Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and water resistance compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for long-lasting mattress support. Polyurethane foam provides excellent cushioning and breathability but may compress faster and retain more moisture over time.
Table of Comparison
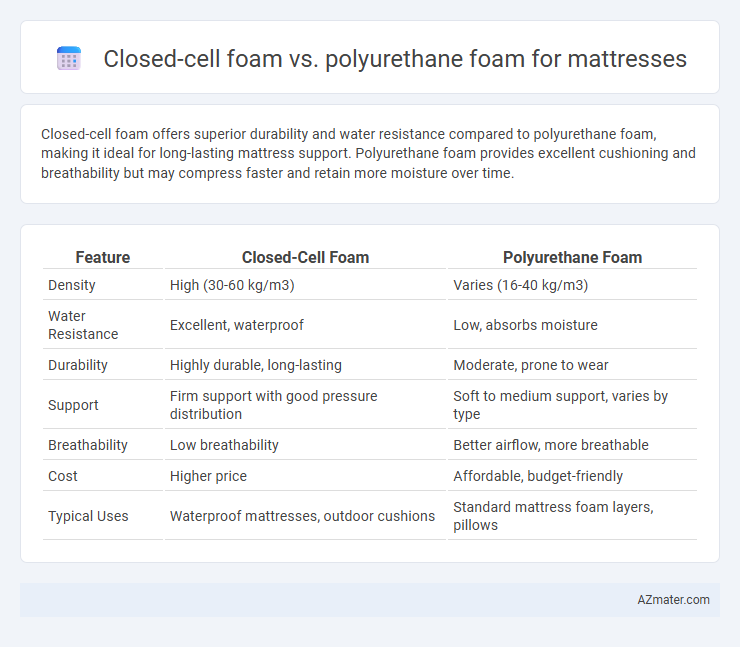
| Feature | Closed-Cell Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | High (30-60 kg/m3) | Varies (16-40 kg/m3) |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, waterproof | Low, absorbs moisture |
| Durability | Highly durable, long-lasting | Moderate, prone to wear |
| Support | Firm support with good pressure distribution | Soft to medium support, varies by type |
| Breathability | Low breathability | Better airflow, more breathable |
| Cost | Higher price | Affordable, budget-friendly |
| Typical Uses | Waterproof mattresses, outdoor cushions | Standard mattress foam layers, pillows |
Introduction to Mattress Foams
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for mattresses that require long-lasting support and minimal absorption of liquids. Polyurethane foam, commonly used in mattress construction, provides excellent cushioning and breathability, enhancing comfort and airflow for a cooler sleep experience. Both foams cater to different needs in mattress design, with closed-cell foam emphasizing structural integrity and polyurethane foam focusing on softness and pressure relief.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam is a type of polyurethane foam characterized by its dense, airtight structure where each foam cell is completely enclosed, providing superior resistance to moisture and increased durability. This foam offers high thermal insulation and firmness, making it ideal for mattress support layers that require long-lasting structural integrity and pressure relief. Unlike open-cell polyurethane foam, closed-cell foam prevents air and water absorption, enhancing mattress longevity and hygiene.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile, open-cell material widely used in mattresses for its cushioning and durability properties. Unlike closed-cell foam, polyurethane foam offers superior breathability and flexibility, enhancing comfort by conforming to body contours while promoting airflow. Its ability to provide balanced support and pressure relief makes it a popular choice in memory foam and hybrid mattress constructions.
Key Differences Between Closed-Cell and Polyurethane Foam
Closed-cell foam features a dense structure with cells tightly packed together, offering superior moisture resistance and higher durability compared to polyurethane foam, which has an open-cell structure allowing for greater breathability and flexibility. Polyurethane foam provides excellent cushioning and is generally softer, making it ideal for comfort in mattresses, while closed-cell foam excels in support and resilience, often used for pressure relief and longevity. The thermal insulation properties of closed-cell foam surpass those of polyurethane, impacting mattress temperature regulation and overall sleep experience.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Closed-cell foam provides superior firm support and high-density resilience, making it ideal for maintaining spinal alignment and pressure relief during sleep. Polyurethane foam offers a softer, more contouring comfort experience with moderate support, adapting well to body shapes but may lack durability and firmness over time. For optimal mattress performance, closed-cell foam excels in support longevity, while polyurethane foam caters more to immediate comfort and cushioning.
Durability and Lifespan
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability compared to polyurethane foam due to its dense structure, which resists compression and wear over time. Polyurethane foam tends to degrade faster, losing its shape and support within 3 to 5 years, whereas closed-cell foam can maintain its integrity and comfort for 7 to 10 years or longer. The higher resilience of closed-cell foam makes it a preferred choice for mattresses that require long-lasting support and durability.
Breathability and Temperature Regulation
Closed-cell foam features a dense structure with tightly packed cells that limit airflow, resulting in lower breathability and potential heat retention. Polyurethane foam, especially open-cell varieties, promotes better airflow and enhanced temperature regulation due to its porous composition. Choosing open-cell polyurethane foam can significantly improve mattress breathability and maintain a cooler sleeping surface compared to closed-cell foam alternatives.
Cost and Affordability
Closed-cell foam offers higher durability and moisture resistance but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to polyurethane foam, making it less affordable for budget-conscious consumers. Polyurethane foam, widely used in mattresses, provides a more cost-effective solution with reasonable comfort and support, appealing to a broader market segment. Selecting between the two depends largely on balancing upfront investment against long-term performance and affordability needs.
Health and Safety Considerations
Closed-cell foam offers superior resistance to moisture and mold growth, making it a healthier choice for mattresses by reducing allergens and microbial buildup. Polyurethane foam, while popular for comfort, can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that may affect indoor air quality and pose respiratory risks. Selecting mattresses with low-VOC certifications and hypoallergenic properties is crucial for ensuring safety and reducing potential health hazards.
Which Foam is Best for Your Mattress?
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and higher density compared to traditional polyurethane foam, making it ideal for supportive mattress cores. Polyurethane foam provides excellent comfort and affordability but tends to break down faster and retain more heat. Choosing the best foam depends on balancing durability, support needs, and temperature regulation preferences for optimal mattress performance.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Polyurethane foam for Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com