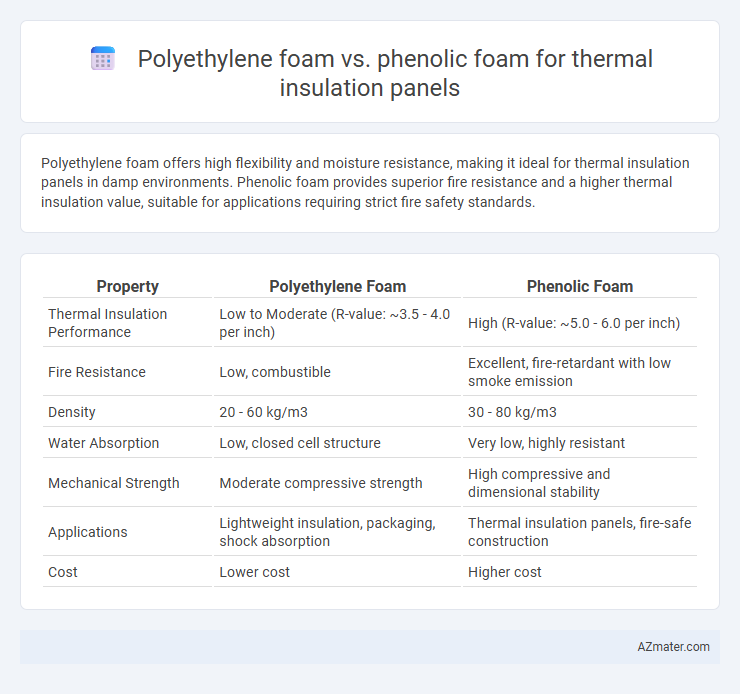
Polyethylene foam offers high flexibility and moisture resistance, making it ideal for thermal insulation panels in damp environments. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and a higher thermal insulation value, suitable for applications requiring strict fire safety standards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation Performance | Low to Moderate (R-value: ~3.5 - 4.0 per inch) | High (R-value: ~5.0 - 6.0 per inch) |
| Fire Resistance | Low, combustible | Excellent, fire-retardant with low smoke emission |
| Density | 20 - 60 kg/m3 | 30 - 80 kg/m3 |
| Water Absorption | Low, closed cell structure | Very low, highly resistant |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate compressive strength | High compressive and dimensional stability |
| Applications | Lightweight insulation, packaging, shock absorption | Thermal insulation panels, fire-safe construction |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Panels
Thermal insulation panels are critical components in construction and industrial applications, designed to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency. Polyethylene foam offers lightweight, moisture-resistant properties with moderate thermal conductivity, making it suitable for insulation in HVAC systems and packaging. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and low thermal conductivity, often preferred for high-performance insulation in building envelopes and cryogenic applications.
Overview of Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam offers excellent thermal insulation with low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.035 W/m*K, making it highly effective for reducing heat transfer in panels. Its closed-cell structure provides good moisture resistance and durability, ensuring long-lasting performance in insulation applications. Compared to phenolic foam, polyethylene foam is lighter, more flexible, and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for thermal insulation panels in construction and packaging industries.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a highly effective thermal insulation material known for its superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal performance compared to polyethylene foam. It exhibits a closed-cell structure that provides low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for energy-efficient building panels and HVAC applications. Phenolic foam's rigidity and dimensional stability under high temperatures enhance safety and durability in insulation systems.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polyethylene foam exhibits lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.030 to 0.040 W/m*K, providing effective insulation for moderate temperature ranges. Phenolic foam offers superior thermal performance with thermal conductivity values as low as 0.020 to 0.025 W/m*K, making it ideal for higher temperature applications and enhanced fire resistance. The choice between polyethylene foam and phenolic foam significantly impacts overall energy efficiency, with phenolic foam delivering better insulation due to its improved thermal stability and reduced heat transfer.
Fire Resistance and Safety Characteristics
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and safety characteristics compared to polyethylene foam, with a higher limiting oxygen index (LOI) typically above 30%, making it self-extinguishing and reducing smoke production during combustion. Polyethylene foam is more flammable, with an LOI around 18-20%, and emits denser smoke and toxic gases under fire conditions. Due to its charring behavior and low smoke generation, phenolic foam is preferred in applications requiring stringent fire safety standards in thermal insulation panels.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Polyethylene foam exhibits superior moisture resistance with low water absorption rates below 2%, making it highly effective in preventing water ingress in thermal insulation panels. Phenolic foam, while offering good thermal insulation properties, tends to absorb more moisture due to its porous cellular structure, which can compromise its insulating performance over time. The hydrophobic nature of polyethylene foam ensures consistent thermal efficiency in humid environments, whereas phenolic foam requires additional protective coatings to enhance water resistance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyethylene foam offers moderate mechanical strength with excellent flexibility, making it resistant to impact and deformation under stress, suitable for applications requiring lightweight yet durable insulation. Phenolic foam provides superior mechanical strength and rigidity, ensuring high compressive resistance and long-term structural stability in thermal insulation panels exposed to harsh environments. Phenolic foam also exhibits enhanced durability with outstanding fire resistance and minimal aging effects compared to polyethylene foam, which can degrade faster under UV exposure and mechanical wear.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene foam, derived from petrochemical sources, is less biodegradable and presents more challenges in recycling compared to phenolic foam, which contains formaldehyde but demonstrates superior fire resistance and lower smoke emissions. Phenolic foam panels offer enhanced thermal insulation with lower global warming potential (GWP) due to their reduced embodied energy and longer service life. Both materials have environmental trade-offs; however, phenolic foam's better fire performance and lower toxicity during use contribute to increased sustainability in building applications.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Polyethylene foam offers lower material costs and easier handling due to its lightweight and flexible nature, reducing labor expenses during installation of thermal insulation panels. Phenolic foam, although more expensive upfront, provides superior fire resistance and higher thermal performance, potentially lowering long-term energy costs. Installation of phenolic panels requires skilled labor to maintain its structural integrity and fire safety standards, impacting overall project timelines and budgets.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Thermal Insulation
Polyethylene foam offers excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight and impact-absorbing insulation. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and higher thermal stability, suitable for environments with strict safety regulations. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing factors such as thermal performance, fire safety standards, moisture exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal insulation effectiveness.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs Phenolic foam for Thermal insulation panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com