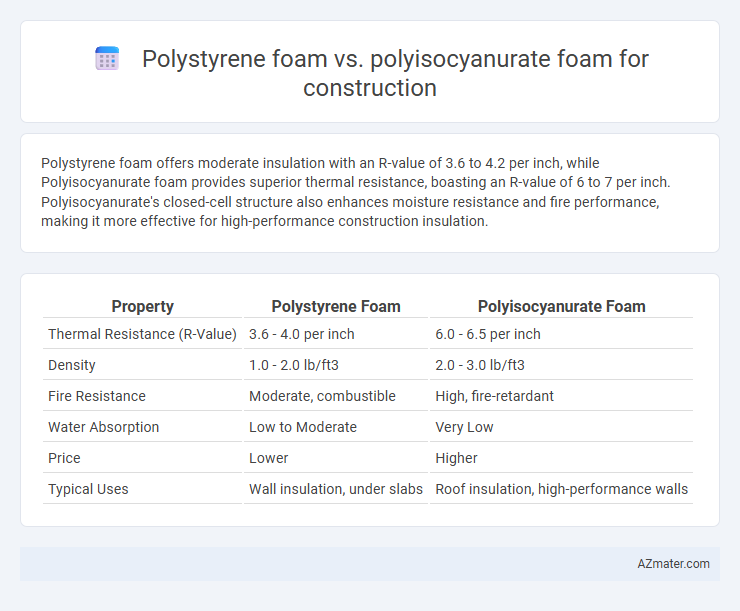
Polystyrene foam offers moderate insulation with an R-value of 3.6 to 4.2 per inch, while Polyisocyanurate foam provides superior thermal resistance, boasting an R-value of 6 to 7 per inch. Polyisocyanurate's closed-cell structure also enhances moisture resistance and fire performance, making it more effective for high-performance construction insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene Foam | Polyisocyanurate Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance (R-Value) | 3.6 - 4.0 per inch | 6.0 - 6.5 per inch |
| Density | 1.0 - 2.0 lb/ft3 | 2.0 - 3.0 lb/ft3 |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate, combustible | High, fire-retardant |
| Water Absorption | Low to Moderate | Very Low |
| Price | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Uses | Wall insulation, under slabs | Roof insulation, high-performance walls |
Introduction to Foam Insulation Materials
Polystyrene foam and polyisocyanurate foam are widely used insulation materials in construction, each offering distinct thermal performance and moisture resistance. Polystyrene foam, available in expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) forms, provides effective thermal insulation with moderate R-values and excellent water resistance, making it suitable for below-grade and foundation applications. Polyisocyanurate foam exhibits higher R-values per inch and superior fire resistance, commonly used in roofing systems and wall assemblies to enhance energy efficiency and building envelope durability.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam is a widely used insulation material in construction, known for its lightweight properties and ease of installation. It offers excellent thermal resistance with an R-value typically around 4 to 5 per inch, making it effective for reducing energy costs. While less fire-resistant compared to polyisocyanurate foam, polystyrene remains popular for its moisture resistance and affordability in wall and roof insulation applications.
Overview of Polyisocyanurate Foam
Polyisocyanurate foam is a high-performance rigid insulation known for its superior thermal resistance, often exceeding R-6 per inch, making it ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent moisture resistance and dimensional stability, enhancing durability in construction applications. Compared to polystyrene foam, polyisocyanurate offers better fire resistance and higher R-value retention over time, contributing to long-term insulation effectiveness.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polystyrene foam, including expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) types, offers R-values ranging from 3.6 to 5 per inch, providing moderate thermal insulation widely used in construction. Polyisocyanurate (polyiso) foam delivers higher thermal resistance, with R-values typically between 6 and 6.5 per inch, making it superior for energy-efficient building envelopes. The closed-cell structure of polyiso enhances thermal performance, especially at higher temperatures, whereas polystyrene foams maintain stable insulation but generally exhibit lower R-values under similar conditions.
Moisture Resistance and Vapor Permeability
Polystyrene foam exhibits moderate moisture resistance with a closed-cell structure that limits water absorption, but its vapor permeability is relatively low, which can trap moisture within wall assemblies. Polyisocyanurate foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its dense, closed-cell composition and features a lower vapor permeability, effectively reducing water vapor transmission and preventing moisture buildup. When prioritizing moisture control and vapor barrier performance in construction, polyisocyanurate foam is generally preferred for exterior insulation systems and energy-efficient building envelopes.
Fire Resistance and Safety Ratings
Polyisocyanurate foam offers superior fire resistance compared to polystyrene foam, characterized by higher ignition temperatures and lower flame spread ratings, making it a safer option in construction applications. Building codes often favor polyisocyanurate due to its enhanced safety ratings, including a Class A fire rating on ASTM E84 tests, whereas polystyrene typically has a Class C rating and requires additional fire barriers. The improved thermal stability and reduced smoke emission of polyisocyanurate foam contribute to increased occupant safety during fire events.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polystyrene foam, commonly used in construction insulation, has a higher environmental impact due to its petroleum-based origin and slow biodegradability, releasing toxic styrene when burned. Polyisocyanurate foam offers improved thermal insulation efficiency and uses less raw material for the same R-value, reducing overall consumption and energy expenditure during manufacturing. Polyisocyanurate foam also contains fewer ozone-depleting substances and has better recyclability potential, promoting a more sustainable building solution.
Installation Process and Ease of Use
Polystyrene foam offers a straightforward installation process, often cut and fitted on-site with minimal specialized tools, making it user-friendly for various construction applications. Polyisocyanurate foam typically requires professional handling due to its rigid panels and complex adhesive systems, but provides superior thermal insulation and fire resistance. While polystyrene excels in ease of use, polyisocyanurate's installation demands may lead to longer setup times but ensure enhanced overall performance.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Polystyrene foam generally offers lower upfront costs compared to Polyisocyanurate foam, making it a budget-friendly option for initial insulation needs in construction projects. Polyisocyanurate foam provides significantly higher R-values per inch and better long-term thermal performance, resulting in greater energy savings and reduced HVAC costs over time. When evaluating total cost of ownership, the enhanced durability and superior insulation efficiency of Polyisocyanurate often lead to a more cost-effective investment despite its higher initial price.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Construction Project
Polystyrene foam offers cost-effective thermal insulation with high moisture resistance, making it ideal for foundation and wall insulation in construction projects seeking budget-friendly options. Polyisocyanurate foam provides superior R-values per inch and enhanced fire resistance, suitable for roofing and areas requiring maximum energy efficiency and compliance with stringent building codes. Selecting the right foam depends on project-specific factors such as thermal performance needs, fire safety requirements, moisture exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal long-term durability and cost savings.
Infographic: Polystyrene foam vs Polyisocyanurate foam for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com