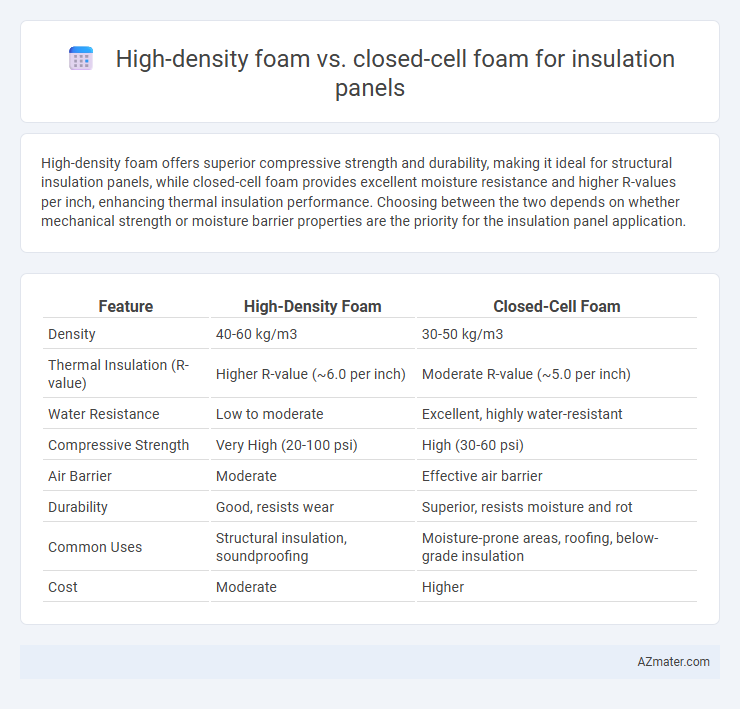
High-density foam offers superior compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for structural insulation panels, while closed-cell foam provides excellent moisture resistance and higher R-values per inch, enhancing thermal insulation performance. Choosing between the two depends on whether mechanical strength or moisture barrier properties are the priority for the insulation panel application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High-Density Foam | Closed-Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 40-60 kg/m3 | 30-50 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | Higher R-value (~6.0 per inch) | Moderate R-value (~5.0 per inch) |
| Water Resistance | Low to moderate | Excellent, highly water-resistant |
| Compressive Strength | Very High (20-100 psi) | High (30-60 psi) |
| Air Barrier | Moderate | Effective air barrier |
| Durability | Good, resists wear | Superior, resists moisture and rot |
| Common Uses | Structural insulation, soundproofing | Moisture-prone areas, roofing, below-grade insulation |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Foam Insulation Panels
High-density foam and closed-cell foam are both popular materials used in insulation panels due to their superior thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties. High-density foam offers enhanced structural strength and soundproofing capabilities, making it ideal for applications requiring robust support. Closed-cell foam provides excellent insulation with low permeability, which prevents water absorption and improves energy efficiency in building envelopes.
What is High-Density Foam Insulation?
High-density foam insulation is a type of rigid foam characterized by its high compressive strength and low thermal conductivity, making it highly effective for energy-efficient building insulation panels. It is often made from polyurethane or polyisocyanurate, providing excellent air and moisture resistance properties that enhance durability and reduce heat transfer. Compared to closed-cell foam, high-density foam usually offers greater mechanical strength and long-term thermal performance, ideal for applications requiring robust insulation solutions.
What is Closed-Cell Foam Insulation?
Closed-cell foam insulation is a rigid, high-density material characterized by tightly packed cells filled with insulating gas, providing superior thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties. Its closed structure prevents water absorption, making it highly effective for preventing mold and structural damage in insulation panels. Compared to high-density foam, closed-cell foam offers enhanced durability, higher R-values per inch, and improved long-term performance in both thermal insulation and moisture control.
Key Differences Between High-Density and Closed-Cell Foam
High-density foam and closed-cell foam differ primarily in their density and structural composition, impacting insulation performance and durability. High-density foam typically exhibits greater rigidity and higher compressive strength, making it ideal for structural support and load-bearing applications. Closed-cell foam features a uniform cell structure that provides superior moisture resistance and higher R-values per inch, enhancing thermal insulation efficiency in panels.
Thermal Performance Comparison
High-density foam insulation panels typically offer superior thermal resistance with R-values ranging from 6 to 7 per inch, providing enhanced energy efficiency for buildings. Closed-cell foam, although often slightly lower in density, delivers excellent moisture resistance and an R-value around 5 to 6 per inch, making it effective in preventing thermal bridging and condensation. Both materials improve thermal performance, but high-density foam panels generally provide better overall insulation due to their higher compressive strength and reduced air infiltration.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
High-density foam and closed-cell foam both offer superior moisture resistance, with closed-cell foam providing a more impermeable barrier that effectively prevents water absorption and mold growth, making it ideal for insulation panels in damp environments. High-density foam, while also moisture-resistant, is generally more rigid and durable, retaining its structural integrity under pressure and reducing long-term wear and tear. When selecting insulation panels for moisture resistance and durability, closed-cell foam excels in waterproofing, whereas high-density foam is preferred for mechanical strength and longevity.
Installation Process and Flexibility
High-density foam panels offer superior rigidity during the installation process, making them ideal for structural insulation applications where a firm, stable barrier is required. Closed-cell foam provides greater flexibility and compressive strength, allowing it to conform to irregular surfaces and fill gaps more effectively while maintaining high insulation performance. Installation efficiency improves with closed-cell foam due to its ability to expand slightly and create airtight seals, reducing the need for additional sealing materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
High-density foam insulation panels typically have a higher environmental impact due to their petroleum-based composition and energy-intensive manufacturing process, contributing to greater carbon emissions compared to closed-cell foam. Closed-cell foam offers superior insulation performance with better moisture resistance, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency and reduced heating and cooling demands, indirectly supporting sustainability goals. Both foams present challenges in recyclability, but advancements in bio-based and recycled materials are beginning to mitigate their environmental footprints.
Cost Analysis: High-Density vs Closed-Cell Foam
High-density foam insulation panels typically cost more upfront than closed-cell foam due to greater material density and enhanced structural properties. Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance and higher R-values per inch, potentially reducing long-term energy expenses despite its moderate initial price. Evaluating cost-effectiveness requires balancing installation costs, thermal performance, and durability specific to building project requirements.
Choosing the Best Foam Insulation for Your Project
High-density foam offers superior compressive strength and long-term durability, making it ideal for structural insulation panels requiring load-bearing capabilities. Closed-cell foam provides excellent moisture resistance and a higher R-value per inch, ensuring effective thermal insulation in damp or exterior environments. Selecting the best foam insulation depends on project-specific factors such as load requirements, moisture exposure, and desired thermal performance.
Infographic: High-density foam vs Closed-cell foam for Insulation panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com