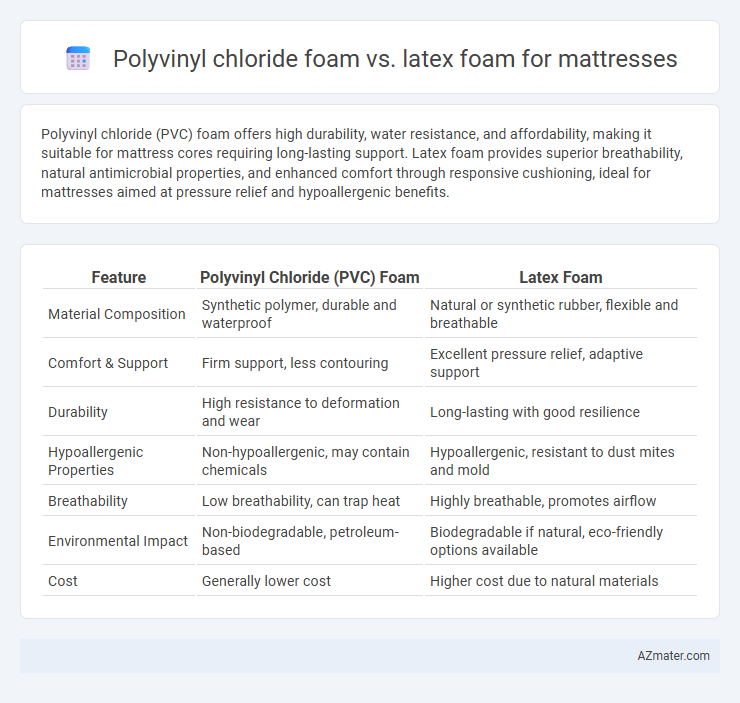
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers high durability, water resistance, and affordability, making it suitable for mattress cores requiring long-lasting support. Latex foam provides superior breathability, natural antimicrobial properties, and enhanced comfort through responsive cushioning, ideal for mattresses aimed at pressure relief and hypoallergenic benefits.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Latex Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Synthetic polymer, durable and waterproof | Natural or synthetic rubber, flexible and breathable |
| Comfort & Support | Firm support, less contouring | Excellent pressure relief, adaptive support |
| Durability | High resistance to deformation and wear | Long-lasting with good resilience |
| Hypoallergenic Properties | Non-hypoallergenic, may contain chemicals | Hypoallergenic, resistant to dust mites and mold |
| Breathability | Low breathability, can trap heat | Highly breathable, promotes airflow |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based | Biodegradable if natural, eco-friendly options available |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to natural materials |
Introduction to Mattress Foams: Polyvinyl Chloride vs Latex
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers durability and water resistance, making it suitable for mattresses in humid environments or for users prone to allergies. Latex foam provides natural elasticity, breathability, and pressure relief, often preferred for its hypoallergenic and eco-friendly properties. Both materials differ significantly in density, comfort, and environmental impact, guiding consumer choice based on specific needs.
What Is Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material known for its high durability, water resistance, and chemical stability, making it suitable for mattress applications requiring long-lasting support and moisture protection. This synthetic foam offers firm cushioning with excellent resistance to mold, mildew, and abrasion, contrasting with the softer, more flexible nature of latex foam. PVC foam's versatility in density and firmness levels allows manufacturers to tailor mattress performance to specific comfort and support needs.
What Is Latex Foam?
Latex foam is a natural or synthetic material derived from the sap of rubber trees, known for its durability, elasticity, and hypoallergenic properties. Unlike polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, latex foam provides superior breathability and conforms closely to body contours, offering enhanced comfort and pressure relief. Its natural resistance to dust mites and mold makes latex foam a healthier choice for mattresses compared to PVC foam, which is often less breathable and contains synthetic chemicals.
Key Material Differences: PVC Foam vs Latex Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers a dense, durable structure with excellent water resistance, making it highly suitable for mattress support layers requiring longevity and moisture control. Latex foam, derived from natural or synthetic rubber, provides superior elasticity, breathability, and pressure relief, enhancing comfort and adaptability. Key distinctions include PVC foam's chemical stability and rigidity versus latex foam's hypoallergenic properties and natural resilience.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers firm support with high density and durability, making it suitable for maintaining mattress shape over time, while latex foam provides superior comfort through natural elasticity and pressure relief, adapting closely to body contours. Latex foam's breathability and hypoallergenic properties contribute to a cooler, healthier sleep environment compared to PVC foam's less breathable structure. For optimal mattress performance, combining PVC foam's structural support with latex foam's cushioning benefits results in balanced comfort and extended mattress lifespan.
Durability and Longevity of PVC and Latex Foams
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior durability compared to latex foam due to its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and wear, making it ideal for environments requiring long-lasting materials. Latex foam provides excellent elasticity and comfort but tends to degrade faster over time due to its natural composition, especially when exposed to heat and UV light. PVC foam mattresses typically have a longer lifespan, often exceeding 10 years, while latex foam mattresses generally last between 7 to 10 years depending on usage and care.
Health and Safety Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and contain plasticizers that can pose respiratory and skin irritation risks, making them less ideal for individuals with chemical sensitivities. Latex foam mattresses, especially those made from natural latex, offer hypoallergenic and antimicrobial properties, reducing the likelihood of mold, dust mites, and allergens, thus promoting better indoor air quality. Choosing certifications like OEKO-TEX or GOLS ensures both PVC alternatives and natural latex mattresses meet high health and safety standards without harmful chemical exposure.
Environmental Impact: Eco-Friendliness of Each Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses have a higher environmental impact due to the release of toxic chemicals during production and difficulties in recycling, contributing to long-term pollution. Latex foam mattresses, especially those made from natural or organic latex, are more eco-friendly because they biodegrade naturally and are produced using renewable resources with minimal harmful emissions. Choosing natural latex foam supports sustainable practices and reduces ecological footprints compared to synthetic PVC foam alternatives.
Cost Analysis: PVC Foam vs Latex Foam Mattresses
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses generally offer a more budget-friendly option compared to latex foam mattresses, with PVC foam priced significantly lower due to cheaper raw materials and manufacturing processes. Latex foam mattresses, often made from natural or synthetic latex, command higher prices as they provide enhanced durability, breathability, and pressure relief, but their initial investment is greater. Considering long-term use, PVC foam may require more frequent replacement due to lower longevity, potentially increasing overall costs despite the lower upfront price.
Which Foam Is Best for Your Mattress Needs?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers durability, water resistance, and firm support ideal for mattresses used in humid or high-traffic environments, while latex foam provides superior breathability, natural hypoallergenic properties, and excellent contouring comfort for pressure relief. Choosing the best foam depends on mattress needs: PVC foam excels in longevity and moisture management, making it suitable for outdoor or medical mattresses, whereas latex foam suits those seeking natural materials, enhanced airflow, and responsive cushioning. Evaluating factors such as environmental sensitivity, comfort preference, and mattress use will guide selecting the most appropriate foam type.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Latex foam for Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com