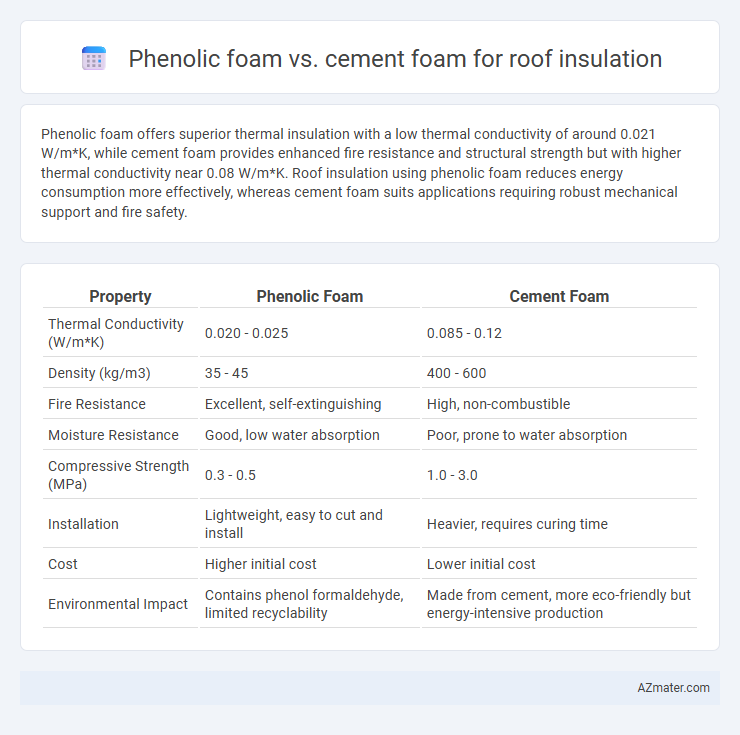
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of around 0.021 W/m*K, while cement foam provides enhanced fire resistance and structural strength but with higher thermal conductivity near 0.08 W/m*K. Roof insulation using phenolic foam reduces energy consumption more effectively, whereas cement foam suits applications requiring robust mechanical support and fire safety.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phenolic Foam | Cement Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.020 - 0.025 | 0.085 - 0.12 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 35 - 45 | 400 - 600 |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent, self-extinguishing | High, non-combustible |
| Moisture Resistance | Good, low water absorption | Poor, prone to water absorption |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 0.3 - 0.5 | 1.0 - 3.0 |
| Installation | Lightweight, easy to cut and install | Heavier, requires curing time |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Contains phenol formaldehyde, limited recyclability | Made from cement, more eco-friendly but energy-intensive production |
Introduction to Roof Insulation Materials
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of around 0.022 W/m*K, providing excellent energy efficiency and moisture resistance for roof applications. Cement foam, while heavier with thermal conductivity approximately 0.07 W/m*K, delivers enhanced fire resistance, durability, and sound insulation due to its mineral-based composition. Selecting the optimal roof insulation material depends on balancing thermal performance, fire safety standards, structural load capacity, and environmental factors.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a high-performance insulation material known for its superior thermal resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent fire retardant properties, making it ideal for roof insulation applications. Its closed-cell structure provides exceptional moisture resistance and dimensional stability, enhancing the durability of roofing systems compared to conventional cement foam. Phenolic foam's lightweight nature combined with high compressive strength allows for easy installation while maintaining efficient energy conservation in buildings.
Overview of Cement Foam
Cement foam insulation is a lightweight, durable material composed of cement, water, and a foaming agent that creates a porous structure with excellent thermal insulation properties. It offers superior fire resistance, high compressive strength, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for roofing applications in harsh climates. This eco-friendly solution also provides sound insulation and enhanced structural integrity compared to organic foam insulations like phenolic foam.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation performance compared to cement foam, with a lower thermal conductivity typically around 0.020 W/m*K, resulting in better heat resistance and energy efficiency for roof applications. Cement foam generally has higher thermal conductivity values, ranging from 0.06 to 0.10 W/m*K, which limits its effectiveness in reducing heat transfer. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam enhances its insulating properties, making it a preferred choice for high-performance roofing insulation systems.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance with a high limiting oxygen index (LOI) typically around 37%, which means it self-extinguishes quickly and emits low smoke during combustion, enhancing overall roof safety. Cement foam, while inherently non-combustible and providing excellent fireproofing, tends to be heavier and less effective in thermal insulation compared to phenolic foam. Both materials improve roof fire safety, but phenolic foam balances effective insulation and fire retardancy with lower smoke toxicity, making it a preferred choice in high-performance building applications.
Moisture and Water Absorption
Phenolic foam exhibits exceptionally low moisture absorption rates, typically below 1%, making it highly resistant to water penetration and ideal for roof insulation in humid environments. In contrast, cement foam tends to have higher water absorption, often exceeding 10%, which can compromise its insulating properties and durability when exposed to prolonged moisture. Selecting phenolic foam enhances thermal insulation performance by maintaining structural integrity and minimizing mold growth caused by moisture infiltration.
Durability and Lifespan
Phenolic foam offers superior durability with excellent resistance to moisture, chemical exposure, and mold, often maintaining its insulating properties for over 50 years. Cement foam provides robust mechanical strength and fire resistance but may be prone to cracking and degradation under prolonged freeze-thaw cycles, resulting in a shorter lifespan of around 20-30 years. When longevity and consistent thermal performance are critical, phenolic foam generally outperforms cement foam in roof insulation applications.
Installation Process and Practicality
Phenolic foam offers lightweight properties and easy-cut installation, allowing seamless fitting and faster application on roofs, while cement foam requires mixing and curing, making the process more labor-intensive and time-consuming. Phenolic foam's consistent thickness and water-resistant nature enhance its practicality in diverse weather conditions, whereas cement foam provides superior fire resistance and structural strength but can be challenging to handle and finish smoothly. The choice between phenolic and cement foam depends on project priorities such as ease of installation, durability, and specific roofing requirements.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with a higher R-value per inch, resulting in reduced heating and cooling expenses despite its higher initial cost compared to cement foam. Cement foam, while more affordable upfront and providing excellent fire resistance and durability, may lead to increased long-term energy costs due to its lower insulation performance. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and energy savings, Phenolic foam often proves more economical for roof insulation in energy-efficient building projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with low embodied carbon due to its high R-value per inch and lightweight composition, making it a sustainable choice for reducing energy consumption in roofs. Cement foam, composed of natural materials like cement and water, provides excellent fire resistance and durability but has a higher carbon footprint due to cement manufacturing emissions. Selecting phenolic foam supports eco-friendly building practices by minimizing insulation waste and enhancing energy efficiency, whereas cement foam's sustainability benefits stem from its recyclability and long lifespan.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Cement foam for Roof insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com