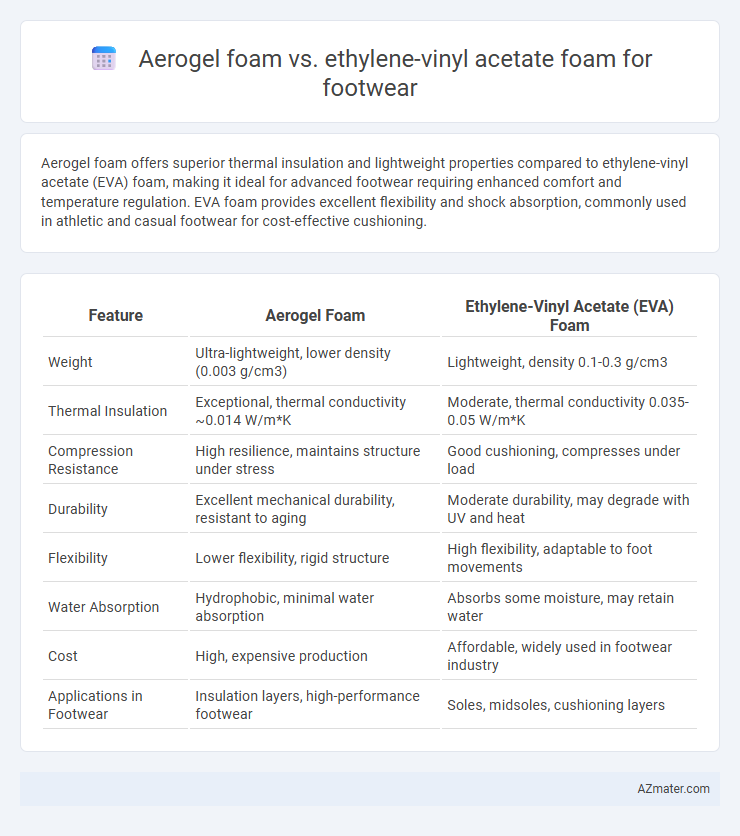
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, making it ideal for advanced footwear requiring enhanced comfort and temperature regulation. EVA foam provides excellent flexibility and shock absorption, commonly used in athletic and casual footwear for cost-effective cushioning.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aerogel Foam | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Ultra-lightweight, lower density (0.003 g/cm3) | Lightweight, density 0.1-0.3 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Insulation | Exceptional, thermal conductivity ~0.014 W/m*K | Moderate, thermal conductivity 0.035-0.05 W/m*K |
| Compression Resistance | High resilience, maintains structure under stress | Good cushioning, compresses under load |
| Durability | Excellent mechanical durability, resistant to aging | Moderate durability, may degrade with UV and heat |
| Flexibility | Lower flexibility, rigid structure | High flexibility, adaptable to foot movements |
| Water Absorption | Hydrophobic, minimal water absorption | Absorbs some moisture, may retain water |
| Cost | High, expensive production | Affordable, widely used in footwear industry |
| Applications in Footwear | Insulation layers, high-performance footwear | Soles, midsoles, cushioning layers |
Introduction to Advanced Footwear Foams
Aerogel foam and Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam represent two advanced materials increasingly used in high-performance footwear for their unique cushioning properties. Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight cushioning due to its nanoporous structure, enhancing comfort and temperature regulation in footwear. EVA foam provides excellent shock absorption and flexibility, making it widely favored for its durability and impact resistance in athletic and casual shoes.
What is Aerogel Foam?
Aerogel foam is an ultra-lightweight material composed of a porous silica-based matrix that offers exceptional thermal insulation and shock absorption, making it ideal for advanced footwear applications. Compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, aerogel foam provides superior compressive strength and lower thermal conductivity, enhancing both comfort and energy efficiency in shoes. These properties enable manufacturers to create lightweight, durable footwear that maintains temperature regulation and impact resistance better than traditional EVA foam.
Understanding Ethylene-vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a lightweight, flexible, and highly durable material widely used in footwear midsoles for its excellent shock absorption and cushioning properties. Compared to aerogel foam, EVA offers superior resilience and energy return, making it ideal for athletic and everyday shoes requiring impact protection and comfort. EVA foam's moisture resistance and ease of molding also contribute to its popularity in footwear manufacturing, enhancing overall performance and wearability.
Comparative Cushioning Performance
Aerogel foam offers superior cushioning performance in footwear due to its exceptional energy absorption and ultra-lightweight properties, reducing impact forces more effectively than Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam. EVA foam provides moderate cushioning with good shock absorption and flexibility, but it tends to compress over time, leading to diminished support and durability. The low-density structure and thermal insulation capabilities of aerogel foam enhance comfort and protection, making it an advanced material choice for high-performance footwear applications.
Weight and Density Differences
Aerogel foam is significantly lighter than ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, with densities ranging from 0.003 to 0.1 g/cm3 compared to EVA's typical 0.1 to 0.3 g/cm3, making aerogel an ideal choice for ultra-lightweight footwear applications. The low density of aerogel foam enhances cushioning while reducing overall shoe weight, improving comfort and reducing fatigue during prolonged wear. Conversely, EVA foam offers higher density and moderate weight, providing durability and shock absorption but increasing the footwear's overall mass relative to aerogel counterparts.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Aerogel foam exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam due to its extremely low thermal conductivity, often around 0.013 W/m*K, which significantly reduces heat transfer in footwear applications. EVA foam, while lightweight and cushioning, typically has higher thermal conductivity between 0.035 and 0.06 W/m*K, offering moderate insulation but less effective than aerogels in extreme temperature conditions. Incorporating aerogel foam in footwear enhances heat retention and protects against cold environments, making it ideal for high-performance winter boots, whereas EVA foam remains preferred for general comfort and flexibility.
Durability and Longevity
Aerogel foam offers superior durability and longevity in footwear due to its exceptional resistance to compression and environmental degradation, maintaining cushioning properties over extended use. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, while lightweight and flexible, tends to compress and deteriorate faster, reducing its lifespan in high-impact or heavily used footwear. Choosing aerogel foam enhances shoe durability and extends functional wear life, especially in demanding conditions.
Breathability and Comfort
Aerogel foam offers superior breathability compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, due to its highly porous structure that enhances air circulation and moisture evaporation, reducing foot sweat and odor. EVA foam provides cushioning and flexibility, but its closed-cell structure limits airflow, making it less effective in breathability and potentially causing discomfort during prolonged wear. For footwear applications prioritizing comfort and temperature regulation, Aerogel foam stands out by delivering lightweight insulation combined with excellent ventilation properties.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation and durability with a lower environmental footprint due to its long lifespan and recyclability compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, which is derived from non-renewable petroleum resources and is less biodegradable. EVA foam contributes significantly to microplastic pollution and landfill waste because of its limited recycling options and slow degradation rate. Sustainable footwear increasingly favors aerogel foam for its potential to reduce carbon emissions and improve material circularity in the ecosystem.
Future Trends in Footwear Foam Technology
Aerogel foam, known for its ultra-lightweight thermal insulation and superior cushioning, is poised to revolutionize high-performance footwear by enhancing comfort and energy efficiency. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, widely used for its flexibility, durability, and shock absorption, continues to evolve with bio-based and recycled formulations driving sustainability trends. Future footwear foam technology will likely blend aerogel's advanced insulation properties with EVA's adaptable cushioning, fostering innovation in lightweight, eco-friendly, and high-performance shoe designs.
Infographic: Aerogel foam vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam for Footwear
 azmater.com
azmater.com