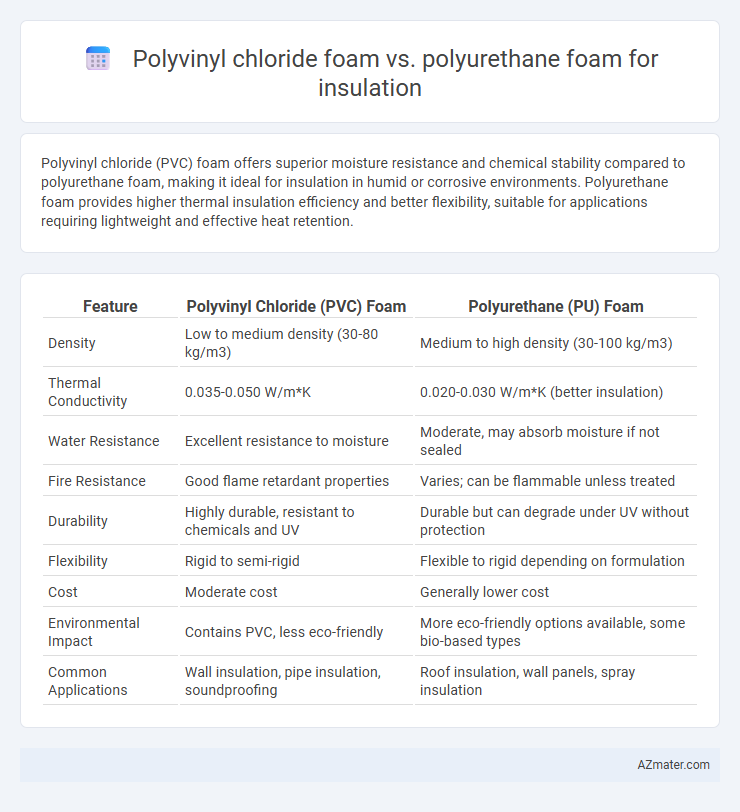
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior moisture resistance and chemical stability compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for insulation in humid or corrosive environments. Polyurethane foam provides higher thermal insulation efficiency and better flexibility, suitable for applications requiring lightweight and effective heat retention.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Polyurethane (PU) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium density (30-80 kg/m3) | Medium to high density (30-100 kg/m3) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.035-0.050 W/m*K | 0.020-0.030 W/m*K (better insulation) |
| Water Resistance | Excellent resistance to moisture | Moderate, may absorb moisture if not sealed |
| Fire Resistance | Good flame retardant properties | Varies; can be flammable unless treated |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to chemicals and UV | Durable but can degrade under UV without protection |
| Flexibility | Rigid to semi-rigid | Flexible to rigid depending on formulation |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally lower cost |
| Environmental Impact | Contains PVC, less eco-friendly | More eco-friendly options available, some bio-based types |
| Common Applications | Wall insulation, pipe insulation, soundproofing | Roof insulation, wall panels, spray insulation |
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a lightweight, rigid material commonly used in insulation due to its excellent thermal resistance, moisture tolerance, and fire retardant properties. Its closed-cell structure provides superior durability and resistance to chemical and environmental degradation compared to polyurethane foam. PVC foam is favored in applications requiring high dimensional stability and low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for building insulation and industrial purposes.
Introduction to Polyurethane (PU) Foam
Polyurethane (PU) foam is a versatile insulation material known for its excellent thermal resistance and lightweight properties, making it highly efficient in reducing energy consumption in buildings. Unlike polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, PU foam offers superior flexibility and higher moisture resistance, which enhances its durability in various environmental conditions. Its closed-cell structure provides effective air sealing and improved soundproofing, making it a preferred choice for insulating walls, roofs, and floors.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers moderate thermal insulation with a typical R-value ranging from 3.0 to 4.0 per inch, making it effective for applications requiring moisture resistance and durability. Polyurethane (PU) foam provides superior thermal insulation, boasting R-values between 6.0 and 7.0 per inch due to its closed-cell structure which traps heat more efficiently. While polyurethane foam excels in energy savings and reducing heat transfer, PVC foam remains valuable in environments demanding chemical resistance and fire retardancy.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for applications requiring high impact resistance and structural integrity. PVC foam also offers enhanced durability due to its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation, ensuring long-lasting performance in harsh environments. In contrast, polyurethane foam provides good insulation efficiency but tends to degrade faster under mechanical stress and environmental exposure.
Fire Resistance and Safety Ratings
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to polyurethane foam, as it has a higher ignition temperature and emits fewer toxic gases during combustion. PVC foam typically carries fire safety ratings such as Class B or better under ASTM E84 standards, making it suitable for applications requiring stringent fire codes. In contrast, polyurethane foam is more flammable and often requires fire retardant additives to meet safety regulations, which can affect its insulation properties and overall performance.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior moisture resistance and significantly lower water absorption compared to polyurethane (PU) foam, making it ideal for insulation in humid or wet environments. PVC foam's closed-cell structure prevents water infiltration and maintains insulation properties, whereas PU foam, especially open-cell variants, tend to absorb moisture, compromising thermal performance and increasing the risk of mold growth. These characteristics position PVC foam as a more durable solution for building insulation requiring long-term exposure to moisture.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam insulation often raises environmental concerns due to its production involving chlorine and the release of toxic chemicals during disposal, which can harm ecosystems and human health. Polyurethane foam, while providing superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency, is typically made from petrochemical derivatives and may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs), impacting indoor air quality and contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable alternatives favor closed-cell polyurethane foams with bio-based polyols and PVC foams manufactured with recycled content and lower chlorine emissions to reduce environmental impact.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam generally offers lower upfront costs compared to polyurethane foam, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale insulation projects. However, polyurethane foam provides superior thermal resistance and durability, potentially reducing long-term energy expenses and maintenance costs. Economic considerations should weigh initial investment against lifecycle savings, with polyurethane favored for high-performance insulation despite its higher initial price.
Common Applications in Construction
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is commonly used in construction for window frames, siding, and roofing insulation due to its durability, moisture resistance, and fire-retardant properties. Polyurethane (PU) foam is widely applied in wall cavities, ceilings, and floor insulation because of its superior thermal insulation performance and ability to expand and fill gaps for airtight sealing. Both materials offer energy efficiency benefits, but PVC foam excels in exterior applications, while PU foam is preferred for internal insulation tasks.
Selecting the Right Foam for Your Insulation Needs
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent moisture resistance, high durability, and fire retardancy, making it ideal for environments prone to humidity and exposure to chemicals. Polyurethane foam provides superior thermal insulation values (higher R-values) and flexibility, suitable for applications requiring efficient heat retention and soundproofing. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing moisture resistance, insulation efficiency, structural strength, and budget constraints specific to your insulation needs.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Polyurethane foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com