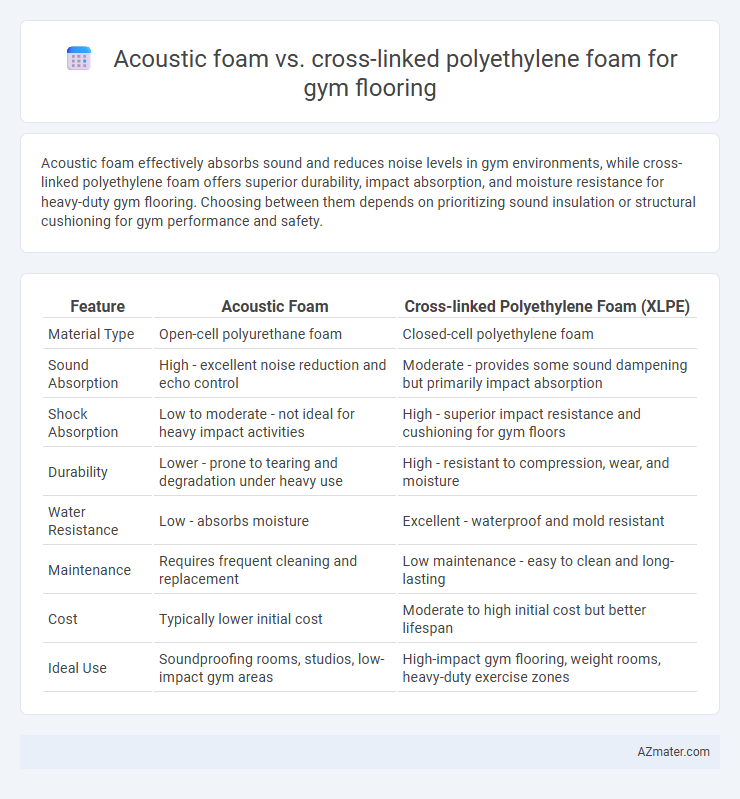
Acoustic foam effectively absorbs sound and reduces noise levels in gym environments, while cross-linked polyethylene foam offers superior durability, impact absorption, and moisture resistance for heavy-duty gym flooring. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing sound insulation or structural cushioning for gym performance and safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acoustic Foam | Cross-linked Polyethylene Foam (XLPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Open-cell polyurethane foam | Closed-cell polyethylene foam |
| Sound Absorption | High - excellent noise reduction and echo control | Moderate - provides some sound dampening but primarily impact absorption |
| Shock Absorption | Low to moderate - not ideal for heavy impact activities | High - superior impact resistance and cushioning for gym floors |
| Durability | Lower - prone to tearing and degradation under heavy use | High - resistant to compression, wear, and moisture |
| Water Resistance | Low - absorbs moisture | Excellent - waterproof and mold resistant |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent cleaning and replacement | Low maintenance - easy to clean and long-lasting |
| Cost | Typically lower initial cost | Moderate to high initial cost but better lifespan |
| Ideal Use | Soundproofing rooms, studios, low-impact gym areas | High-impact gym flooring, weight rooms, heavy-duty exercise zones |
Introduction to Gym Flooring Materials
Acoustic foam and cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) foam serve distinct purposes in gym flooring, with acoustic foam primarily designed for sound absorption and noise reduction, while XLPE foam provides superior shock absorption and durability under heavy exercise equipment. Gym flooring materials require a balance of cushioning, impact resistance, and sound dampening, making XLPE foam a preferred choice for high-traffic workout areas. Acoustic foam is often used in combination with other flooring types to improve acoustics but lacks the structural support necessary for rigorous gym activities.
Overview of Acoustic Foam
Acoustic foam is designed to absorb sound waves, reducing noise and echo within gym environments. Made from polyurethane or melamine materials, it features a porous structure that enhances sound dampening properties and improves overall acoustics. This foam typically offers better noise control compared to cross-linked polyethylene foam, which is primarily valued for its durability and impact resistance rather than sound absorption.
