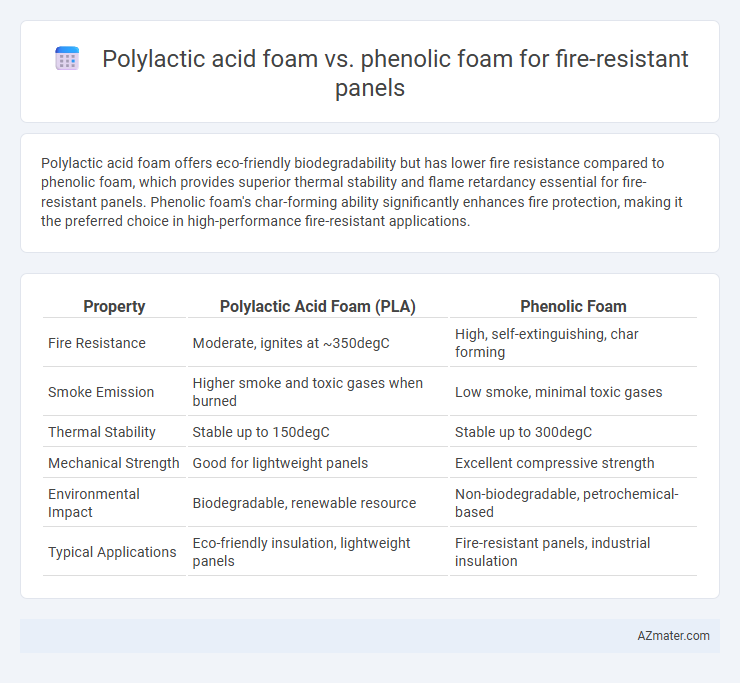
Polylactic acid foam offers eco-friendly biodegradability but has lower fire resistance compared to phenolic foam, which provides superior thermal stability and flame retardancy essential for fire-resistant panels. Phenolic foam's char-forming ability significantly enhances fire protection, making it the preferred choice in high-performance fire-resistant applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polylactic Acid Foam (PLA) | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Moderate, ignites at ~350degC | High, self-extinguishing, char forming |
| Smoke Emission | Higher smoke and toxic gases when burned | Low smoke, minimal toxic gases |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 150degC | Stable up to 300degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Good for lightweight panels | Excellent compressive strength |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable resource | Non-biodegradable, petrochemical-based |
| Typical Applications | Eco-friendly insulation, lightweight panels | Fire-resistant panels, industrial insulation |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Panels
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam and phenolic foam are widely used materials for fire-resistant panels, each offering distinct fire-retardant properties. Phenolic foam is renowned for its excellent fire resistance, low smoke emission, and thermal insulation, making it a preferred choice in high-performance fire-safe constructions. In contrast, PLA foam, derived from renewable sources, provides a balance between biodegradability and moderate fire resistance, suitable for applications where sustainability is prioritized alongside fire safety.
Overview of Polylactic Acid (PLA) Foam
Polylactic Acid (PLA) foam is a biodegradable, bio-based material derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, offering a sustainable alternative for fire-resistant panels. PLA foam provides good thermal insulation and moderate fire resistance but typically requires additives or coatings to enhance flame retardancy compared to phenolic foam, which inherently exhibits superior fire resistance and low smoke emission. The lightweight nature and environmental benefits of PLA foam make it attractive for green building applications, although phenolic foam remains the preferred choice where strict fire safety standards are essential.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a highly fire-resistant material commonly used in fire-resistant panels due to its excellent thermal stability and low smoke emission during combustion. Its closed-cell structure provides superior insulation properties, making it effective in preventing heat transfer and maintaining structural integrity under high temperatures. Compared to polylactic acid foam, phenolic foam offers enhanced flame retardancy, making it a preferred choice in applications requiring strict fire safety standards.
Key Fire-Resistant Properties of PLA Foam
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam exhibits strong fire-resistant properties such as low flammability, low smoke production, and low heat release rate, making it a safer choice for fire-resistant panels. It also offers excellent thermal insulation and biodegradability, distinguishing it from phenolic foam which, while effective in fire resistance and charring behavior, tends to emit higher smoke and toxic gases. PLA foam's combination of sustainable origin and superior fire performance enhances its application in eco-friendly, fire-safe building materials.
Key Fire-Resistant Properties of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance with a high Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) typically above 35%, significantly outperforming polylactic acid foam, which has lower fire-retardant capabilities. Its inherent char-forming properties and low smoke emission make phenolic foam a preferred choice for fire-resistant panels in construction and transportation industries. The material's excellent thermal stability and self-extinguishing behavior under flame exposure ensure enhanced safety compliance in critical applications.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam exhibits lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.030-0.035 W/m*K, providing superior thermal insulation compared to phenolic foam, which ranges between 0.035-0.045 W/m*K. Despite PLA foam's renewable bio-based origins, phenolic foam demonstrates enhanced fire resistance with a higher Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) of approximately 28-33%, critical for fire-resistant panel applications. The choice between PLA and phenolic foam balances thermal insulation efficiency and fire retardant requirements, with phenolic foam commonly preferred for stringent fire safety standards.
Environmental Impact: PLA vs Phenolic Foam
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam offers a significant environmental advantage over phenolic foam due to its biodegradability and derivation from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, reducing reliance on petroleum-based materials. Phenolic foam, derived from phenol and formaldehyde, involves toxic chemical production processes and generates hazardous waste, raising concerns about long-term ecological effects and indoor air quality. PLA foam's compostability and lower carbon footprint contribute to a more sustainable lifecycle, while phenolic foam's resistance to biodegradation complicates disposal and recycling efforts.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative with moderate fire resistance but tends to be costlier due to raw material expenses and limited large-scale production, affecting its market availability. Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire-retardant properties and is widely available with a competitive cost advantage driven by established manufacturing processes and extensive industry adoption. For fire-resistant panels, phenolic foam is generally preferred in cost-sensitive and high-demand markets, while PLA foam appeals to niche markets prioritizing sustainability despite its higher price point.
Applications in Construction and Industrial Sectors
Polylactic acid foam offers eco-friendly fire-resistant panels with moderate thermal insulation ideal for interior wall linings and ceiling panels in sustainable construction projects. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent structural rigidity, making it preferable for industrial applications such as chemical plants, power stations, and high-risk urban buildings. Both materials contribute to fire safety compliance, but phenolic foam's higher flame retardancy suits environments requiring stringent fire protection standards.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Fire-Resistant Panel Material
Polylactic acid foam offers biodegradable and renewable advantages with moderate fire resistance, making it suitable for environmentally conscious applications where sustainability is prioritized. Phenolic foam delivers superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal insulation, ideal for high-risk fire safety requirements in construction and industrial settings. Selecting the optimal fire-resistant panel material depends on balancing environmental impact with regulatory fire performance standards and specific project needs.
Infographic: Polylactic acid foam vs Phenolic foam for Fire-resistant panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com