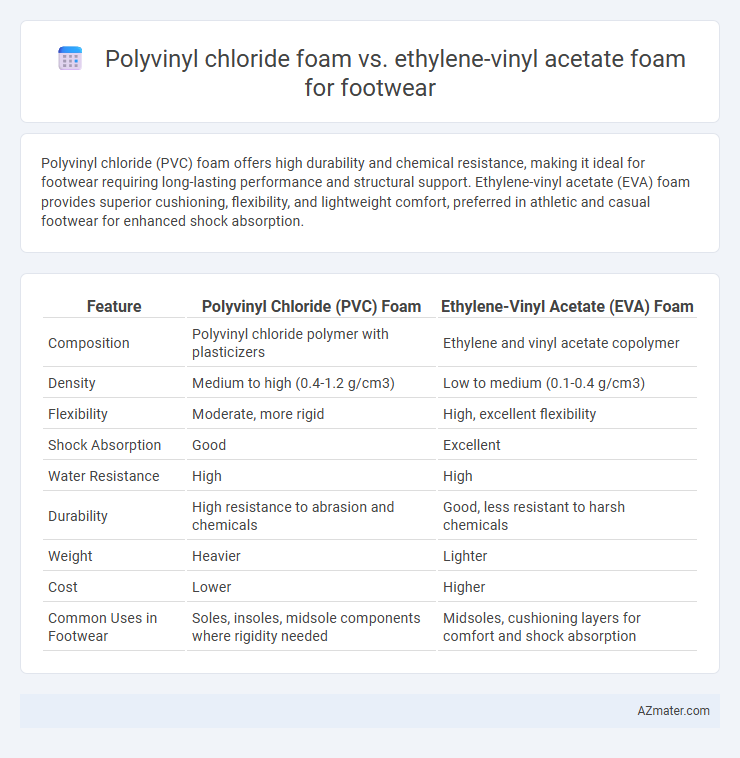
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers high durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for footwear requiring long-lasting performance and structural support. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight comfort, preferred in athletic and casual footwear for enhanced shock absorption.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polyvinyl chloride polymer with plasticizers | Ethylene and vinyl acetate copolymer |
| Density | Medium to high (0.4-1.2 g/cm3) | Low to medium (0.1-0.4 g/cm3) |
| Flexibility | Moderate, more rigid | High, excellent flexibility |
| Shock Absorption | Good | Excellent |
| Water Resistance | High | High |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and chemicals | Good, less resistant to harsh chemicals |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Uses in Footwear | Soles, insoles, midsole components where rigidity needed | Midsoles, cushioning layers for comfort and shock absorption |
Introduction to Foam Materials in Footwear
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam and Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam are widely used materials in footwear manufacturing, each offering distinct properties for comfort and durability. PVC foam provides excellent rigidity and resistance to abrasion, making it suitable for structural components like midsoles and outsoles. EVA foam is favored for its lightweight, flexibility, and superior cushioning, enhancing shock absorption and overall foot support in athletic and casual shoes.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a durable, lightweight material commonly used in footwear for its excellent cushioning and impact resistance. Its closed-cell structure provides superior moisture resistance and durability, making it ideal for insoles, midsoles, and outsoles in footwear applications. PVC foam's versatility allows customization in density and hardness, enhancing comfort and support for various footwear designs.
Overview of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam
Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam is a lightweight, flexible material widely used in footwear for its superior cushioning, shock absorption, and resilience compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam. EVA features excellent compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for midsoles and insoles in athletic and casual shoes, while offering better environmental resistance and comfort. Its closed-cell structure enhances water resistance and reduces weight, providing enhanced performance in diverse footwear applications.
Physical Properties: PVC Foam vs EVA Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits higher density and rigidity compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, offering superior durability and resistance to compression in footwear applications. EVA foam provides enhanced cushioning and flexibility due to its lower density and greater elasticity, making it ideal for shock absorption and comfort in athletic shoes. While PVC foam resists water and chemicals effectively, EVA foam outperforms in lightweight and breathable properties essential for prolonged wear.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior density and durability, providing robust cushioning that maintains shape under heavy impact, making it ideal for long-lasting footwear support. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam excels in lightweight flexibility and shock absorption, delivering enhanced comfort by conforming to foot contours and reducing fatigue during extended wear. In terms of comfort and cushioning performance, EVA foam generally outperforms PVC foam due to its higher resilience and better energy return, contributing to improved overall foot comfort in athletic and casual footwear.
Durability and Longevity in Footwear Applications
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior durability in footwear applications due to its rigid structure and resistance to wear, making it ideal for long-lasting soles and insoles. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent cushioning and flexibility but tends to compress and degrade faster under repeated stress, leading to reduced longevity. PVC foam's resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and UV exposure further enhances its lifespan compared to EVA foam in footwear use.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers cost-effective solutions for footwear due to its durability and low production expense, making it widely available in global markets. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, although slightly higher in price, provides superior cushioning and flexibility, contributing to its growing demand in athletic and comfort footwear segments. Market availability of PVC foam is extensive, while EVA foam's presence is expanding rapidly, driven by consumer preference for lightweight and shock-absorbing materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam in footwear is less environmentally sustainable due to its production involving chlorine-based chemicals, which release harmful dioxins and other pollutants during manufacturing and disposal. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is considered more eco-friendly, as it is generally non-toxic, has better recyclability, and produces fewer emissions, though it is still derived from fossil fuels. Sustainable footwear increasingly prefers EVA foam for its lower environmental footprint and greater potential for reuse and recycling compared to PVC foam.
Applications in Footwear: Best Use Cases
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam excels in durable, water-resistant footwear components such as midsoles and outsoles, offering strong abrasion resistance and enhanced structural support. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam delivers superior cushioning and flexibility, making it ideal for athletic shoes, running sneakers, and casual footwear that require lightweight comfort and shock absorption. The best use case for PVC foam is in rugged, outdoor footwear, while EVA foam is preferred in performance-focused and everyday comfort shoes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Footwear
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty footwear applications requiring long-lasting performance. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior cushioning, lightweight comfort, and flexibility, which enhances shock absorption and wearer comfort in athletic and casual shoes. Selecting the right foam depends on the specific footwear needs, with PVC favored for robust protection and EVA preferred for comfort and impact absorption.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam for Footwear
 azmater.com
azmater.com