Cross-linked polyethylene foam offers superior durability, shock absorption, and moisture resistance compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for high-impact cushion applications. Polystyrene foam provides lightweight cushioning but lacks the flexibility and long-term resilience of cross-linked polyethylene foam.
Table of Comparison
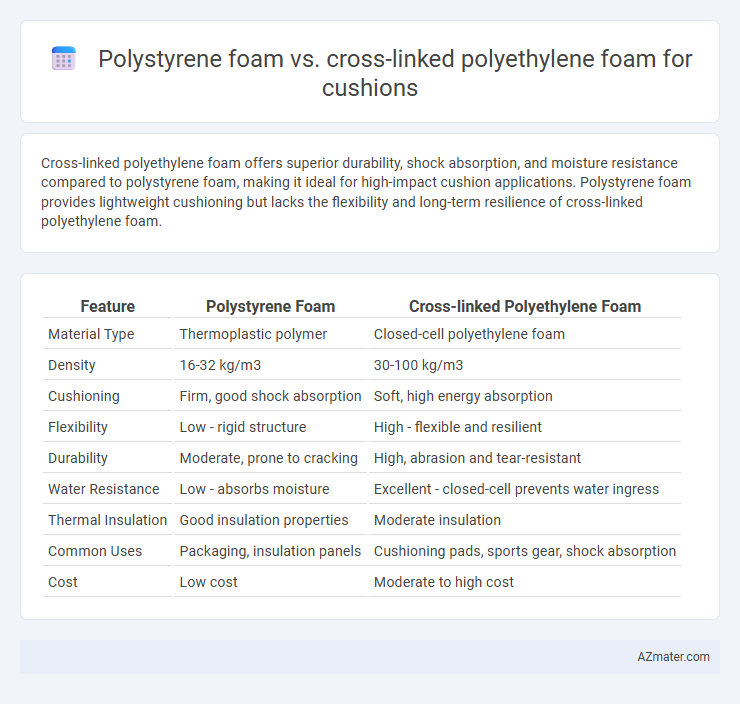
| Feature | Polystyrene Foam | Cross-linked Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Closed-cell polyethylene foam |
| Density | 16-32 kg/m3 | 30-100 kg/m3 |
| Cushioning | Firm, good shock absorption | Soft, high energy absorption |
| Flexibility | Low - rigid structure | High - flexible and resilient |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking | High, abrasion and tear-resistant |
| Water Resistance | Low - absorbs moisture | Excellent - closed-cell prevents water ingress |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation properties | Moderate insulation |
| Common Uses | Packaging, insulation panels | Cushioning pads, sports gear, shock absorption |
| Cost | Low cost | Moderate to high cost |
Introduction to Cushion Foams: Polystyrene vs. Cross-linked Polyethylene
Polystyrene foam offers rigid, lightweight cushioning commonly used for packaging and thermal insulation, providing excellent impact resistance but limited flexibility. Cross-linked polyethylene foam delivers a softer, more durable cushioning solution with superior compressive strength, resilience, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. Selecting between polystyrene and cross-linked polyethylene foams depends on desired cushioning performance, flexibility, and environmental conditions.
Material Composition and Structure
Polystyrene foam consists of rigid, closed-cell beads of polystyrene, offering high compressive strength and excellent insulation due to its lightweight, brittle structure. Cross-linked polyethylene foam features a flexible, closed-cell structure formed by chemically cross-linking polyethylene chains, providing superior cushioning, impact absorption, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. The molecular cross-linking in polyethylene foam enhances durability and resilience compared to the more rigid, brittle nature of polystyrene foam.
Cushioning Performance and Comfort
Polystyrene foam offers excellent rigidity and impact resistance, making it suitable for cushioning applications requiring firm support and shock absorption, while cross-linked polyethylene foam provides superior softness, resilience, and long-term comfort due to its closed-cell structure and flexibility. Cross-linked polyethylene foam exhibits higher compression set resistance and better energy return, enhancing cushioning performance in applications demanding prolonged cushioning and comfort. Polystyrene foam's brittleness under prolonged stress contrasts with cross-linked polyethylene foam's durability and consistent cushioning, making the latter more ideal for ergonomic and comfort-focused cushioning solutions.
Durability and Longevity
Polystyrene foam offers excellent rigidity and shock absorption but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and repeated compressive stress, reducing its overall durability and longevity for cushion applications. Cross-linked polyethylene foam provides superior resilience, maintaining cushioning properties and structural integrity over extended use due to its closed-cell structure and enhanced resistance to chemicals, moisture, and temperature variations. For cushions requiring long-term durability, cross-linked polyethylene foam is the preferred choice, delivering sustained comfort and performance in demanding environments.
Water and Moisture Resistance
Polystyrene foam offers low water absorption but can be susceptible to moisture penetration over time, making it less ideal for prolonged exposure to damp environments. Cross-linked polyethylene foam exhibits superior water and moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, preventing water infiltration and enhancing durability in wet conditions. This makes cross-linked polyethylene foam a preferred choice for cushions requiring long-term moisture protection and resilience.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Polystyrene foam offers excellent thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of approximately 0.033 W/m*K, making it highly effective at reducing heat transfer in cushion applications. Cross-linked polyethylene foam, while providing moderate thermal insulation around 0.038 W/m*K, excels in flexibility and impact absorption, suitable for cushioning that requires both comfort and temperature regulation. For optimal thermal performance in cushions, polystyrene foam generally outperforms cross-linked polyethylene foam due to its superior insulating properties and rigidity.
Weight and Portability
Polystyrene foam is significantly lighter than cross-linked polyethylene foam, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction enhances portability. Cross-linked polyethylene foam offers greater durability and cushioning but is denser, which increases the overall weight. For lightweight, easy-to-carry cushions, polystyrene foam provides a better balance between comfort and transport convenience.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene foam, commonly used in cushioning, poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and difficulty in recycling, leading to persistent pollution and landfill accumulation. Cross-linked polyethylene foam offers improved environmental benefits with higher durability and potential for mechanical recycling, reducing waste and reliance on virgin materials. Despite its advantages, cross-linked polyethylene foam recycling infrastructure remains limited, necessitating advancements to fully realize sustainable cushioning solutions.
Typical Applications in Cushion Products
Polystyrene foam is commonly used in automotive seat cushions, packaging inserts, and sound insulation due to its rigidity and lightweight properties. Cross-linked polyethylene foam excels in sports equipment padding, medical cushions, and furniture because of its superior cushioning, durability, and shock absorption. Both materials are essential in cushion products, with polystyrene providing structural support and cross-linked polyethylene offering enhanced comfort and resilience.
Cost Comparison and Value
Polystyrene foam typically offers a lower upfront cost compared to cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) foam, making it a budget-friendly choice for basic cushioning needs. However, XLPE foam provides superior durability, resilience, and longevity, which can result in better long-term value despite its higher initial price. When evaluating cost versus performance, XLPE foam delivers enhanced cushioning efficiency and sustained comfort, often reducing replacement frequency and overall expenses.
Infographic: Polystyrene foam vs Cross-linked polyethylene foam for Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com