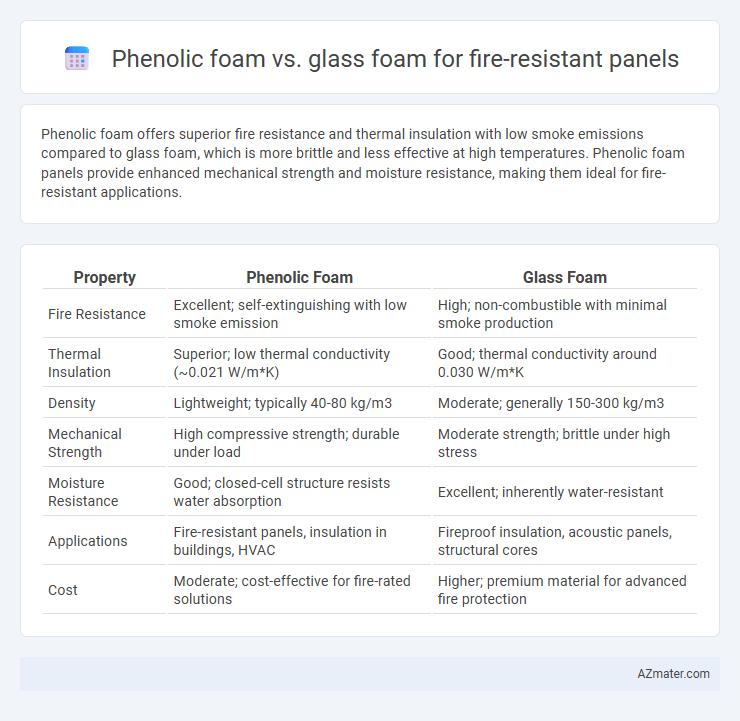
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and thermal insulation with low smoke emissions compared to glass foam, which is more brittle and less effective at high temperatures. Phenolic foam panels provide enhanced mechanical strength and moisture resistance, making them ideal for fire-resistant applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phenolic Foam | Glass Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Excellent; self-extinguishing with low smoke emission | High; non-combustible with minimal smoke production |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior; low thermal conductivity (~0.021 W/m*K) | Good; thermal conductivity around 0.030 W/m*K |
| Density | Lightweight; typically 40-80 kg/m3 | Moderate; generally 150-300 kg/m3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength; durable under load | Moderate strength; brittle under high stress |
| Moisture Resistance | Good; closed-cell structure resists water absorption | Excellent; inherently water-resistant |
| Applications | Fire-resistant panels, insulation in buildings, HVAC | Fireproof insulation, acoustic panels, structural cores |
| Cost | Moderate; cost-effective for fire-rated solutions | Higher; premium material for advanced fire protection |
Overview of Fire-Resistant Panel Materials
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and low smoke emission, making it a preferred choice in fire-resistant panels for buildings requiring stringent fire safety standards. Glass foam, composed of recycled glass, provides excellent thermal insulation and is non-combustible but typically generates more smoke compared to phenolic foam. Both materials contribute to fire safety in construction, with phenolic foam favored for flame retardancy and glass foam valued for environmental sustainability and thermal performance.
Introduction to Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a high-performance, fire-resistant insulation material known for its superior thermal stability and low smoke emission compared to traditional insulating foams. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent fire retardancy and dimensional stability, making it ideal for fire-resistant panels in construction and industrial applications. Phenolic foam outperforms glass foam in terms of flame resistance, mechanical strength, and environmental sustainability.
Introduction to Glass Foam
Glass foam, a lightweight and porous material, offers exceptional fire resistance and thermal insulation, making it an ideal choice for fire-resistant panels in buildings. Unlike phenolic foam, glass foam is non-combustible, provides superior structural stability under high temperatures, and resists moisture absorption, enhancing the panel's durability and safety. Its closed-cell structure also contributes to excellent soundproofing and energy efficiency, positioning glass foam as a premium solution in fire-resistant construction applications.
Fire Resistance Performance: Phenolic vs Glass Foam
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance performance compared to glass foam due to its low heat release rate and self-extinguishing properties, making it ideal for fire-resistant panels. Glass foam demonstrates moderate fire resistance but tends to have higher thermal conductivity and lower structural integrity under high temperatures. Phenolic foam's enhanced char formation ensures better insulation and smoke suppression during fire exposure, outperforming glass foam in critical fire safety applications.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity typically around 0.020 W/m*K, making it highly effective for fire-resistant panel applications. Glass foam, while also providing good thermal insulation, generally has a higher thermal conductivity near 0.040 W/m*K, resulting in slightly less efficient heat resistance. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam ensures better thermal performance and stability under fire exposure compared to the more porous glass foam.
Mechanical Strength and Structural Integrity
Phenolic foam offers superior mechanical strength and enhanced structural integrity compared to glass foam, making it ideal for fire-resistant panels requiring robust performance under stress. Its closed-cell structure contributes to higher compressive strength and improved durability, ensuring long-term stability in fire-rated applications. In contrast, glass foam, while lightweight and thermally insulating, generally exhibits lower mechanical strength and is more brittle, limiting its suitability for load-bearing fire-resistant panels.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Phenolic foam demonstrates superior moisture resistance compared to glass foam, making it ideal for environments with high humidity or potential water exposure. Glass foam offers excellent chemical resistance due to its inert silica base, maintaining structural integrity in corrosive settings. Both materials provide robust fire resistance, but phenolic foam's closed-cell structure limits water absorption better, enhancing durability in moisture-prone applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam exhibits low smoke emission and high fire resistance, making it an eco-friendly choice with a lower global warming potential compared to traditional insulating materials. Glass foam, made from recycled glass, offers excellent durability and thermal insulation while promoting circular economy principles through its use of post-consumer waste. Both materials provide sustainable fire-resistant panel solutions, but glass foam's reliance on recycled content enhances its environmental benefits by reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Phenolic foam offers a lower cost per square meter compared to glass foam, making it a more budget-friendly choice for fire-resistant panels in large-scale construction projects. Glass foam, while more expensive, provides superior thermal insulation and higher resistance to moisture, which can reduce long-term maintenance costs. Market availability of phenolic foam is broader, with numerous suppliers globally, whereas glass foam remains more niche, predominantly supplied by specialized manufacturers in Europe and North America.
Selecting the Best Foam for Fire-Resistant Panels
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance with low smoke emission and high thermal insulation, making it ideal for fire-resistant panels in buildings requiring strict fire safety standards. Glass foam provides excellent fire resistance and durability but typically has higher thermal conductivity and is heavier, influencing structural load considerations. Selecting the best foam depends on balancing fire performance, thermal insulation requirements, weight constraints, and environmental impact, with phenolic foam often preferred for stringent fire safety applications.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Glass foam for Fire-resistant panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com