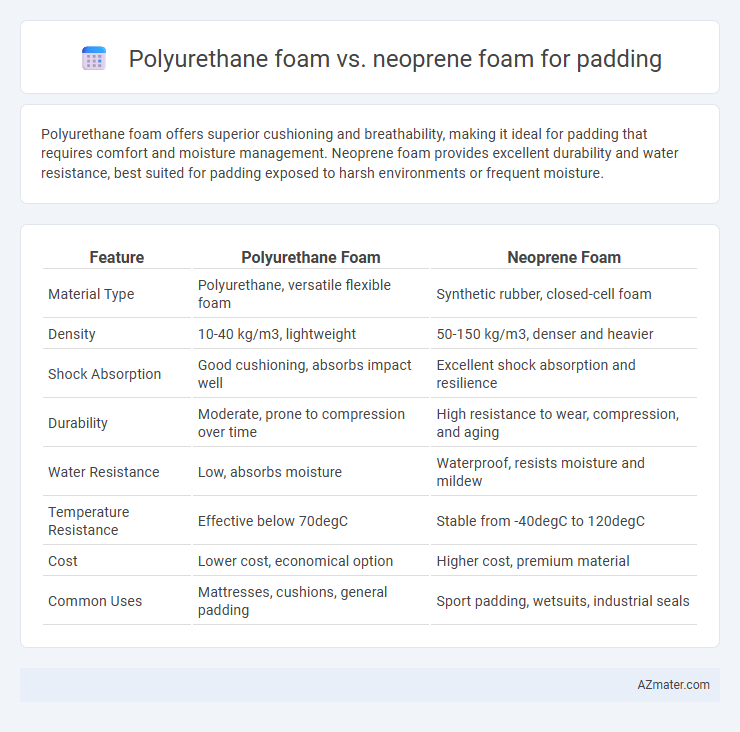
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for padding that requires comfort and moisture management. Neoprene foam provides excellent durability and water resistance, best suited for padding exposed to harsh environments or frequent moisture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Neoprene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyurethane, versatile flexible foam | Synthetic rubber, closed-cell foam |
| Density | 10-40 kg/m3, lightweight | 50-150 kg/m3, denser and heavier |
| Shock Absorption | Good cushioning, absorbs impact well | Excellent shock absorption and resilience |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to compression over time | High resistance to wear, compression, and aging |
| Water Resistance | Low, absorbs moisture | Waterproof, resists moisture and mildew |
| Temperature Resistance | Effective below 70degC | Stable from -40degC to 120degC |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical option | Higher cost, premium material |
| Common Uses | Mattresses, cushions, general padding | Sport padding, wetsuits, industrial seals |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Neoprene Foams
Polyurethane foam is a versatile polymer known for its lightweight, flexible, and cushioning properties, making it ideal for padding applications that require comfort and impact absorption. Neoprene foam, a synthetic rubber, offers superior durability, chemical resistance, and excellent thermal insulation, often preferred in environments needing robust protection and moisture resistance. Both materials serve distinct roles in padding, with polyurethane favored for softness and cost-effectiveness, while neoprene excels in resilience and environmental protection.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polyurethane foam consists of urethane polymer chains formed by reacting polyols with diisocyanates, resulting in a flexible yet durable cellular structure ideal for impact absorption. Neoprene foam is a synthetic rubber composed primarily of polychloroprene, featuring a closed-cell structure that offers excellent water resistance and resilience. The chemical composition of polyurethane foam allows for greater cushioning and energy dispersion, while neoprene's molecular configuration provides superior elasticity and resistance to oils and chemicals.
Physical Properties and Performance
Polyurethane foam offers excellent cushioning with high resilience and breathability, making it ideal for applications requiring comfort and shock absorption. Neoprene foam, known for superior chemical resistance, water impermeability, and thermal insulation, excels in environments exposed to moisture and temperature fluctuations. Both materials provide durable padding, but polyurethane foam typically delivers better flexibility and lightweight performance, while neoprene foam ensures enhanced durability and protection in harsh conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane foam offers excellent cushioning but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to heat, moisture, and UV light, reducing its overall durability and lifespan. Neoprene foam exhibits superior resistance to environmental factors such as water, oils, and temperature fluctuations, making it more durable and longer-lasting for padding applications. For long-term use and sustaining performance in harsh conditions, neoprene foam is the preferred choice over polyurethane foam.
Comfort and Cushioning Abilities
Polyurethane foam provides excellent cushioning with high-density support and superior breathability, making it ideal for prolonged comfort in padding applications. Neoprene foam offers enhanced durability and water resistance while delivering firm, consistent cushioning that maintains shape under pressure. Choosing between the two depends on whether comfort and airflow or resilience and moisture protection are prioritized in the padded product.
Water and Chemical Resistance
Polyurethane foam provides excellent cushioning and flexibility but has limited water and chemical resistance, making it prone to degradation when exposed to harsh environments. Neoprene foam offers superior water repellency and high resistance to oils, chemicals, and ozone, maintaining durability and structural integrity in wet or chemically aggressive conditions. For applications requiring prolonged exposure to moisture and chemicals, neoprene foam outperforms polyurethane foam in both performance and longevity.
Applications in Padding Industries
Polyurethane foam is widely used in furniture, automotive seats, and mattress padding due to its excellent cushioning, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness. Neoprene foam offers superior resistance to water, oil, and temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for protective padding in sports equipment, wetsuits, and industrial applications. Both materials provide unique benefits tailored to specific padding industry requirements, with polyurethane favored for comfort and neoprene preferred for durability and environmental resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane foam, widely used for padding, often involves petroleum-based chemicals and releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production, raising environmental concerns. Neoprene foam, derived from synthetic rubber, typically has higher durability and resistance but presents challenges in biodegradability and recycling due to its chloroprene composition. Sustainable alternatives emphasize bio-based polyurethanes and recycled neoprene to reduce carbon footprint and promote circular economy in padding materials.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Polyurethane foam generally offers a more cost-effective solution for padding due to its lower production costs and widespread availability, making it ideal for budget-sensitive projects. Neoprene foam, while more expensive, provides superior durability, water resistance, and cushioning performance, justifying its higher price in applications requiring long-term resilience. Analyzing upfront cost versus lifecycle value is essential for selecting the appropriate foam material based on specific padding needs and budget constraints.
Choosing the Best Foam for Your Padding Needs
Polyurethane foam offers excellent cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for comfort-focused padding applications, while neoprene foam provides superior water resistance, durability, and insulation, suited for high-impact or outdoor uses. When choosing the best foam for your padding needs, consider factors like moisture exposure, compression resistance, and intended use environment. Selecting the optimal foam enhances protection, longevity, and user comfort in products ranging from sports gear to upholstery.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Neoprene foam for Padding
 azmater.com
azmater.com