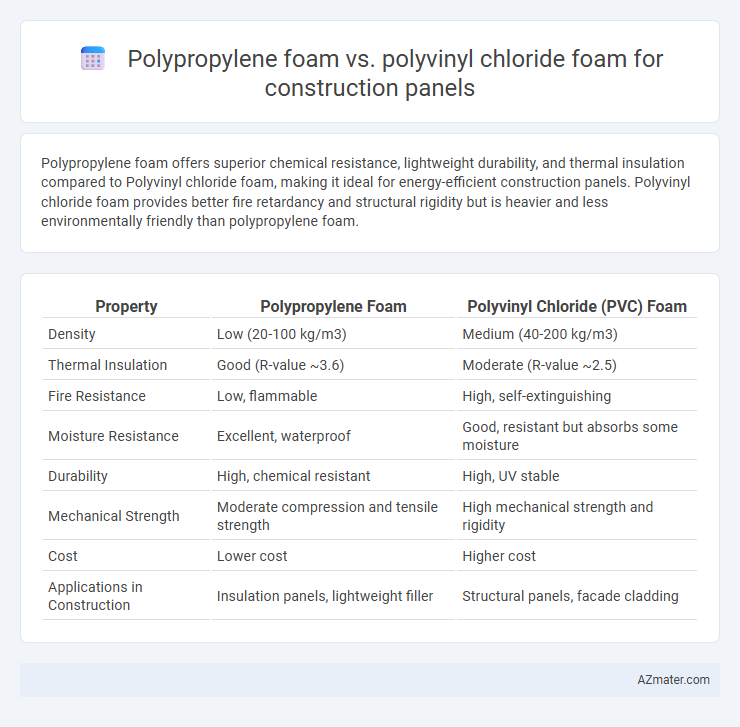
Polypropylene foam offers superior chemical resistance, lightweight durability, and thermal insulation compared to Polyvinyl chloride foam, making it ideal for energy-efficient construction panels. Polyvinyl chloride foam provides better fire retardancy and structural rigidity but is heavier and less environmentally friendly than polypropylene foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low (20-100 kg/m3) | Medium (40-200 kg/m3) |
| Thermal Insulation | Good (R-value ~3.6) | Moderate (R-value ~2.5) |
| Fire Resistance | Low, flammable | High, self-extinguishing |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent, waterproof | Good, resistant but absorbs some moisture |
| Durability | High, chemical resistant | High, UV stable |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate compression and tensile strength | High mechanical strength and rigidity |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications in Construction | Insulation panels, lightweight filler | Structural panels, facade cladding |
Introduction to Construction Panel Foams
Construction panel foams, such as Polypropylene (PP) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foams, serve critical roles in insulation, lightweight structuring, and durability within the building industry. Polypropylene foam offers excellent thermal resistance, chemical inertness, and superior impact absorption, making it ideal for energy-efficient and resilient construction panels. In contrast, Polyvinyl chloride foam provides enhanced fire retardancy, rigidity, and moisture resistance, often favored for exterior cladding and waterproof panel applications.
Overview of Polypropylene Foam
Polypropylene foam is a lightweight, durable material widely used in construction panels due to its excellent thermal insulation and high chemical resistance. It offers superior moisture resistance and impact strength compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, making it ideal for structural applications exposed to harsh environments. The closed-cell structure of polypropylene foam ensures long-lasting performance with minimal water absorption and enhanced energy efficiency in building insulation.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior durability and fire resistance compared to polypropylene foam, making it a preferred material for construction panels where safety and longevity are critical. PVC foam features excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, maintaining performance under varying environmental conditions such as moisture and temperature fluctuations. Its closed-cell structure provides enhanced insulation properties and soundproofing, positioning it as a versatile solution for interior and exterior panel applications in construction.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polypropylene foam offers superior mechanical strength with higher tensile and impact resistance compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, making it more durable under dynamic loads in construction panels. PVC foam demonstrates good rigidity and compression strength but tends to be more brittle and susceptible to cracking under stress. The enhanced elasticity and energy absorption capacity of polypropylene foam contribute to its preferred use in applications requiring long-term structural resilience and flexibility.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Polypropylene foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, which minimizes heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency in construction panels. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides moderate insulation but is denser, resulting in lower thermal resistance compared to polypropylene foam. The lightweight nature of polypropylene foam combined with its high thermal performance makes it ideal for applications requiring enhanced temperature control and insulation in building envelopes.
Water and Chemical Resistance
Polypropylene foam exhibits superior water resistance due to its low moisture absorption and hydrophobic properties, making it highly suitable for damp or wet construction environments. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam also offers good chemical resistance, especially against acids, alkalis, and oils, but is generally less resistant to prolonged water exposure compared to polypropylene. When selecting panels for construction, polypropylene foam is preferred for applications requiring enhanced water resistance, while PVC foam is chosen for environments demanding robust chemical resistance.
Fire Retardancy and Safety Performance
Polypropylene foam exhibits superior fire retardancy with a higher ignition temperature and emits fewer toxic gases compared to Polyvinyl chloride foam in construction panels. Polyvinyl chloride foam, while offering some fire resistance, releases hydrochloric acid fumes when burned, posing significant safety risks. Choosing polypropylene foam enhances overall safety performance by minimizing flame propagation and toxic smoke production during fire incidents.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene foam exhibits superior environmental benefits compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, primarily due to its lower carbon footprint and recyclability, making it a more sustainable choice for construction panels. PVC foam production involves hazardous chemicals and generates toxic byproducts, which contribute to environmental pollution and pose health risks during manufacturing and disposal. Polypropylene foam's biodegradability and energy-efficient production process further enhance its sustainability profile in green building applications.
Cost and Availability
Polypropylene foam offers a cost-effective solution for construction panels due to its lower raw material prices and simpler manufacturing process compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam. PVC foam panels, while generally more expensive, provide broader availability in the construction market because of established supply chains and extensive industry use. Choosing between polypropylene and PVC foam depends on balancing budget constraints with material accessibility tailored to specific project requirements.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Polypropylene foam offers superior chemical resistance, lightweight properties, and excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for wall insulation and roofing panels in construction projects requiring durability and moisture resistance. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides higher rigidity, fire resistance, and dimensional stability, better suited for decorative panels, exterior cladding, and environments with higher fire safety standards. For applications prioritizing energy efficiency and moisture control, polypropylene foam is recommended, while PVC foam is preferable for structural paneling and fire-retardant construction needs.
Infographic: Polypropylene foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Construction panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com