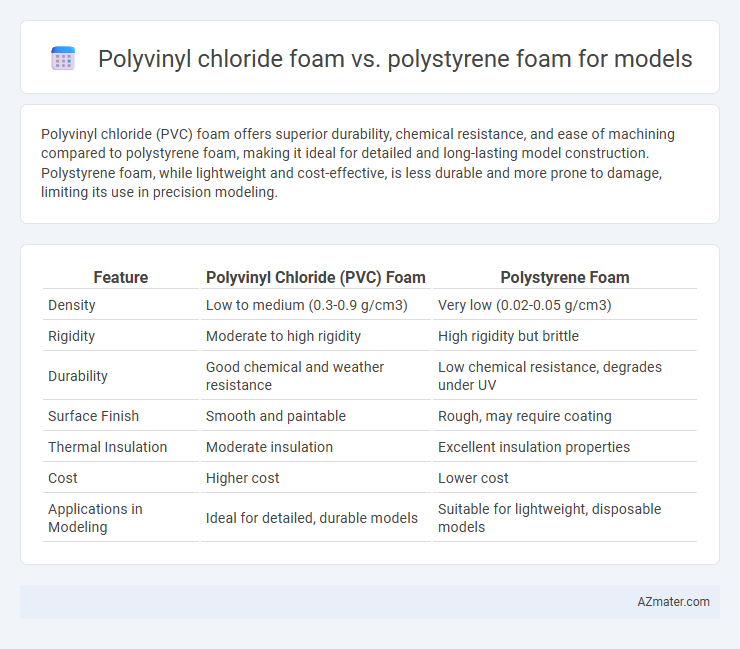
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior durability, chemical resistance, and ease of machining compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for detailed and long-lasting model construction. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, is less durable and more prone to damage, limiting its use in precision modeling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium (0.3-0.9 g/cm3) | Very low (0.02-0.05 g/cm3) |
| Rigidity | Moderate to high rigidity | High rigidity but brittle |
| Durability | Good chemical and weather resistance | Low chemical resistance, degrades under UV |
| Surface Finish | Smooth and paintable | Rough, may require coating |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation | Excellent insulation properties |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Applications in Modeling | Ideal for detailed, durable models | Suitable for lightweight, disposable models |
Introduction to Model Foams: PVC vs Polystyrene
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers higher durability, chemical resistance, and structural stability compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for detailed and long-lasting models. Polystyrene foam, lightweight and easy to shape, provides excellent insulation and is cost-effective but is less resistant to solvents and mechanical stress. Model makers often choose PVC foam for precision projects requiring strength, while polystyrene suits budget-conscious builds and rapid prototyping.
Material Overview: Polyvinyl Chloride Foam
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam is a lightweight, durable material commonly used in model making due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and weather resistance. Unlike Polystyrene foam, PVC foam offers higher impact resistance and can be easily cut, shaped, and painted without crumbling or melting. Its closed-cell structure provides superior dimensional stability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for detailed, long-lasting architectural and prototype models.
Material Overview: Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam, a lightweight and rigid thermoplastic, offers exceptional moldability and smooth surface finish, ideal for precise model making. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent insulation and dimensional stability, enhancing the durability of detailed scale models. Compared to polyvinyl chloride foam, polystyrene exhibits superior rigidity and cost-effectiveness but is less flexible and more brittle under stress.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers higher density and greater impact resistance compared to polystyrene foam, making it more durable for model construction. PVC foam exhibits superior moisture resistance and flexibility, while polystyrene foam is lighter but more brittle and prone to fracturing under stress. Thermal insulation properties favor polystyrene foam due to its low thermal conductivity, whereas PVC foam provides enhanced structural strength and chemical stability.
Weight and Density Differences
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam typically has a higher density ranging from 40 to 200 kg/m3 compared to polystyrene foam, which generally falls between 15 to 50 kg/m3, making PVC foam denser and heavier. This increased density provides PVC foam with superior strength and durability for detailed model construction, whereas polystyrene foam offers lighter weight that benefits models requiring easy handling and transport. Selecting between these foams depends on the balance needed between sturdiness and lightweight properties in model applications.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior durability and impact resistance compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for models subjected to frequent handling or mechanical stress. PVC foam's closed-cell structure resists dents and deformation, while polystyrene foam, typically more brittle, is prone to cracking under impact. For long-lasting model construction with enhanced shock absorption, PVC foam provides a more robust and resilient material choice.
Ease of Shaping and Model Construction
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior ease of shaping due to its smooth surface and consistent density, allowing for precise cutting and sanding without crumbling. Polystyrene foam tends to be more brittle and prone to chipping, requiring careful handling and specific tools like hot-wire cutters for effective shaping. Model construction benefits from PVC foam's durability and adaptability, making it ideal for detailed, sturdy prototypes compared to the more fragile and less resilient polystyrene foam.
Surface Finish and Paint Compatibility
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers a smoother surface finish compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for detailed model applications that require fine texture and sharp edges. PVC foam's surface is denser and less porous, which enhances paint adhesion and reduces the chances of surface imperfections such as bubbling or peeling. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and easy to shape, often requires additional priming to achieve comparable paint compatibility and can result in uneven finishes due to its open-cell structure.
Environmental Impact and Safety Concerns
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam and polystyrene foam differ significantly in environmental impact and safety concerns when used for models. PVC foam tends to have higher environmental toxicity due to chlorine content, leading to harmful dioxin emissions during production and disposal, while polystyrene foam is less toxic but highly flammable and can release styrene, a hazardous compound. PVC foam offers better flame retardancy and durability, whereas polystyrene foam poses greater risks of off-gassing and environmental persistence in landfills.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam generally costs more than polystyrene foam but offers greater durability and resistance to moisture, making it a preferred choice for long-term or outdoor model applications. Polystyrene foam, widely available and inexpensive, is favored for quick prototyping or indoor models due to its ease of cutting and shaping. The widespread availability of polystyrene foam across craft and hardware stores significantly lowers initial investment, while PVC foam's higher price reflects superior material properties and extended lifespan.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Polystyrene foam for Model
 azmater.com
azmater.com