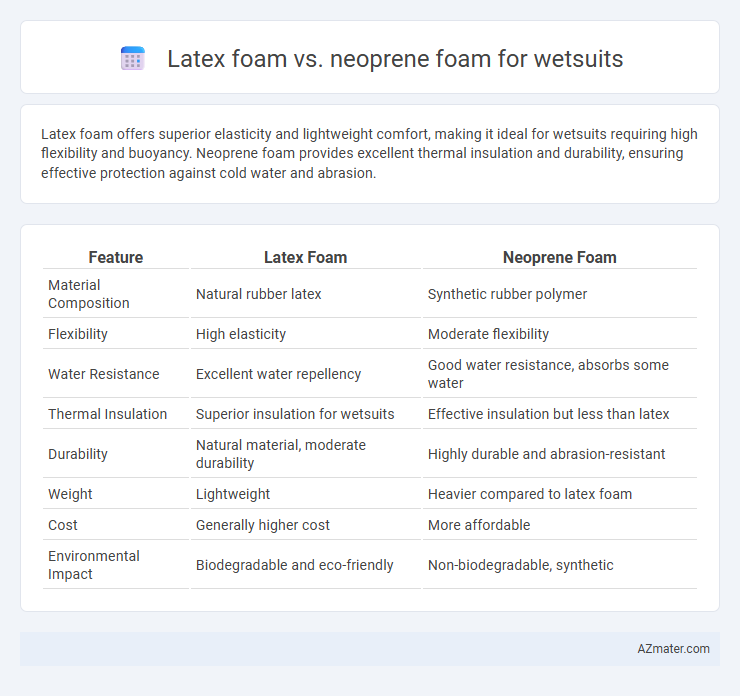
Latex foam offers superior elasticity and lightweight comfort, making it ideal for wetsuits requiring high flexibility and buoyancy. Neoprene foam provides excellent thermal insulation and durability, ensuring effective protection against cold water and abrasion.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Latex Foam | Neoprene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural rubber latex | Synthetic rubber polymer |
| Flexibility | High elasticity | Moderate flexibility |
| Water Resistance | Excellent water repellency | Good water resistance, absorbs some water |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior insulation for wetsuits | Effective insulation but less than latex |
| Durability | Natural material, moderate durability | Highly durable and abrasion-resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier compared to latex foam |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | More affordable |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, synthetic |
Introduction to Wetsuit Materials
Latex foam and neoprene foam are two primary materials used in wetsuit manufacturing, each offering distinct thermal insulation and flexibility properties essential for water sports. Neoprene foam, made from synthetic rubber, provides superior durability, stretch, and buoyancy, making it the most common choice for wetsuits across various water temperatures. Latex foam, known for its lightweight and high elasticity, is less resistant to abrasion and UV exposure but offers exceptional fit and comfort in specialized wetsuit applications.
Overview of Latex Foam
Latex foam, derived from natural rubber, offers exceptional elasticity and durability, making it a preferred choice for wetsuit insulation. Its closed-cell structure provides superior water resistance and thermal retention compared to other foams. Lightweight and flexible, latex foam enhances mobility and comfort for extended water activities.
Overview of Neoprene Foam
Neoprene foam is a synthetic rubber material widely used in wetsuits due to its excellent insulation, flexibility, and durability in marine environments. It consists of closed-cell foam that traps nitrogen gas bubbles, providing superior thermal protection by minimizing heat loss in cold water. Its resistance to water absorption and resistance to abrasion make neoprene foam ideal for prolonged underwater activities compared to latex foam.
Key Physical Differences
Latex foam exhibits superior elasticity and is lighter with higher tensile strength compared to neoprene foam, making it ideal for snug wetsuits with excellent flexibility. Neoprene foam offers better thermal insulation and durability due to its closed-cell structure, providing enhanced resistance against compression and water absorption. While latex foam excels in flexibility, neoprene foam delivers greater resilience and warmth retention for prolonged water exposure.
Thermal Insulation Comparison
Latex foam offers superior thermal insulation in wetsuits due to its closed-cell structure that traps body heat effectively, maintaining warmth in cold water conditions. Neoprene foam, while widely used for its flexibility and durability, provides moderate insulation by allowing some water penetration that warms gradually with body heat. Selection between latex and neoprene foam depends on balancing thermal efficiency with comfort and mobility needs for specific water temperatures.
Flexibility and Comfort
Latex foam offers exceptional flexibility and a lightweight feel ideal for wetsuits, enabling a wide range of motion without restriction. Neoprene foam provides superior thermal insulation and durability but can be slightly less flexible compared to high-grade latex. Combining latex's stretch with neoprene's insulation often results in wetsuits that maximize comfort and performance in cold water conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Latex foam offers excellent elasticity and comfort but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and saltwater conditions, reducing its overall durability in wetsuit applications. Neoprene foam is highly resistant to abrasion, UV damage, and chemical degradation, resulting in superior longevity and maintaining its insulating properties over extended use. The inherent resilience of neoprene foam makes it the preferred choice for wetsuit materials requiring long-term durability and consistent performance.
Environmental Impact
Latex foam, derived from natural rubber, offers better biodegradability and lower carbon emissions than neoprene foam, which is petroleum-based and highly energy-intensive to produce. Neoprene's manufacturing process releases toxic chemicals harmful to marine ecosystems and contributes to long-term pollution. Choosing latex foam for wetsuits significantly reduces environmental footprint by supporting sustainable harvesting and minimizing non-renewable resource dependence.
Price and Accessibility
Latex foam wetsuits generally come at a higher price point due to the material's superior flexibility and durability, making them a premium choice often favored by professional divers. Neoprene foam wetsuits are more widely accessible and affordable, commonly found in entry-level and mid-range options suitable for casual water sports enthusiasts. The broader availability and cost-effectiveness of neoprene make it the preferred material for budget-conscious buyers seeking reliable thermal protection.
Which Foam is Best for Your Wetsuit?
Latex foam offers superior flexibility and excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for wetsuits designed for colder water conditions. Neoprene foam provides greater durability and resistance to abrasion while maintaining good insulation, preferred for versatile and long-lasting wetsuits. Choosing the best foam depends on the balance between flexibility, insulation needs, and durability required for your specific water activities.
Infographic: Latex foam vs Neoprene foam for Wetsuit
 azmater.com
azmater.com