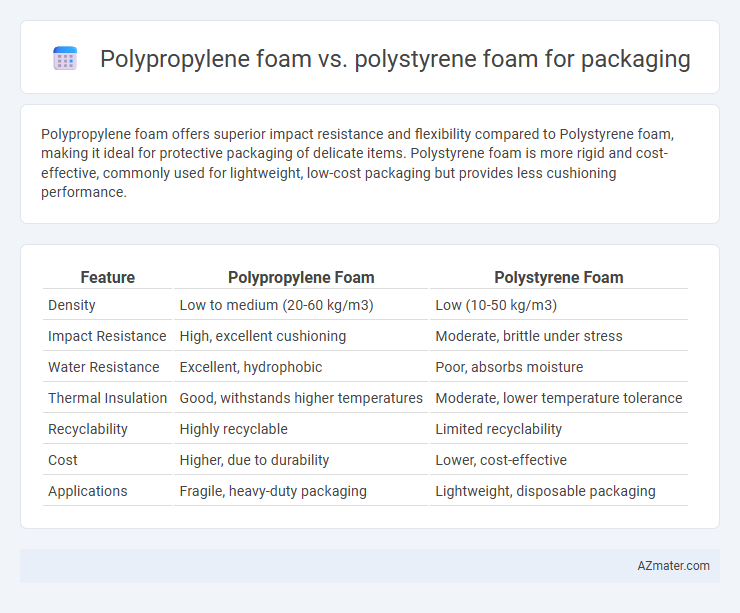
Polypropylene foam offers superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to Polystyrene foam, making it ideal for protective packaging of delicate items. Polystyrene foam is more rigid and cost-effective, commonly used for lightweight, low-cost packaging but provides less cushioning performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polypropylene Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium (20-60 kg/m3) | Low (10-50 kg/m3) |
| Impact Resistance | High, excellent cushioning | Moderate, brittle under stress |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, hydrophobic | Poor, absorbs moisture |
| Thermal Insulation | Good, withstands higher temperatures | Moderate, lower temperature tolerance |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable | Limited recyclability |
| Cost | Higher, due to durability | Lower, cost-effective |
| Applications | Fragile, heavy-duty packaging | Lightweight, disposable packaging |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polystyrene Foams
Polypropylene foam is a lightweight, durable material known for its excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for protective packaging applications. Polystyrene foam, often recognized by its rigid, cushioning properties, provides effective insulation and shock absorption but tends to be more brittle compared to polypropylene. Both foams offer unique advantages in packaging, with polypropylene preferred for reusable and sustainable options, while polystyrene is commonly used for cost-effective, disposable packaging solutions.
Material Composition and Structure
Polypropylene foam consists of closed-cell polypropylene polymers offering excellent flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance, while polystyrene foam is made from expanded polystyrene beads with a rigid, brittle cellular structure. The cellular morphology of polypropylene foam provides superior impact absorption and cushioning, making it highly effective for protective packaging applications. In contrast, polystyrene foam's lightweight, rigid structure excels in thermal insulation but lacks the resilience and recyclability seen in polypropylene counterparts.
Key Differences in Physical Properties
Polypropylene foam exhibits superior impact resistance and higher tensile strength compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for packaging fragile items requiring durability. Polystyrene foam is lighter with better thermal insulation properties but tends to be more brittle and less flexible under stress. The closed-cell structure of polypropylene foam enhances its water resistance, whereas polystyrene foam's open-cell composition leads to greater moisture absorption.
Weight and Density Comparison
Polypropylene foam exhibits a lower density range of approximately 18-60 kg/m3 compared to polystyrene foam's typical density range of 20-100 kg/m3, resulting in lighter packaging materials. The reduced weight of polypropylene foam enhances transport efficiency and minimizes shipping costs while maintaining adequate cushioning properties. Its superior strength-to-weight ratio makes polypropylene foam a preferable choice for lightweight yet durable packaging solutions.
Insulation and Thermal Performance
Polypropylene foam offers superior insulation and thermal performance compared to polystyrene foam, maintaining higher energy efficiency in temperature-sensitive packaging. Its closed-cell structure provides enhanced resistance to moisture absorption and better thermal stability across a wide temperature range. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, exhibits lower thermal insulation properties and greater susceptibility to deformation under heat.
Cushioning and Shock Absorption
Polypropylene foam offers superior cushioning and shock absorption compared to polystyrene foam due to its open-cell structure, which effectively disperses impact forces. Its higher resilience and flexibility make it ideal for protecting delicate or heavy items during transportation. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, tends to be more rigid and less effective at absorbing shocks, increasing the risk of damage to fragile products.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Polypropylene foam offers a lower environmental impact compared to polystyrene foam due to its higher recyclability and reduced greenhouse gas emissions during production. Unlike polystyrene, which is difficult to recycle and often ends up in landfills or oceans, polypropylene can be reprocessed into new packaging materials, reducing plastic waste. The biodegradability of polypropylene foam is limited, but its capacity for multiple recycling cycles makes it a more sustainable packaging option.
Cost and Availability
Polypropylene foam typically offers higher durability and better impact resistance compared to polystyrene foam, but it comes at a higher cost, making polystyrene foam a more budget-friendly option for packaging. Polystyrene foam is widely available and commonly used due to its low price and ease of manufacturing, while polypropylene foam availability may be more limited depending on the supplier and region. Cost-effectiveness and material accessibility are crucial factors influencing the choice between polypropylene and polystyrene foams in packaging applications.
Applications in Packaging Industries
Polypropylene foam excels in protective packaging for fragile electronics and automotive components due to its superior impact resistance and lightweight structure. Polystyrene foam is widely used for food packaging and disposable containers thanks to its excellent insulation properties and cost-effectiveness. Packaging industries prefer polypropylene foam for reusable and durable applications, whereas polystyrene foam dominates single-use, low-cost packaging solutions.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Polypropylene foam offers superior durability, chemical resistance, and eco-friendly recyclability compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for protective packaging of electronics and fragile items. Polystyrene foam provides excellent thermal insulation and cost-effective cushioning, suitable for lightweight, low-impact packaging such as food containers and disposable coolers. Assessing factors like shock absorption, weight, environmental impact, and product sensitivity is essential to choosing the right foam material for efficient and sustainable packaging solutions.
Infographic: Polypropylene foam vs Polystyrene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com