Overview of Cross-linked Polyethylene (XLPE) Foam
Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) foam is a highly durable and resilient material widely used in gym flooring for its excellent shock absorption and energy return properties. Its closed-cell structure offers superior moisture resistance and enhanced insulation, making it ideal for high-impact activities and heavy gym equipment. Compared to acoustic foam, XLPE foam provides better support and longevity under rigorous physical use, ensuring both safety and comfort in athletic environments.
Sound Absorption Capabilities Compared
Acoustic foam offers superior sound absorption capabilities due to its open-cell structure that effectively traps and dissipates sound waves, reducing echo and noise levels in gym environments. Cross-linked polyethylene foam, while durable and shock-absorbent, has a closed-cell structure that provides limited sound absorption, primarily serving as an impact cushioning material rather than noise control. Gyms seeking to minimize sound reverberation and enhance acoustic comfort should prioritize acoustic foam for optimal noise reduction.
Shock Absorption and Impact Resistance
Acoustic foam provides moderate shock absorption but is primarily designed for soundproofing rather than heavy impact resistance, making it less ideal for gym flooring where intense physical activity occurs. Cross-linked polyethylene foam (XPE) offers superior impact resistance and excellent shock absorption due to its closed-cell structure, making it highly durable and effective in protecting joints and equipment during high-impact workouts. The density and resilience of XPE foam significantly reduce injury risk and equipment wear, positioning it as the preferred material for gym flooring solutions.
Durability and Longevity in Gym Environments
Cross-linked polyethylene foam offers superior durability and longevity for gym flooring due to its closed-cell structure, which resists moisture, impact, and wear from heavy equipment. Acoustic foam, while effective in sound absorption, tends to degrade faster under constant pressure and high traffic, making it less suitable for rigorous gym environments. Choosing cross-linked polyethylene foam ensures sustained performance and maintains flooring integrity over extended use.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Acoustic foam offers easy installation through simple adhesive application or interlocking panels, making it ideal for quick gym flooring setups, whereas cross-linked polyethylene foam requires precise cutting and fitting due to its denser, more rigid structure. Acoustic foam demands regular cleaning to maintain sound absorption properties and can degrade faster under heavy gym equipment, while cross-linked polyethylene foam provides superior durability and low maintenance with resistance to moisture, chemicals, and impact. The higher density and closed-cell nature of cross-linked polyethylene foam contribute to longer-lasting flooring performance with less frequent replacement compared to acoustic foam.
Safety and User Comfort Considerations
Acoustic foam offers superior sound absorption, reducing noise levels in gym environments, which enhances user comfort by creating a quieter workout space. Cross-linked polyethylene foam provides excellent shock absorption and impact resistance, significantly improving safety by cushioning falls and reducing joint stress during high-impact exercises. Both materials contribute to user safety and comfort, but cross-linked polyethylene foam is often preferred for gym flooring due to its durability and enhanced protective qualities.
Cost Comparison and Value for Money
Acoustic foam typically costs between $1 to $3 per square foot, offering moderate sound absorption but lower durability for gym flooring applications. Cross-linked polyethylene foam ranges from $2 to $5 per square foot, providing superior impact resistance, cushioning, and longevity that justify its higher initial investment. When evaluating value for money, cross-linked polyethylene foam delivers enhanced durability and safety benefits, making it a cost-effective solution for high-traffic gym environments despite the upfront expense.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type
Acoustic foam is best suited for gym environments requiring sound absorption and noise reduction, such as weight rooms or group fitness areas with loud equipment or classes. Cross-linked polyethylene foam excels in impact absorption, durability, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic zones needing protective flooring like free weight sections, functional training areas, and zones with heavy equipment. Choosing acoustic foam focuses on enhancing auditory comfort, while cross-linked polyethylene foam prioritizes cushioning and long-term wear resistance in gym flooring applications.
Infographic: Acoustic foam vs Cross-linked polyethylene foam for Gym flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com