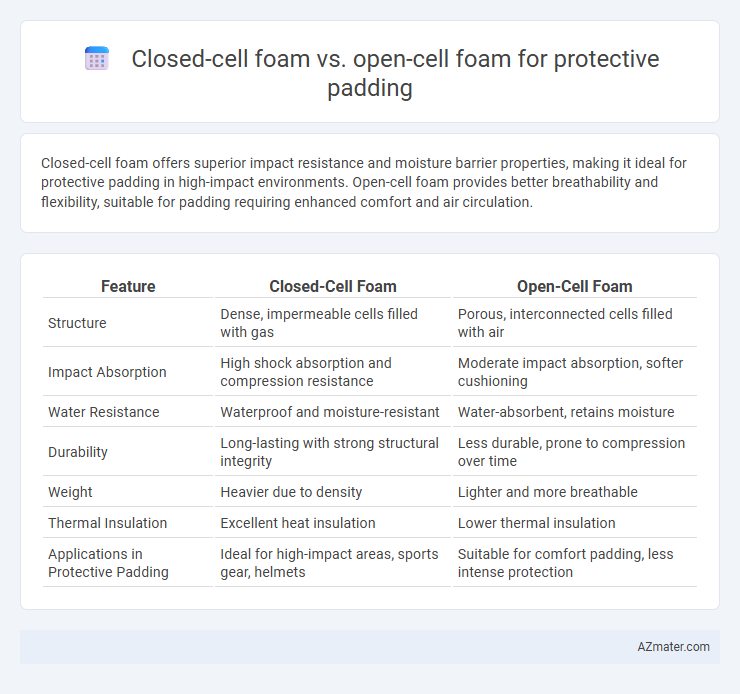
Closed-cell foam offers superior impact resistance and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for protective padding in high-impact environments. Open-cell foam provides better breathability and flexibility, suitable for padding requiring enhanced comfort and air circulation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-Cell Foam | Open-Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Dense, impermeable cells filled with gas | Porous, interconnected cells filled with air |
| Impact Absorption | High shock absorption and compression resistance | Moderate impact absorption, softer cushioning |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof and moisture-resistant | Water-absorbent, retains moisture |
| Durability | Long-lasting with strong structural integrity | Less durable, prone to compression over time |
| Weight | Heavier due to density | Lighter and more breathable |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent heat insulation | Lower thermal insulation |
| Applications in Protective Padding | Ideal for high-impact areas, sports gear, helmets | Suitable for comfort padding, less intense protection |
Introduction to Protective Foam: Closed-Cell vs Open-Cell
Closed-cell foam offers high density and superior impact resistance, making it ideal for protective padding where moisture resistance and durability are critical. Open-cell foam features a softer, more flexible structure with excellent shock absorption and breathability, suitable for comfort-focused protection. Choosing between closed-cell and open-cell foam depends on the specific requirements for cushioning, protection, and environmental exposure.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Closed-cell foam consists of tightly packed cells filled with gas, resulting in a dense, rigid material that offers superior impact resistance and water resistance, ideal for protective padding. Open-cell foam features a porous structure with interconnected cells, providing greater flexibility and breathability but less compression resistance and durability compared to closed-cell foam. Material composition in closed-cell foam typically includes polyethylene or EVA, while open-cell foam is commonly polyurethane-based, influencing their distinct cushioning and shock absorption properties.
Impact Absorption Capabilities
Closed-cell foam exhibits superior impact absorption capabilities due to its dense, rigid structure that effectively disperses shock and prevents compression. Open-cell foam, characterized by a softer and more flexible composition, absorbs impacts by allowing air to pass through its interconnected cells, offering excellent cushioning but less structural support. Protective padding utilizing closed-cell foam provides enhanced protection in high-impact scenarios, while open-cell foam is preferred for applications requiring comfort and moderate shock absorption.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Closed-cell foam offers a higher density, providing greater weight but superior impact resistance, while open-cell foam is lighter and more flexible due to its less compact structure. Closed-cell foam's rigid, airtight cells enhance durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty protective padding. Open-cell foam's open, porous structure allows for better compression and cushioning, offering enhanced comfort and flexibility in applications requiring lightweight protection.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance and minimal water absorption due to its dense, non-permeable structure, making it ideal for protective padding in wet environments. Open-cell foam, with its porous and breathable design, absorbs significantly more moisture, which can lead to reduced durability and increased weight when exposed to water. Choosing closed-cell foam enhances longevity and performance of protective gear by preventing water infiltration and maintaining structural integrity.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Closed-cell foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its dense structure and impermeable cells that trap air, reducing heat transfer effectively in protective padding. In contrast, open-cell foam has a more breathable design with interconnected cells, resulting in lower thermal resistance and reduced insulation performance. The choice between closed-cell and open-cell foam significantly influences the temperature regulation and comfort of protective gear in varying environmental conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Closed-cell foam exhibits superior durability and longevity for protective padding due to its high-density structure, which resists moisture, compression, and abrasion more effectively than open-cell foam. The rigid, impermeable matrix of closed-cell foam maintains shape and cushioning properties over extended use, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term impact absorption and resistance to environmental factors. Open-cell foam, while softer and more breathable, tends to degrade faster under repeated stress and exposure to moisture, resulting in reduced protective performance over time.
Cost Considerations for Protective Padding
Closed-cell foam generally costs more than open-cell foam due to its higher density and superior durability, making it ideal for protective padding requiring impact resistance and water resistance. Open-cell foam offers a more budget-friendly option with better breathability and flexibility but may degrade faster under heavy use. Evaluating cost-effectiveness involves balancing initial expense against longevity and performance requirements in protective padding applications.
Application Suitability: Sports, Industrial, and Medical Uses
Closed-cell foam provides superior impact resistance and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for high-impact sports gear, industrial equipment padding, and medical immobilization devices. Open-cell foam offers enhanced breathability and comfort, suited for low-impact sports padding, cushioning in industrial settings, and medical applications requiring pressure relief. Selecting foam depends on balancing protection, comfort, and environmental exposure specific to sports, industrial, or medical use cases.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Protective Padding Needs
Closed-cell foam offers superior impact resistance and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for protective padding in high-impact or wet environments. Open-cell foam provides better breathability and cushioning, suitable for applications requiring comfort and airflow. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing factors such as shock absorption, weight, durability, and environmental exposure for optimal protection.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Open-cell foam for Protective padding
 azmater.com
azmater.com