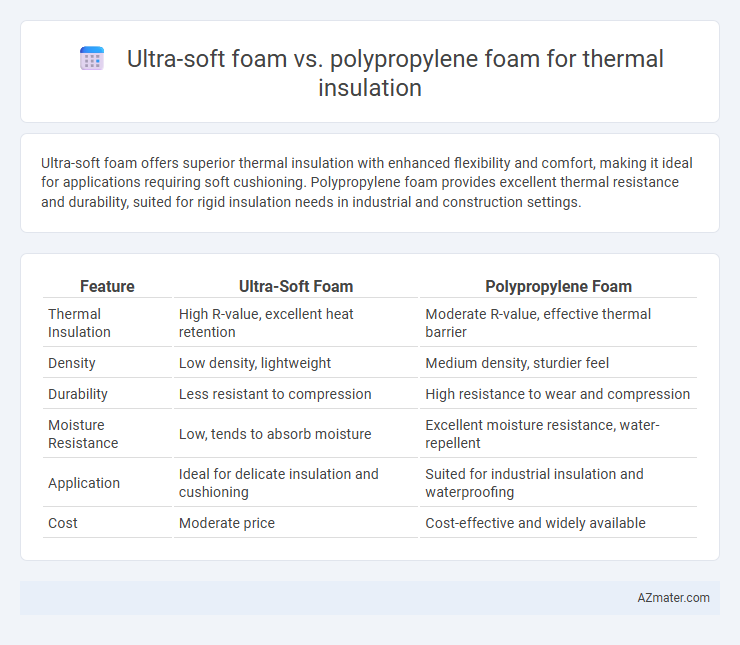
Ultra-soft foam offers superior thermal insulation with enhanced flexibility and comfort, making it ideal for applications requiring soft cushioning. Polypropylene foam provides excellent thermal resistance and durability, suited for rigid insulation needs in industrial and construction settings.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Soft Foam | Polypropylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High R-value, excellent heat retention | Moderate R-value, effective thermal barrier |
| Density | Low density, lightweight | Medium density, sturdier feel |
| Durability | Less resistant to compression | High resistance to wear and compression |
| Moisture Resistance | Low, tends to absorb moisture | Excellent moisture resistance, water-repellent |
| Application | Ideal for delicate insulation and cushioning | Suited for industrial insulation and waterproofing |
| Cost | Moderate price | Cost-effective and widely available |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Materials
Ultra-soft foam and polypropylene foam serve distinct roles in thermal insulation, with ultra-soft foam offering superior flexibility and enhanced sound absorption, making it ideal for applications requiring comfort and noise reduction. Polypropylene foam exhibits excellent thermal resistance, durability, and moisture resistance, which ensures long-lasting insulation in industrial and construction environments. Both materials contribute effectively to reducing heat transfer, yet polypropylene foam is generally preferred for high-performance thermal insulation due to its structural stability and energy efficiency.
What is Ultra-Soft Foam?
Ultra-soft foam is a highly pliable material characterized by its low density and exceptional cushioning properties, making it ideal for thermal insulation in environments requiring gentle yet effective heat retention. Its cellular structure traps air efficiently, providing superior thermal resistance compared to traditional materials like polypropylene foam, which offers higher rigidity and moisture resistance but less flexibility. Ultra-soft foam's enhanced compressibility and breathability ensure it adapts well to varied surfaces, optimizing insulation performance in applications such as wearable technology, automotive interiors, and acoustic panels.
Understanding Polypropylene Foam
Polypropylene foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure that effectively reduces heat transfer and moisture absorption. This material provides excellent durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for industrial and building insulation applications compared to ultra-soft foam. Understanding polypropylene foam's properties highlights its ability to maintain consistent thermal performance under varying environmental conditions.
Key Properties Comparison
Ultra-soft foam offers superior compressibility and cushioning with low thermal conductivity around 0.03 W/mK, ideal for delicate applications requiring both insulation and comfort. Polypropylene foam typically exhibits higher rigidity and resilience, thermal conductivity close to 0.04 W/mK, providing durable, moisture-resistant insulation for industrial and construction uses. Key differences include ultra-soft foam's enhanced flexibility and lower density compared to polypropylene foam's strength, chemical resistance, and longer lifespan under thermal stress.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Ultra-soft foam typically offers lower thermal insulation performance due to its open-cell structure, which allows more air permeability compared to the closed-cell composition of polypropylene foam. Polypropylene foam excels in thermal insulation because its dense, closed-cell structure significantly reduces heat transfer and improves energy efficiency in applications. The higher R-value of polypropylene foam makes it a preferred choice for effective thermal barriers in building and packaging industries.
Durability and Longevity
Ultra-soft foam offers moderate durability but tends to degrade faster under prolonged heat exposure compared to polypropylene foam, which exhibits superior resistance to thermal aging and environmental wear. Polypropylene foam maintains its structural integrity and insulation properties over extended periods, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term thermal performance. Its enhanced chemical and moisture resistance further contributes to its longevity in demanding insulation environments.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Ultra-soft foam offers limited moisture resistance and can absorb water, compromising its thermal insulation performance over time. Polypropylene foam exhibits superior chemical resistance and repels moisture effectively, maintaining its insulating properties in humid and corrosive environments. This makes polypropylene foam a preferred choice for applications requiring long-term durability against moisture and chemicals.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ultra-soft foam typically contains higher levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and is less recyclable, contributing to greater environmental pollution compared to polypropylene foam, which is known for its durability and recyclability. Polypropylene foam offers enhanced sustainability due to its lower global warming potential (GWP) and reduced greenhouse gas emissions during production, making it a more eco-friendly choice for thermal insulation. Both materials provide thermal resistance, but polypropylene foam's ability to be efficiently recycled and its lower toxicity profile significantly reduce its environmental footprint.
Cost Analysis and Practical Applications
Ultra-soft foam typically offers superior thermal insulation at a higher cost compared to polypropylene foam, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum energy efficiency in residential and specialized commercial settings. Polypropylene foam presents a more cost-effective solution with adequate insulation properties, suitable for large-scale industrial uses and budget-conscious projects. The choice between these materials hinges on balancing upfront investment against long-term thermal performance and application-specific demands.
Which Foam is Best for Thermal Insulation?
Ultra-soft foam offers excellent thermal insulation due to its low density and high air-trapping capacity, reducing heat transfer effectively. Polypropylene foam is also a strong insulator, providing durability, moisture resistance, and a higher melting point which is ideal for industrial applications. For superior thermal insulation, ultra-soft foam generally outperforms polypropylene foam in residential and lightweight uses, while polypropylene foam is preferred in environments requiring enhanced mechanical strength and chemical resistance.
Infographic: Ultra-soft foam vs Polypropylene foam for Thermal insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com