Fire-retardant foam enhances safety by slowing flame spread and reducing smoke during fires, while polyisocyanurate foam offers superior thermal insulation with R-values typically between 6 and 7 per inch, making it more energy-efficient for roofing applications. Polyisocyanurate foam also provides better structural stability and moisture resistance compared to standard fire-retardant foams.
Table of Comparison
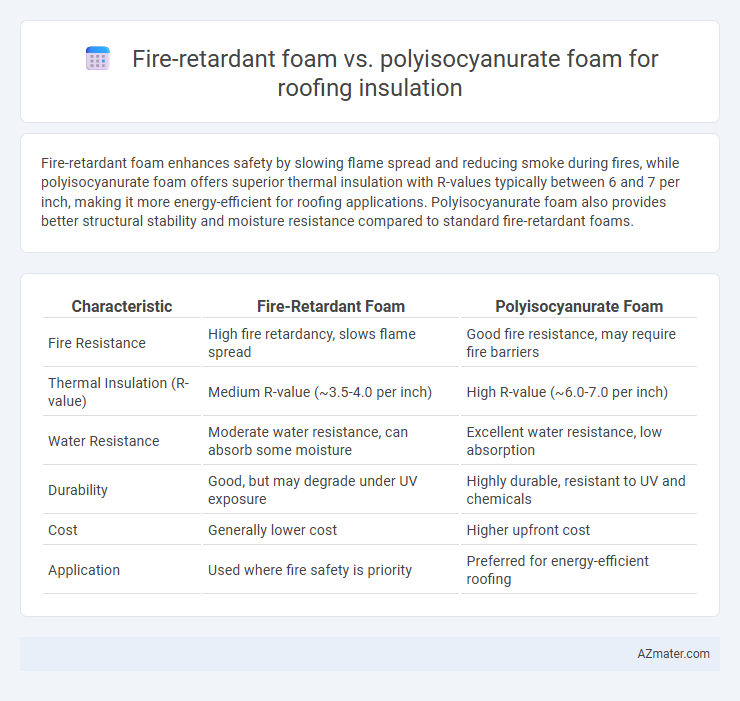
| Characteristic | Fire-Retardant Foam | Polyisocyanurate Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | High fire retardancy, slows flame spread | Good fire resistance, may require fire barriers |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | Medium R-value (~3.5-4.0 per inch) | High R-value (~6.0-7.0 per inch) |
| Water Resistance | Moderate water resistance, can absorb some moisture | Excellent water resistance, low absorption |
| Durability | Good, but may degrade under UV exposure | Highly durable, resistant to UV and chemicals |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher upfront cost |
| Application | Used where fire safety is priority | Preferred for energy-efficient roofing |
Introduction to Roofing Insulation Materials
Fire-retardant foam and polyisocyanurate foam are prominent roofing insulation materials known for enhancing thermal performance and safety. Fire-retardant foam provides superior resistance to ignition and flame spread, making it ideal for buildings requiring stringent fire codes, while polyisocyanurate foam offers high R-values per inch, ensuring excellent energy efficiency and moisture resistance. Selecting between these materials depends on specific project requirements such as fire safety standards, thermal insulation needs, and environmental factors.
What is Fire-retardant Foam?
Fire-retardant foam is a type of insulation material specifically treated to resist ignition and slow the spread of flames, enhancing building safety during fire incidents. Unlike standard polyisocyanurate foam, fire-retardant foam contains chemical additives that improve its fire resistance while maintaining thermal insulation properties. This makes fire-retardant foam a preferred choice for roofing insulation where enhanced fire safety standards and compliance with building codes are critical.
What is Polyisocyanurate Foam?
