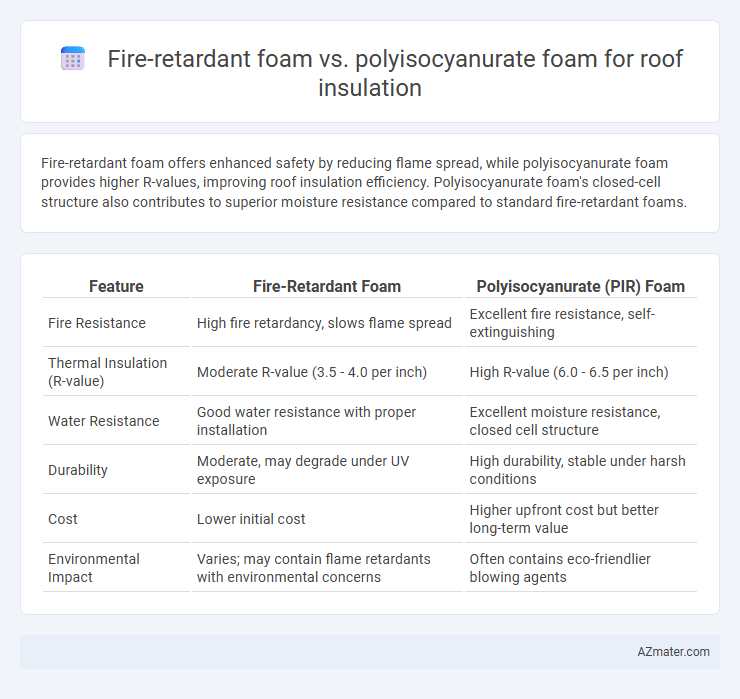
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced safety by reducing flame spread, while polyisocyanurate foam provides higher R-values, improving roof insulation efficiency. Polyisocyanurate foam's closed-cell structure also contributes to superior moisture resistance compared to standard fire-retardant foams.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Retardant Foam | Polyisocyanurate (PIR) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | High fire retardancy, slows flame spread | Excellent fire resistance, self-extinguishing |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | Moderate R-value (3.5 - 4.0 per inch) | High R-value (6.0 - 6.5 per inch) |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance with proper installation | Excellent moisture resistance, closed cell structure |
| Durability | Moderate, may degrade under UV exposure | High durability, stable under harsh conditions |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost but better long-term value |
| Environmental Impact | Varies; may contain flame retardants with environmental concerns | Often contains eco-friendlier blowing agents |
Introduction to Roof Insulation Materials
Fire-retardant foam and polyisocyanurate foam are essential materials in modern roof insulation, offering distinct benefits for thermal efficiency and safety. Fire-retardant foam enhances building protection by slowing flame spread and reducing heat release during a fire, making it ideal for compliance with stringent fire codes. Polyisocyanurate foam excels in thermal insulation due to its high R-value per inch, moisture resistance, and structural stability, making it a popular choice in energy-efficient roofing systems.
What Is Fire-Retardant Foam?
Fire-retardant foam is a type of insulation material treated with chemical additives that enhance its resistance to fire, reducing flammability and slowing the spread of flames. Unlike polyisocyanurate foam, which offers high thermal resistance but is combustible, fire-retardant foam prioritizes safety by meeting stringent fire safety standards such as ASTM E84 or UL 723. This makes fire-retardant foam a preferred choice for roofing applications in buildings requiring enhanced fire protection without compromising insulating performance.
Understanding Polyisocyanurate (PIR) Foam
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam is a high-performance insulation material favored for its superior thermal resistance and fire-retardant properties, making it ideal for roof insulation applications. Compared to standard fire-retardant foam, PIR foam offers enhanced dimensional stability and moisture resistance, which helps maintain insulation effectiveness over time. Its closed-cell structure and high R-value per inch contribute to energy efficiency and fire safety in commercial and residential roofing systems.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced fire resistance but generally exhibits lower thermal insulation values, with R-values typically around 3.5 to 4.0 per inch. Polyisocyanurate foam provides superior thermal performance, often achieving R-values between 6.0 and 6.5 per inch due to its closed-cell structure and higher insulating capacity. Selecting polyisocyanurate foam maximizes energy efficiency in roof insulation while fire-retardant foam prioritizes safety over optimal thermal resistance.
Fire Resistance and Safety Ratings
Fire-retardant foam typically contains additives that slow ignition and reduce flame spread, providing a moderate fire resistance level suitable for residential roofing applications. Polyisocyanurate foam boasts higher fire resistance with superior thermal stability, often achieving Class A fire ratings due to its dense, closed-cell structure and ability to resist combustion. Safety ratings for polyisocyanurate foam generally surpass those of standard fire-retardant foams, making it the preferred choice for commercial roofing where stringent fire codes are enforced.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Fire-retardant foam offers moderate moisture resistance but may degrade faster in prolonged wet conditions compared to polyisocyanurate foam, which provides superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure and robust thermal insulation properties. Polyisocyanurate foam also exhibits higher durability, maintaining its rigidity and insulation performance over time under varying environmental stresses. Choosing polyisocyanurate foam enhances long-term roof insulation performance by minimizing water absorption and maintaining structural integrity in humid or wet climates.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fire-retardant foam for roof insulation typically contains chemical additives that can release harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and pose disposal challenges, impacting environmental health negatively. Polyisocyanurate foam offers better thermal efficiency and a higher R-value per inch, reducing energy consumption and carbon footprint over the building's life cycle while often incorporating recycled content and lower global warming potential blowing agents. Sustainable roofing solutions favor polyisocyanurate foam due to its improved energy performance and relatively lower toxicity, supporting long-term environmental benefits.
Installation Methods and Ease
Fire-retardant foam insulation typically requires specialized application techniques involving spray or pour methods to ensure even coverage and adherence, which may demand professional installation due to safety considerations. Polyisocyanurate foam panels are pre-cut and rigid, allowing for faster and simpler installation with mechanical fastening or adhesive, often suitable for DIY projects. The ease of handling rigid polyisocyanurate panels generally translates to lower labor costs and quicker project completion compared to the more meticulous spray application of fire-retardant foam.
Cost Analysis: Fire-Retardant vs Polyisocyanurate Foam
Fire-retardant foam insulation typically costs more upfront than polyisocyanurate foam due to specialized chemical additives that enhance its fire resistance properties. Polyisocyanurate foam offers a higher R-value per inch, potentially lowering long-term energy costs despite slightly higher initial expenses compared to standard foam types. Evaluating overall expenses requires factoring in installation, durability, fire safety ratings, and expected energy savings to determine the most cost-effective roof insulation choice.
Choosing the Best Foam for Your Roof Insulation Needs
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced safety by resisting ignition and slowing flame spread, making it ideal for roofs requiring stringent fire codes compliance. Polyisocyanurate foam delivers superior thermal insulation with higher R-values per inch, effectively reducing energy costs and improving roof durability. Selecting the best foam depends on prioritizing fire safety standards versus maximizing thermal efficiency for your specific roof insulation needs.
Infographic: Fire-retardant foam vs Polyisocyanurate foam for Roof insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com