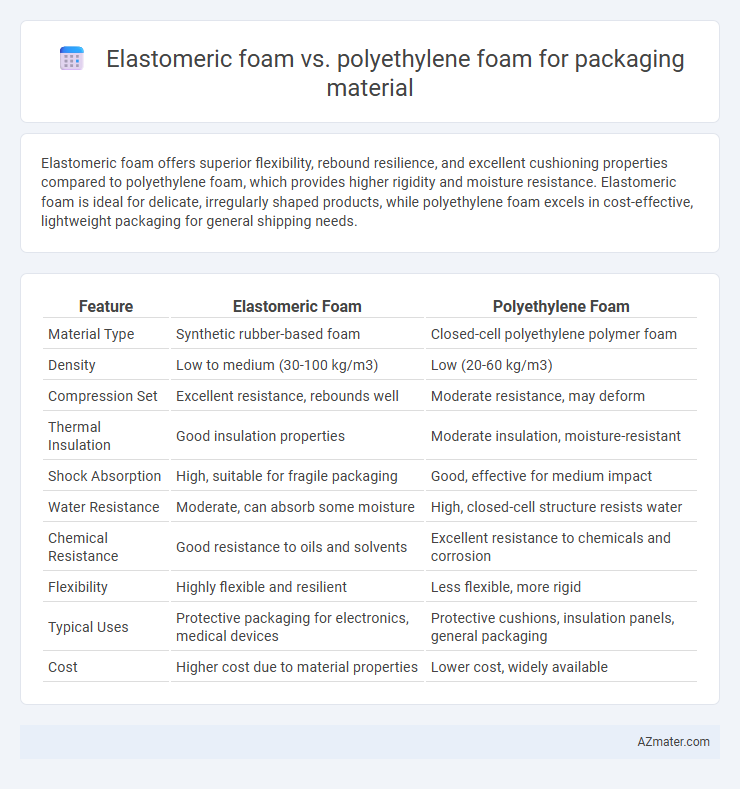
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility, rebound resilience, and excellent cushioning properties compared to polyethylene foam, which provides higher rigidity and moisture resistance. Elastomeric foam is ideal for delicate, irregularly shaped products, while polyethylene foam excels in cost-effective, lightweight packaging for general shipping needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elastomeric Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic rubber-based foam | Closed-cell polyethylene polymer foam |
| Density | Low to medium (30-100 kg/m3) | Low (20-60 kg/m3) |
| Compression Set | Excellent resistance, rebounds well | Moderate resistance, may deform |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation properties | Moderate insulation, moisture-resistant |
| Shock Absorption | High, suitable for fragile packaging | Good, effective for medium impact |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, can absorb some moisture | High, closed-cell structure resists water |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Excellent resistance to chemicals and corrosion |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and resilient | Less flexible, more rigid |
| Typical Uses | Protective packaging for electronics, medical devices | Protective cushions, insulation panels, general packaging |
| Cost | Higher cost due to material properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Foam Packaging Materials
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and resilience, making it ideal for cushioning sensitive or irregularly shaped items in packaging applications. Polyethylene foam provides excellent moisture resistance and impact absorption, frequently used for protecting electronics and fragile goods during shipping. Both foams serve distinct packaging needs, with elastomeric foam excelling in compression recovery and polyethylene foam favored for lightweight and moisture-barrier properties.
Overview of Elastomeric Foam
Elastomeric foam is a flexible, resilient material known for its excellent cushioning and shock absorption properties, making it ideal for protective packaging applications. Its closed-cell structure provides superior resistance to moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations compared to polyethylene foam. Often used in delicate electronics and sensitive equipment packaging, elastomeric foam enhances impact protection while maintaining lightweight durability.
Overview of Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material known for its excellent shock absorption and moisture resistance, making it ideal for protective packaging applications. Its high tensile strength and durability provide reliable cushioning for fragile items during transportation and storage. Commonly used in electronics, medical devices, and food packaging, polyethylene foam effectively minimizes damage and extends product shelf life.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior flexibility and resilience compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for applications requiring repeated compression and impact absorption. Polyethylene foam offers higher compressive strength and excellent resistance to moisture, which enhances its durability in heavy-load packaging scenarios. The mechanical properties of elastomeric foam favor cushioning sensitive products, while polyethylene foam provides robust protection against mechanical stress and environmental factors.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to polyethylene foam due to its closed-cell structure, which effectively minimizes heat transfer. The synthetic rubber composition of elastomeric foam provides higher resistance to temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for packaging temperature-sensitive products. Polyethylene foam, while lightweight and cushioning, offers lower thermal resistance and is better suited for shock absorption rather than insulation.
Cushioning and Shock Absorption
Elastomeric foam offers superior cushioning and shock absorption due to its open-cell structure, which provides excellent resilience and energy dispersion, making it ideal for protecting sensitive or heavy items during transit. Polyethylene foam, characterized by its closed-cell structure, provides good cushioning with higher compressive strength and moisture resistance but generally less shock absorption compared to elastomeric foam. Choosing elastomeric foam enhances protection against impact forces, while polyethylene foam excels in lightweight, moisture-resistant packaging applications.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, making it highly effective in preventing water absorption and protecting sensitive goods during shipping. Polyethylene foam also offers good moisture resistance but is generally less effective against harsh chemicals, whereas elastomeric foam provides enhanced chemical resistance, safeguarding packaging contents from oils, solvents, and acids. Both foams are lightweight and cushioning, but elastomeric foam's improved durability under chemical exposure makes it ideal for packaging applications requiring stringent protective barriers.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Elastomeric foam, commonly made from synthetic rubbers like neoprene or nitrile, offers moderate recyclability but often faces challenges due to its crosslinked structure, leading to limited biodegradability and longer environmental persistence. Polyethylene foam, derived from polyethylene resins, boasts higher recyclability rates with established recovery processes and presents a lower environmental footprint due to its potential for reuse and ease of recycling into new foam products. Evaluating the environmental impact, polyethylene foam generally outperforms elastomeric foam by contributing less to landfill waste and supporting circular economy goals in packaging material applications.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Elastomeric foam generally offers higher cost efficiency due to its superior cushioning properties, reducing damage-related expenses during shipping, though it tends to be more expensive upfront than polyethylene foam. Polyethylene foam is widely available and cost-effective for basic packaging needs, making it a popular choice for bulk or less delicate items. Availability of polyethylene foam is higher globally, with diverse density options, while elastomeric foam is often preferred for specialized packaging requiring enhanced flexibility and resilience.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type
Elastomeric foam excels in packaging applications requiring high resilience, flexibility, and excellent shock absorption, making it ideal for delicate electronics, medical devices, and sensitive instruments. Polyethylene foam is best suited for packaging heavy or bulky items, offering superior impact resistance, moisture barrier properties, and lightweight cushioning for automotive parts, industrial equipment, and consumer goods. Selecting the appropriate foam type depends on the specific protection needs, environmental conditions, and weight considerations of the packaged product.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging material
 azmater.com
azmater.com