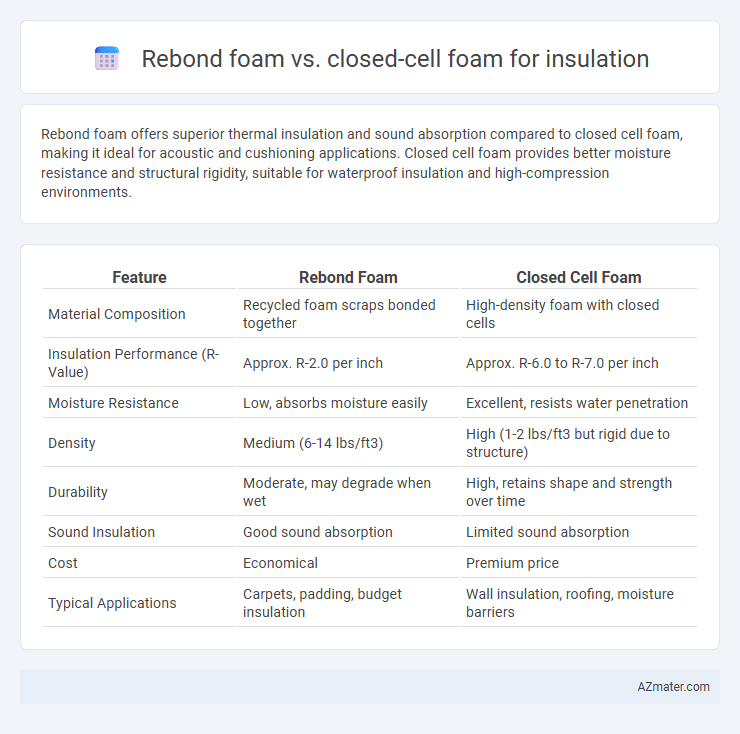
Rebond foam offers superior thermal insulation and sound absorption compared to closed cell foam, making it ideal for acoustic and cushioning applications. Closed cell foam provides better moisture resistance and structural rigidity, suitable for waterproof insulation and high-compression environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rebond Foam | Closed Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled foam scraps bonded together | High-density foam with closed cells |
| Insulation Performance (R-Value) | Approx. R-2.0 per inch | Approx. R-6.0 to R-7.0 per inch |
| Moisture Resistance | Low, absorbs moisture easily | Excellent, resists water penetration |
| Density | Medium (6-14 lbs/ft3) | High (1-2 lbs/ft3 but rigid due to structure) |
| Durability | Moderate, may degrade when wet | High, retains shape and strength over time |
| Sound Insulation | Good sound absorption | Limited sound absorption |
| Cost | Economical | Premium price |
| Typical Applications | Carpets, padding, budget insulation | Wall insulation, roofing, moisture barriers |
Introduction to Foam Insulation Types
Rebond foam and closed cell foam are two popular insulation materials, each with distinct properties suited for different applications. Rebond foam is made from recycled foam scraps bonded together, offering great cushioning and density but moderate insulation value. Closed cell foam features a rigid structure with tightly packed cells that provide superior thermal resistance and moisture barrier capabilities, making it ideal for high-performance insulation needs.
What is Rebond Foam?
Rebond foam is a type of cushioning material made by bonding shredded pieces of polyurethane foam together using adhesives and heat, resulting in a dense, durable, and resilient product. It is widely used in insulating applications due to its excellent sound absorption, impact resistance, and thermal insulation properties. Unlike closed cell foam, which is composed of individual, air-sealed cells offering superior water resistance and rigidity, rebond foam provides enhanced flexibility and cushioning, making it ideal for noise reduction and shock absorption in insulation projects.
Understanding Closed Cell Foam
Closed cell foam offers superior insulation performance due to its dense structure, which significantly reduces air and moisture infiltration, making it ideal for environments requiring high thermal resistance. Its rigid composition provides enhanced structural support and greater durability compared to rebond foam, which is softer and primarily used for cushioning rather than insulation. Closed cell foam's high R-value per inch and water-resistant properties contribute to energy efficiency and long-term protection in building applications.
Key Differences Between Rebond and Closed Cell Foam
Rebond foam, made from recycled polyurethane scraps, offers excellent cushioning and soundproofing but has lower resistance to moisture compared to closed cell foam, which features a dense, impermeable structure ideal for superior insulation and waterproofing. Closed cell foam provides higher R-values per inch, ensuring enhanced thermal insulation, while rebond foam is more cost-effective and flexible for applications requiring impact absorption. The key difference lies in closed cell foam's rigidity and moisture resistance versus rebond foam's softer texture and recyclability, influencing their suitability for different insulation needs.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Rebond foam offers moderate thermal insulation with an R-value typically around 3.5 per inch, providing effective sound absorption but lower resistance to heat flow compared to closed cell foam. Closed cell foam delivers superior thermal insulation, boasting an R-value between 6 and 7 per inch due to its dense, impermeable structure that significantly reduces heat transfer. This higher R-value makes closed cell foam a better choice for applications requiring maximum energy efficiency and moisture resistance.
Moisture and Water Resistance
Closed cell foam offers superior moisture and water resistance due to its dense, non-permeable structure that prevents water absorption and acts as an effective vapor barrier. Rebond foam, being more porous, absorbs moisture more readily, making it less ideal for applications where water resistance is critical. In insulation, closed cell foam maintains its thermal properties and structural integrity in wet conditions, while rebond foam may degrade and lose efficiency over time when exposed to moisture.
Durability and Lifespan in Insulation Projects
Rebond foam offers excellent durability due to its dense, resilient structure, making it ideal for high-traffic insulation areas where compression resistance is crucial. Closed cell foam provides superior lifespan benefits with its impermeable, rigid cells that resist moisture, mold, and thermal degradation, ensuring long-term insulation performance. Both types excel in durability, but closed cell foam typically outlasts rebond foam in harsh environmental conditions where moisture and structural integrity are concerns.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Rebond foam typically offers a more budget-friendly solution for insulation compared to closed cell foam, with costs generally ranging from $0.50 to $1.50 per board foot, making it ideal for large-scale or budget-conscious projects. Closed cell foam insulation, known for its superior density and moisture resistance, commands higher prices, often between $1.00 and $3.00 per board foot, reflecting its enhanced thermal performance and durability. The affordability of rebond foam makes it a popular choice in non-critical insulation applications, while closed cell foam justifies its higher cost through long-term energy savings and structural benefits.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type
Rebond foam excels in soundproofing, cushioning, and carpet underlayment due to its dense structure and impact absorption properties, making it ideal for flooring and acoustic insulation in residential and commercial spaces. Closed cell foam provides superior moisture resistance, high R-value, and structural strength, making it the best choice for outdoor insulation, roofing, and waterproofing applications. Both foam types are effective insulators, but rebond foam suits interior comfort and acoustic solutions, while closed cell foam is preferred for thermal protection and exposure to harsh environments.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Insulation Needs
Rebond foam offers excellent impact absorption and soundproofing, making it ideal for applications requiring cushioning and noise reduction, while closed cell foam provides superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance due to its dense structure. Closed cell foam's high R-value and water-resistant properties make it the preferred choice for moisture-prone areas and energy-efficient insulation in walls and roofs. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing insulation performance, moisture control, and the specific environmental conditions of the installation site.
Infographic: Rebond foam vs Closed cell foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com