Polyisocyanurate foam, commonly used in roofing insulation, is a rigid, closed-cell foam characterized by its high thermal resistance and fire-retardant properties due to its chemical formulation with a higher isocyanate-to-polyol ratio. This foam provides superior energy efficiency and moisture resistance compared to standard polyurethane foams, making it ideal for flat or low-slope roofs. Fire-retardant variants of polyisocyanurate foam further enhance fire safety, meeting strict building codes and improving overall roof durability.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Fire-retardant foam and polyisocyanurate foam exhibit distinct thermal performance characteristics for roofing insulation applications. Polyisocyanurate foam typically offers a higher R-value per inch, often ranging between R-6.0 and R-6.5, providing superior thermal resistance and energy efficiency compared to standard fire-retardant foam, which generally has an R-value near R-3.5 to R-4.5. While fire-retardant foams prioritize enhanced fire safety and code compliance, polyisocyanurate foam remains the preferred choice for maximizing insulation effectiveness and reducing heat transfer in roofing systems.
Fire Resistance Properties
Fire-retardant foam for roofing insulation is specifically engineered with additives that significantly enhance its ability to resist ignition and slow flame spread, providing superior fire protection compared to standard foams. Polyisocyanurate foam, while naturally more fire-resistant than many insulation types due to its closed-cell structure and high thermal stability, may require additional fire-retardant treatments to meet stringent building code requirements. Evaluating fire resistance properties involves assessing ignition resistance, flame spread ratings, and smoke development, with fire-retardant formulations generally offering enhanced protection in high-risk roofing applications.
Durability and Longevity
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced safety through its ability to resist ignition and slow flame spread, making it suitable for fire-prone areas, but it may have slightly shorter lifespan due to chemical additives. Polyisocyanurate foam provides superior insulation performance with a higher R-value per inch and greater dimensional stability, contributing to excellent long-term durability under varying weather conditions. Both materials resist moisture and degradation, but polyisocyanurate's closed-cell structure generally ensures longer-lasting thermal efficiency and structural integrity in roofing insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fire-retardant foam often contains chemical additives that can pose environmental hazards during manufacturing and disposal, whereas polyisocyanurate foam generally demonstrates higher thermal efficiency, reducing overall energy consumption and carbon footprint. Polyisocyanurate foam's closed-cell structure enhances durability and moisture resistance, leading to longer roof lifespan and less frequent replacement, which supports sustainability goals. Both materials require proper handling to minimize environmental impact, but polyisocyanurate foam is typically favored for green building certifications due to its superior insulation properties and potential for recycled content.
Installation and Application Methods
Fire-retardant foam offers superior safety during installation, requiring careful handling to ensure proper curing and avoid hazardous fumes, and is often sprayed directly onto roof surfaces for seamless coverage. Polyisocyanurate foam, typically supplied as rigid boards or spray foam, allows for versatile application methods including adhesive bonding and mechanical fastening, making it suitable for both new construction and retrofit projects. Both materials require precise cutting and fitting to maximize insulation performance and maintain continuous thermal barriers in roofing systems.
Cost Analysis and Value
Fire-retardant foam typically incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized additives enhancing flame resistance, yet it offers improved safety and compliance with fire codes, potentially lowering insurance and liability expenses. Polyisocyanurate foam provides superior thermal insulation with a higher R-value per inch, reducing energy costs over time and offering better long-term value despite slightly lower initial pricing. Evaluating cost-effectiveness depends on balancing initial expenses against energy savings and safety benefits, with polyisocyanurate favored for insulation efficiency and fire-retardant foam prioritized in fire-sensitive applications.
Choosing the Best Foam for Your Roofing Project
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced safety by significantly reducing flammability, making it ideal for projects requiring strict fire codes compliance, whereas polyisocyanurate foam provides superior thermal resistance with R-values typically ranging from 6 to 7 per inch. When choosing the best foam for your roofing project, consider the balance between fire safety requirements and insulation performance, along with factors like moisture resistance and cost-effectiveness. Evaluating local building codes, climate conditions, and long-term energy savings are critical steps in selecting the most suitable foam insulation.
Infographic: Fire-retardant foam vs Polyisocyanurate foam for Roofing insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com