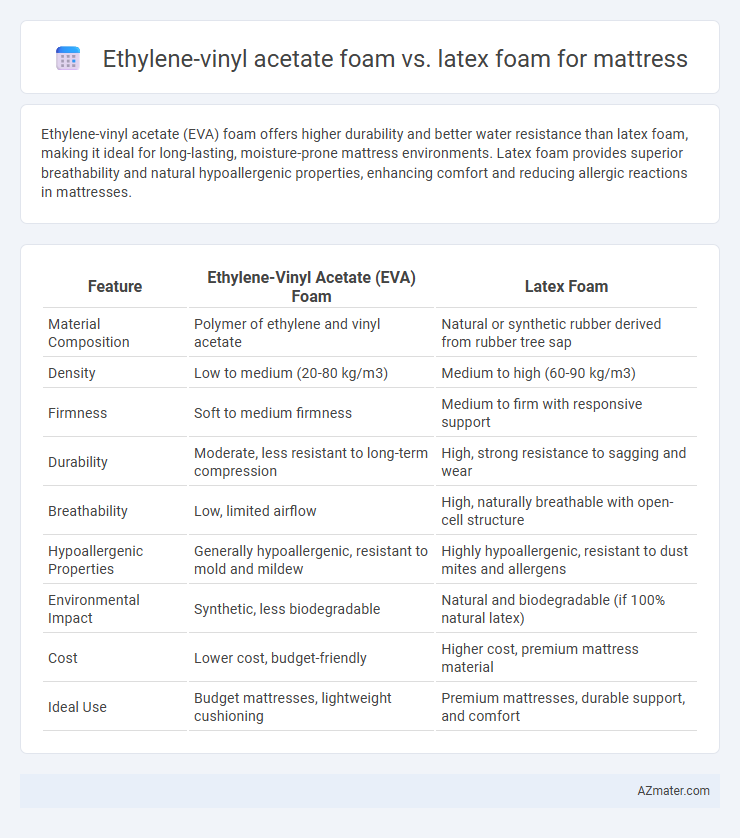
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers higher durability and better water resistance than latex foam, making it ideal for long-lasting, moisture-prone mattress environments. Latex foam provides superior breathability and natural hypoallergenic properties, enhancing comfort and reducing allergic reactions in mattresses.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam | Latex Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate | Natural or synthetic rubber derived from rubber tree sap |
| Density | Low to medium (20-80 kg/m3) | Medium to high (60-90 kg/m3) |
| Firmness | Soft to medium firmness | Medium to firm with responsive support |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to long-term compression | High, strong resistance to sagging and wear |
| Breathability | Low, limited airflow | High, naturally breathable with open-cell structure |
| Hypoallergenic Properties | Generally hypoallergenic, resistant to mold and mildew | Highly hypoallergenic, resistant to dust mites and allergens |
| Environmental Impact | Synthetic, less biodegradable | Natural and biodegradable (if 100% natural latex) |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost, premium mattress material |
| Ideal Use | Budget mattresses, lightweight cushioning | Premium mattresses, durable support, and comfort |
Introduction to Mattress Foam Materials
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers a lightweight, durable, and resilient option commonly used in mattress cushioning, providing excellent shock absorption and moisture resistance. Latex foam, derived from natural or synthetic sources, delivers superior elasticity, breathability, and hypoallergenic properties, often favored for pressure relief and temperature regulation in bedding. Both materials differ significantly in terms of density, firmness, and environmental impact, making material choice essential based on mattress performance and consumer preferences.
What is Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam?
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a durable, flexible polymer foam commonly used in mattress production for its excellent shock absorption and lightweight properties. Its closed-cell structure provides superior moisture resistance and enhanced durability compared to latex foam, making it ideal for longer-lasting mattress support. EVA foam's hypoallergenic and antimicrobial characteristics contribute to a healthier sleep environment, distinguishing it from natural latex.
What is Latex Foam?
Latex foam is a natural or synthetic material made from the sap of rubber trees or petrochemicals, known for its durability, elasticity, and breathability, making it a popular choice for mattresses. Unlike ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, latex foam offers superior pressure relief and hypoallergenic properties, providing enhanced comfort and support. Its open-cell structure promotes airflow and temperature regulation, ensuring a cooler and healthier sleep environment compared to the denser EVA foam.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers denser support and better shock absorption compared to latex foam, making it ideal for users seeking firmer mattress support with enhanced durability. Latex foam provides superior breathability and adaptive contouring, delivering a softer, more responsive sleep surface that reduces pressure points effectively. Both foams differ significantly in elasticity and heat retention, with latex foam typically promoting cooler, more comfortable sleep for those sensitive to temperature.
Durability and Longevity
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior durability and resistance to compression compared to latex foam, making it highly resilient under long-term use. Latex foam, while naturally elastic and resistant to sagging, tends to degrade faster under heavy weight and frequent pressure. EVA foam maintains structural integrity longer, providing extended mattress longevity particularly in high-traffic or intensive use scenarios.
Heat Retention and Breathability
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits lower heat retention due to its open-cell structure, allowing better airflow and enhanced breathability compared to denser latex foam. Latex foam, while offering superior durability and pressure relief, tends to trap more body heat because of its natural elasticity and closed-cell composition, which reduces ventilation. Selecting EVA foam benefits those prioritizing cooler sleep environments, whereas latex foam suits individuals seeking supportive comfort with moderate temperature regulation.
Allergen Resistance and Hypoallergenic Properties
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits strong allergen resistance due to its closed-cell structure, which inhibits dust mite infiltration and mold growth, making it highly suitable for allergy-sensitive sleepers. Latex foam is naturally hypoallergenic and resistant to dust mites, mold, and mildew because of its antimicrobial properties, providing a safe sleep environment for individuals with allergies. Both foams offer excellent hypoallergenic benefits, but latex foam's natural origin enhances its appeal for those seeking chemical-free allergen resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a petroleum-based product that poses environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradability and difficulty in recycling, contributing to long-term landfill waste. In contrast, natural latex foam, derived from rubber tree sap, is biodegradable, renewable, and often produced using sustainable harvesting methods that minimize deforestation and chemical processing. Choosing latex foam mattresses significantly reduces ecological footprints by supporting renewable resources and promoting circular economy principles compared to synthetic EVA foam.
Price and Value Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam mattresses generally offer a lower price point compared to latex foam, making them a budget-friendly option for consumers seeking affordability. Latex foam mattresses, while more expensive, provide superior durability, natural resistance to dust mites and mold, and better pressure relief, which enhances overall sleep quality and long-term value. Investing in latex foam typically yields greater comfort and lifespan, justifying the higher initial cost through improved health benefits and reduced replacement frequency.
Which Foam Is Best for Your Mattress Needs?
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior durability and water resistance, making it ideal for mattresses requiring long-term support and moisture control. Latex foam provides excellent breathability, natural hypoallergenic properties, and responsive comfort, which benefits sleepers seeking eco-friendly and pressure-relieving mattresses. The best foam depends on individual needs: choose EVA for durability and moisture resistance or latex for natural comfort and breathability.
Infographic: Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam vs Latex foam for Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com