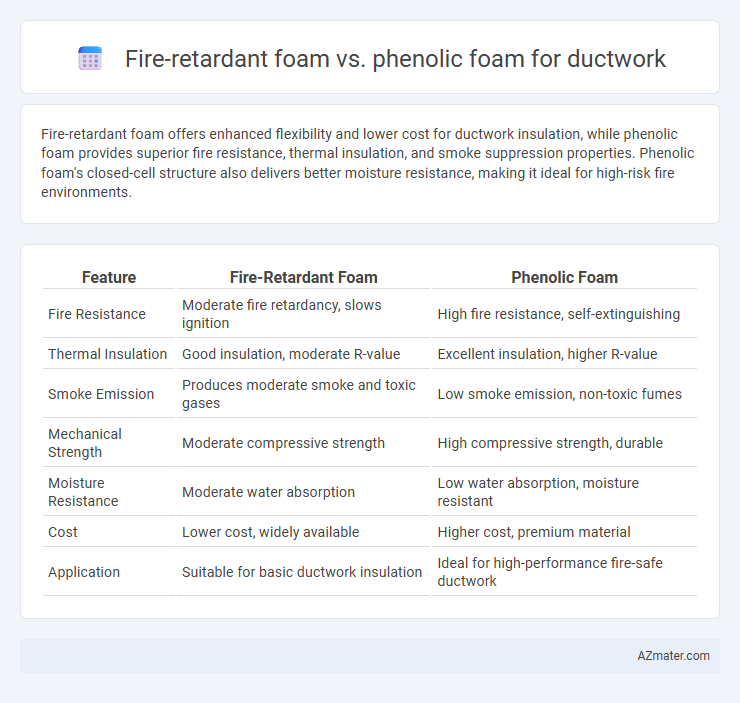
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced flexibility and lower cost for ductwork insulation, while phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance, thermal insulation, and smoke suppression properties. Phenolic foam's closed-cell structure also delivers better moisture resistance, making it ideal for high-risk fire environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Retardant Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Moderate fire retardancy, slows ignition | High fire resistance, self-extinguishing |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation, moderate R-value | Excellent insulation, higher R-value |
| Smoke Emission | Produces moderate smoke and toxic gases | Low smoke emission, non-toxic fumes |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate compressive strength | High compressive strength, durable |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate water absorption | Low water absorption, moisture resistant |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, premium material |
| Application | Suitable for basic ductwork insulation | Ideal for high-performance fire-safe ductwork |
Overview of Insulation Materials for Ductwork
Fire-retardant foam and phenolic foam are widely used insulation materials for ductwork, offering distinct thermal and fire performance characteristics. Fire-retardant foam provides enhanced flame resistance and smoke suppression, making it suitable for high-risk environments, while phenolic foam is valued for its low thermal conductivity and excellent fire-resistant properties with minimal smoke emission. Both materials contribute to energy efficiency and safety in HVAC systems, but phenolic foam typically offers superior insulation efficiency and fire performance in duct applications.
What Is Fire-Retardant Foam?
Fire-retardant foam is a specialized insulation material designed to resist ignition and slow the spread of flames in ductwork systems. This foam typically contains chemical additives that enhance its thermal stability and reduce flammability, providing improved fire safety compared to standard insulation materials. Its application in HVAC ducts ensures critical protection against fire hazards, making it a preferred choice where stringent fire codes and safety standards apply.
Understanding Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and low smoke emission compared to fire-retardant foam, making it highly suitable for ductwork insulation in commercial and industrial buildings. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent thermal insulation while maintaining structural integrity under high temperatures. Phenolic foam's inherent flame retardant properties reduce the risk of fire spreading, ensuring compliance with stringent fire safety standards.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Fire-retardant foam typically offers lower thermal conductivity values ranging around 0.024-0.028 W/m*K, enhancing energy efficiency in ductwork insulation. Phenolic foam provides superior thermal performance with conductivity often below 0.022 W/m*K, resulting in better insulation and reduced heat loss. The denser cellular structure of phenolic foam contributes to its enhanced thermal resistance and fire retardant properties compared to conventional fire-retardant foams.
Fire Resistance: Foam Types Head to Head
Fire-retardant foam offers moderate fire resistance with self-extinguishing properties and low smoke emission, making it suitable for standard ductwork applications requiring basic fire safety. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance due to its charring behavior, excellent thermal stability, and minimal smoke generation, which complies with stringent fire codes for critical HVAC systems. Comparing both, phenolic foam is the preferred choice in environments demanding high fire safety and regulatory compliance for duct insulation.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Fire-retardant foam used in ductwork exhibits moderate moisture resistance but can absorb water over time, potentially compromising insulation efficiency, while phenolic foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, effectively preventing water ingress. In terms of chemical resistance, phenolic foam demonstrates excellent performance against a wide range of chemicals, maintaining its structural integrity in harsh environments, whereas fire-retardant foam may degrade when exposed to certain solvents or aggressive chemicals. Choosing phenolic foam for ductwork insulation enhances durability and longevity in environments prone to moisture and chemical exposure.
Installation Requirements & Methods
Fire-retardant foam for ductwork typically requires straightforward installation involving spray or pour-in-place methods, allowing it to conform easily to complex shapes and providing seamless insulation with minimal joint sealing. Phenolic foam demands precise cutting and fitting due to its rigid board form, necessitating mechanical fasteners and specialized adhesives to ensure a tight seal and maintain fire resistance. Both materials must adhere to ASTM E84 standards for flame spread and smoke development, with phenolic foam often favored in installations prioritizing higher thermal performance and stringent fire safety codes.
Long-term Durability and Maintenance
Fire-retardant foam offers moderate long-term durability with resistance to cracking and moisture absorption in ductwork applications, yet may require periodic inspection and maintenance to prevent degradation over time. Phenolic foam excels in long-term durability due to its superior thermal stability, low smoke emission, and strong resistance to microbial growth, reducing maintenance frequency and preserving insulation integrity in HVAC duct systems. Choosing phenolic foam enhances fire safety and lowers lifecycle costs by minimizing maintenance interventions and extending service life compared to fire-retardant alternatives.
Cost Analysis: Fire-Retardant Foam vs Phenolic Foam
Fire-retardant foam generally offers a lower initial cost compared to phenolic foam, making it a budget-friendly option for ductwork insulation. Phenolic foam, while more expensive upfront, provides superior thermal performance and fire resistance, potentially reducing long-term energy consumption and maintenance costs. Evaluating lifecycle costs reveals phenolic foam can yield greater overall savings despite the higher initial investment due to enhanced durability and fire safety compliance.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Ductwork
Fire-retardant foam offers excellent thermal insulation and enhanced fire safety due to its flame-resistant properties, making it ideal for environments with strict fire codes. Phenolic foam provides superior smoke suppression and thermal stability, often used in commercial ductwork where both fire resistance and low smoke emission are critical. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing fire performance requirements, thermal insulation value, and compliance with local building regulations for optimal ductwork safety and efficiency.
Infographic: Fire-retardant foam vs Phenolic foam for Ductwork
 azmater.com
azmater.com