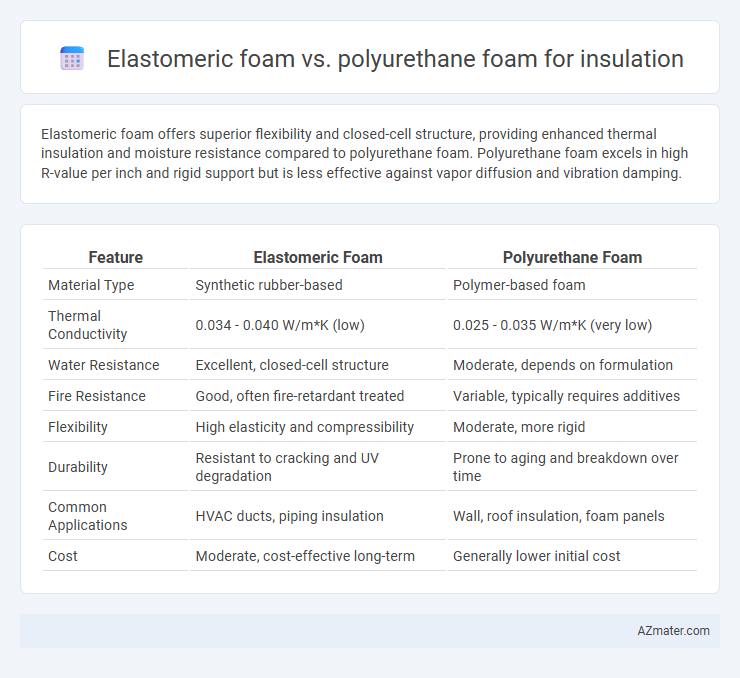
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and closed-cell structure, providing enhanced thermal insulation and moisture resistance compared to polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam excels in high R-value per inch and rigid support but is less effective against vapor diffusion and vibration damping.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elastomeric Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic rubber-based | Polymer-based foam |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.034 - 0.040 W/m*K (low) | 0.025 - 0.035 W/m*K (very low) |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, closed-cell structure | Moderate, depends on formulation |
| Fire Resistance | Good, often fire-retardant treated | Variable, typically requires additives |
| Flexibility | High elasticity and compressibility | Moderate, more rigid |
| Durability | Resistant to cracking and UV degradation | Prone to aging and breakdown over time |
| Common Applications | HVAC ducts, piping insulation | Wall, roof insulation, foam panels |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective long-term | Generally lower initial cost |
Overview of Elastomeric and Polyurethane Foams
Elastomeric foam is a closed-cell insulation material known for its flexibility, resistance to moisture, and excellent thermal performance, making it ideal for HVAC pipes and ducts. Polyurethane foam, including both rigid and spray forms, offers high R-values per inch and strong structural support, commonly used in wall, roof, and floor insulation. Both materials provide energy efficiency, but elastomeric foam excels in vapor barrier properties while polyurethane foam is favored for its versatility and higher compressive strength.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility, closed-cell structure, and excellent resistance to moisture, making it ideal for HVAC insulation and preventing condensation. Polyurethane foam exhibits higher insulating R-values per inch and greater compressive strength, suitable for structural insulation and thermal efficiency. Both materials provide effective thermal insulation, but elastomeric foam outperforms in durability against mold and UV exposure, while polyurethane foam excels in rigidity and load-bearing capacity.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Elastomeric foam offers superior thermal insulation performance due to its closed-cell structure, which minimizes air and moisture infiltration, maintaining consistent R-values over time. Polyurethane foam provides excellent initial thermal resistance with higher R-values per inch but may degrade when exposed to moisture, reducing its effectiveness. Elastomeric foam's flexibility and resilience make it ideal for applications requiring long-term thermal stability and moisture resistance.
Moisture and Water Resistance
Elastomeric foam offers superior moisture and water resistance compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for insulation in damp or wet environments. Its closed-cell structure prevents water absorption and resists mold and mildew growth, enhancing durability and maintaining thermal performance. Polyurethane foam, while effective for insulation, tends to absorb moisture over time, which can reduce its insulating properties and promote microbial growth.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Elastomeric foam insulation exhibits superior fire resistance compared to polyurethane foam, as it is typically self-extinguishing and less likely to propagate flames, making it safer for use in buildings requiring stringent fire codes. Polyurethane foam, while offering excellent thermal insulation values, tends to be more flammable and produces toxic smoke when burned, posing greater safety risks in fire scenarios. Choosing elastomeric foam enhances occupant safety by minimizing fire hazards and complying with fire-resistant building standards.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and ease of installation, conforming effortlessly to pipes and irregular shapes without cracking or breaking, making it ideal for complex insulation tasks. Polyurethane foam, while providing excellent thermal insulation properties, is less flexible and often requires specialized cutting and fitting tools during installation. The inherent elasticity of elastomeric foam reduces installation time and labor costs, particularly in environments needing frequent maintenance or adjustments.
Durability and Lifespan
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior durability and lifespan compared to polyurethane foam due to its closed-cell structure, which resists moisture, UV rays, and microbial growth effectively. Its flexible nature maintains insulation performance over time, reducing cracks and degradation under thermal cycling. Polyurethane foam, while effective initially, tends to become brittle and lose insulating properties faster when exposed to environmental stressors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Elastomeric foam offers superior environmental benefits compared to polyurethane foam due to its lower global warming potential (GWP) and zero ozone depletion potential (ODP), making it a more sustainable choice for insulation. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent thermal performance and moisture resistance, reducing energy consumption and extending building lifespan. Polyurethane foam, while effective in insulation, typically involves higher embodied carbon and the use of blowing agents that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, impacting long-term environmental sustainability.
Cost Analysis and Value for Money
Elastomeric foam offers higher upfront costs compared to polyurethane foam but provides superior thermal insulation and durability, resulting in lower long-term energy expenses. Polyurethane foam features a lower initial price and good insulation properties but may require more frequent replacement or maintenance, increasing overall lifecycle costs. Evaluating cost analysis based on efficiency, lifespan, and maintenance needs, elastomeric foam delivers better value for money in energy savings and durability for insulation applications.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Elastomeric foam excels in HVAC systems and refrigeration insulation due to its flexibility, moisture resistance, and ability to prevent condensation, making it ideal for pipes and ductwork. Polyurethane foam offers superior thermal insulation and structural strength, commonly used in building walls, roofs, and cold storage facilities for energy efficiency. Each material's unique properties determine optimal use: elastomeric foam for moisture-prone environments and polyurethane foam for applications requiring high R-values and rigidity.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Polyurethane foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com