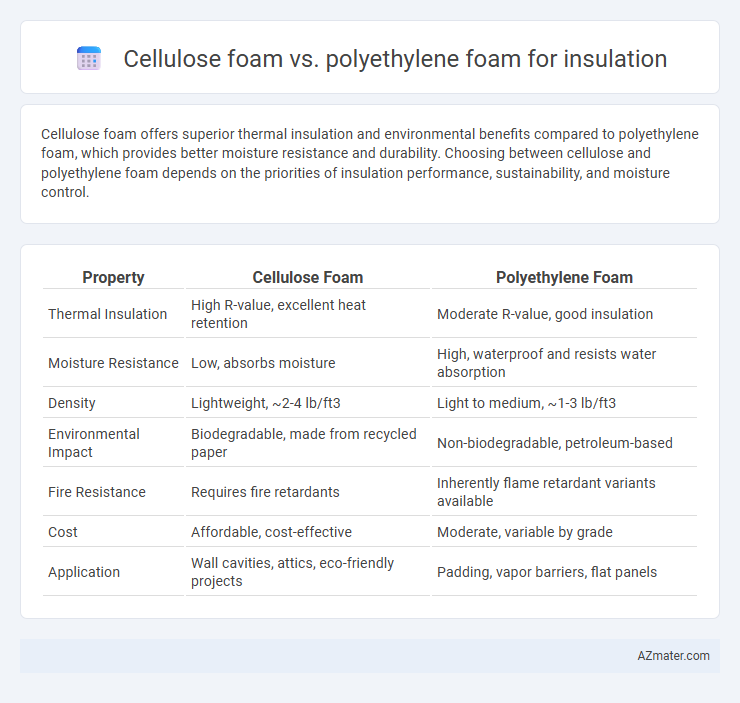
Cellulose foam offers superior thermal insulation and environmental benefits compared to polyethylene foam, which provides better moisture resistance and durability. Choosing between cellulose and polyethylene foam depends on the priorities of insulation performance, sustainability, and moisture control.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellulose Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High R-value, excellent heat retention | Moderate R-value, good insulation |
| Moisture Resistance | Low, absorbs moisture | High, waterproof and resists water absorption |
| Density | Lightweight, ~2-4 lb/ft3 | Light to medium, ~1-3 lb/ft3 |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, made from recycled paper | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Fire Resistance | Requires fire retardants | Inherently flame retardant variants available |
| Cost | Affordable, cost-effective | Moderate, variable by grade |
| Application | Wall cavities, attics, eco-friendly projects | Padding, vapor barriers, flat panels |
Introduction to Foam Insulation Materials
Cellulose foam and polyethylene foam are commonly used insulation materials with distinct properties influencing their thermal performance. Cellulose foam, derived from recycled paper treated with fire-retardant chemicals, offers excellent sound absorption and eco-friendly attributes, while polyethylene foam, a closed-cell plastic polymer, provides superior moisture resistance and higher compressive strength. Selecting between these foams depends on factors such as R-value requirements, application environment, and environmental impact.
What Is Cellulose Foam?
Cellulose foam is an eco-friendly insulation material derived primarily from recycled paper products treated with fire retardants to enhance safety and durability. It offers excellent thermal performance with high R-values and superior sound absorption capabilities compared to polyethylene foam. Unlike polyethylene foam, cellulose foam is biodegradable and provides enhanced moisture regulation, making it an ideal choice for sustainable building projects.
What Is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell foam made from polyethylene resin, known for its excellent thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and cushioning properties. It offers superior durability and is commonly used in packaging, construction, and insulation applications due to its ability to resist water absorption and provide consistent thermal performance. Compared to cellulose foam, polyethylene foam provides enhanced resistance to mold, mildew, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for environments where durability and moisture control are critical.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Cellulose foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.03 W/m*K, which effectively reduces heat transfer compared to polyethylene foam's conductivity of approximately 0.04 W/m*K. The denser structure of cellulose foam enhances its thermal resistance (R-value), making it more efficient for maintaining consistent indoor temperatures and reducing energy consumption. Polyethylene foam, while lightweight and moisture-resistant, generally exhibits lower thermal insulation performance, leading to higher heat loss in building applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellulose foam, derived from recycled paper fibers, offers a highly sustainable insulation option with low embodied energy and excellent biodegradability, reducing landfill waste and reliance on fossil fuels. Polyethylene foam, although effective for insulation, is petroleum-based, non-biodegradable, and contributes to plastic pollution, posing significant environmental challenges throughout its lifecycle. Choosing cellulose foam supports eco-friendly building practices by minimizing carbon footprint and enhancing resource efficiency compared to conventional polyethylene alternatives.
Moisture and Water Resistance
Polyethylene foam exhibits superior moisture and water resistance compared to cellulose foam, making it ideal for environments prone to high humidity or direct water exposure. Cellulose foam, while effective in insulation, is more susceptible to moisture absorption, which can lead to reduced thermal performance and potential mold growth. For applications requiring prolonged exposure to moisture, polyethylene foam offers enhanced durability and maintains insulation efficacy under wet conditions.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Cellulose foam insulation offers superior fire resistance compared to polyethylene foam, as it contains fire-retardant additives like borates that help slow combustion and reduce smoke production. Polyethylene foam is highly flammable and can release toxic fumes when burned, posing greater safety risks in fire scenarios. Choosing cellulose foam enhances building safety by providing a more fire-resistant and less hazardous insulation material.
Durability and Longevity
Cellulose foam offers exceptional durability due to its dense fiber composition, resisting compression and settling over time, which maintains insulation performance for decades. Polyethylene foam demonstrates high longevity by resisting moisture, chemicals, and physical impacts, making it less prone to degradation in harsh environments. Both materials provide long-term insulation benefits, but cellulose excels in thermal stability while polyethylene foam outperforms in moisture and chemical resistance.
Cost Analysis: Cellulose vs Polyethylene Foam
Cellulose foam insulation generally costs between $0.60 and $2.00 per square foot, making it more cost-effective compared to polyethylene foam, which ranges from $1.50 to $3.00 per square foot. The lower raw material and manufacturing costs of cellulose foam contribute to its affordability, while polyethylene foam offers higher durability and moisture resistance at a premium price. Budget-conscious insulation projects often favor cellulose foam for its balance of cost and performance in thermal efficiency.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Cellulose foam excels in eco-friendly insulation for residential and commercial buildings, providing superior soundproofing and thermal resistance due to its natural composition and fire-retardant properties. Polyethylene foam is ideal for packaging, sports equipment, and waterproof insulation applications, offering excellent chemical resistance, moisture barrier capabilities, and impact cushioning. Choosing between cellulose and polyethylene foam depends on the need for sustainable, breathable insulation versus durable, moisture-resistant padding in specific environments.
Infographic: Cellulose foam vs Polyethylene foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com