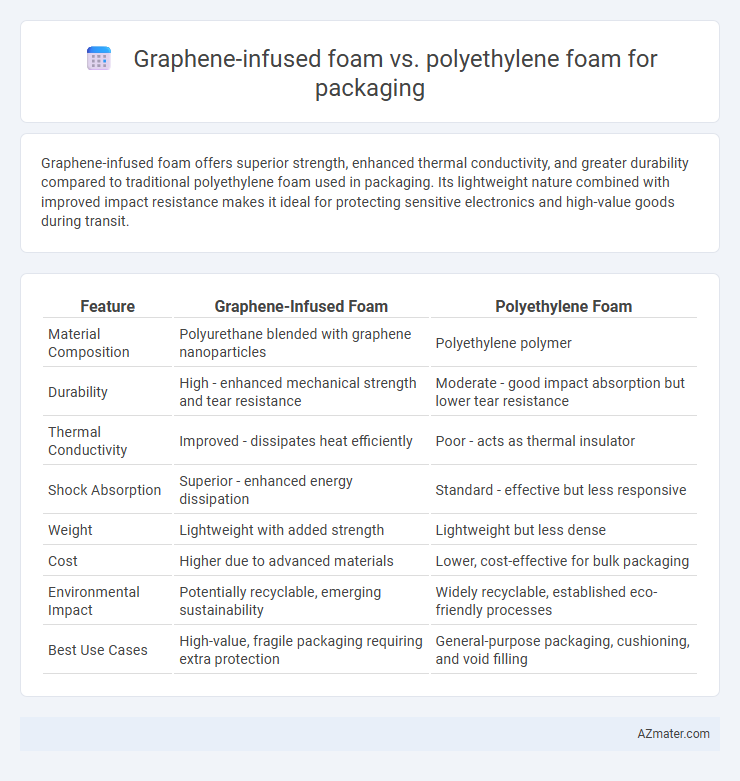
Graphene-infused foam offers superior strength, enhanced thermal conductivity, and greater durability compared to traditional polyethylene foam used in packaging. Its lightweight nature combined with improved impact resistance makes it ideal for protecting sensitive electronics and high-value goods during transit.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphene-Infused Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyurethane blended with graphene nanoparticles | Polyethylene polymer |
| Durability | High - enhanced mechanical strength and tear resistance | Moderate - good impact absorption but lower tear resistance |
| Thermal Conductivity | Improved - dissipates heat efficiently | Poor - acts as thermal insulator |
| Shock Absorption | Superior - enhanced energy dissipation | Standard - effective but less responsive |
| Weight | Lightweight with added strength | Lightweight but less dense |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced materials | Lower, cost-effective for bulk packaging |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially recyclable, emerging sustainability | Widely recyclable, established eco-friendly processes |
| Best Use Cases | High-value, fragile packaging requiring extra protection | General-purpose packaging, cushioning, and void filling |
Introduction to Advanced Packaging Foams
Graphene-infused foam offers superior mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and electrical properties compared to traditional polyethylene foam, making it an advanced solution for enhanced packaging protection. Polyethylene foam excels in lightweight cushioning and cost-effectiveness, widely used for impact absorption and moisture resistance in shipping fragile items. The integration of graphene nanoparticles within foam matrices introduces innovative packaging materials that significantly improve durability, thermal management, and electrostatic dissipation, driving advancements in protective packaging technology.
What is Graphene-Infused Foam?
Graphene-infused foam integrates graphene nanoparticles into a polyurethane or polyethylene matrix, significantly enhancing strength, thermal conductivity, and durability compared to traditional foams. This advanced composite material offers superior impact absorption and resistance to compression, making it highly effective for protective packaging applications. Its lightweight yet robust structure improves product safety during transit while maintaining flexibility and cushioning properties.
Overview of Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, resilient material widely used in packaging for its excellent cushioning and shock absorption properties. Its closed-cell structure provides water resistance, chemical inertness, and good thermal insulation, making it ideal for protecting sensitive items during transit. Compared to graphene-infused foam, polyethylene foam offers cost-effective durability but lacks the enhanced mechanical strength and conductivity provided by graphene additives.
Material Properties: Graphene-Infused vs Polyethylene Foam
Graphene-infused foam exhibits superior mechanical strength and thermal conductivity compared to traditional polyethylene foam, making it more resistant to impact and temperature fluctuations during packaging. Its enhanced electrical conductivity and lighter weight contribute to improved durability and protection for sensitive electronics and fragile goods. Polyethylene foam remains favored for cost-effectiveness and excellent cushioning but lacks the advanced reinforcement and barrier properties characteristic of graphene-enhanced materials.
Impact Resistance and Durability Comparison
Graphene-infused foam exhibits superior impact resistance compared to polyethylene foam due to the enhanced mechanical strength and flexibility provided by graphene's atomic structure. This material significantly improves durability by resisting deformation and maintaining structural integrity under repetitive stress, outperforming traditional polyethylene foam in long-term use. The integration of graphene also reduces foam density while boosting cushioning efficiency, making it an advanced choice for high-performance packaging applications.
Protective Performance in Packaging Applications
Graphene-infused foam exhibits superior protective performance in packaging applications due to its enhanced tensile strength, shock absorption, and thermal conductivity compared to polyethylene foam. Its nanostructured graphene layers significantly improve resistance to compression and impact, reducing damage risks for fragile or high-value products during transit. Polyethylene foam, while cost-effective and lightweight, offers comparatively lower durability and less effective energy dissipation, making graphene-infused foam the preferred choice for advanced protective packaging solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene-infused foam offers enhanced durability and mechanical strength, reducing material consumption and waste in packaging applications compared to traditional polyethylene foam. Polyethylene foam, while widely used, is derived from fossil fuels and exhibits slower degradation rates, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. Sustainable packaging solutions favor graphene-infused foam for its potential recyclability, lower environmental footprint, and reduced carbon emissions during production.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Graphene-infused foam offers superior strength and durability compared to polyethylene foam but comes at a significantly higher initial production cost, impacting overall cost-effectiveness in large-scale packaging applications. Polyethylene foam remains economically viable for mass packaging due to its low manufacturing expenses and widespread availability despite lower mechanical properties. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including longevity and protective performance, is essential when considering graphene-infused foam for premium or fragile goods packaging.
Industry Use Cases and Market Trends
Graphene-infused foam offers superior strength, thermal conductivity, and lightweight durability compared to traditional polyethylene foam, making it ideal for high-tech electronics and aerospace packaging where protection from impact and heat is critical. Polyethylene foam remains widely used in cost-sensitive sectors such as food, consumer goods, and shipping due to its affordability, cushioning properties, and chemical resistance. Market trends indicate increasing adoption of graphene-infused foam driven by rising demand for sustainable, high-performance materials across automotive, medical device packaging, and advanced manufacturing industries.
Conclusion: Which Foam is Best for Packaging?
Graphene-infused foam offers superior strength, enhanced durability, and excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance packaging applications requiring impact resistance and temperature control. Polyethylene foam provides cost-effective cushioning with good resilience and moisture resistance, suitable for general packaging needs. For premium protection with advanced material properties, graphene-infused foam is the best choice, while polyethylene foam remains optimal for budget-friendly, everyday packaging solutions.
Infographic: Graphene-infused foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com