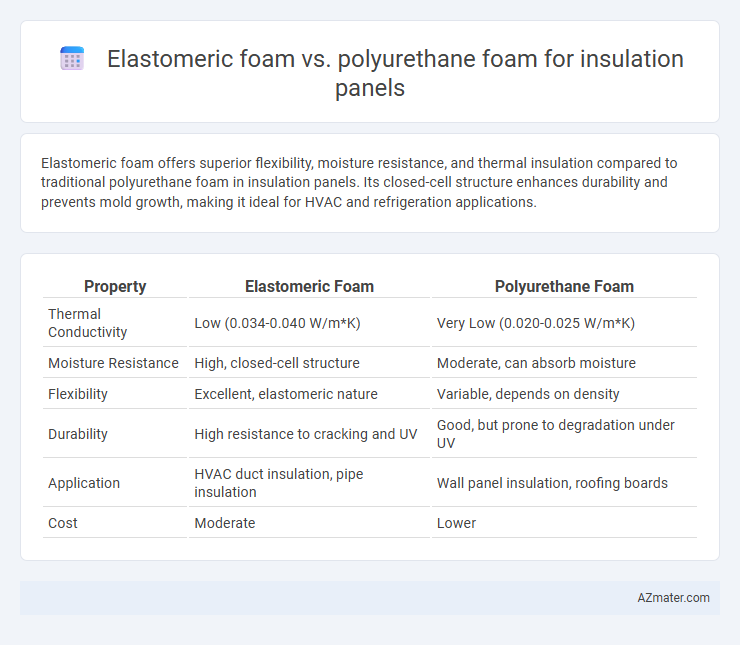
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation compared to traditional polyurethane foam in insulation panels. Its closed-cell structure enhances durability and prevents mold growth, making it ideal for HVAC and refrigeration applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Elastomeric Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.034-0.040 W/m*K) | Very Low (0.020-0.025 W/m*K) |
| Moisture Resistance | High, closed-cell structure | Moderate, can absorb moisture |
| Flexibility | Excellent, elastomeric nature | Variable, depends on density |
| Durability | High resistance to cracking and UV | Good, but prone to degradation under UV |
| Application | HVAC duct insulation, pipe insulation | Wall panel insulation, roofing boards |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower |
Introduction to Insulation Panels
Elastomeric foam insulation panels provide superior flexibility, excellent resistance to moisture, and effective thermal insulation for HVAC and piping applications. Polyurethane foam panels offer high R-values per inch, making them efficient for thermal insulation in walls and roofs, but are less flexible and more susceptible to moisture absorption. Both materials enhance energy efficiency and thermal performance in building envelopes, with choice dependent on specific project demands such as moisture exposure and flexibility requirements.
What is Elastomeric Foam?
Elastomeric foam is a flexible, closed-cell insulation material known for its excellent thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties, commonly used in HVAC systems and building insulation panels. Unlike polyurethane foam, elastomeric foam exhibits superior flexibility, resistance to mold and mildew, and enhanced durability in varying temperature environments. Its composition typically includes synthetic rubber compounds that provide effective energy efficiency and sound absorption in insulation applications.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile insulation material composed of polymer chains formed by reacting polyols and diisocyanates, known for its excellent thermal resistance and high R-values per inch, making it effective in minimizing heat transfer. Its closed-cell structure provides strong moisture resistance and durability, suitable for a variety of applications including wall panels, roofing, and refrigeration insulation. Compared to elastomeric foam, polyurethane foam typically offers superior compressive strength and thermal insulation performance but may have less flexibility and resilience under dynamic stress.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Elastomeric foam typically exhibits a lower thermal conductivity, ranging from 0.030 to 0.045 W/m*K, making it highly effective for insulation panels aimed at reducing heat transfer. Polyurethane foam, with thermal conductivity values generally between 0.020 and 0.030 W/m*K, often provides superior insulation performance due to its closed-cell structure that minimizes air permeability. The specific application requirements, including temperature range and moisture resistance, influence the optimal choice between elastomeric and polyurethane foam for thermal insulation panels.
Moisture Resistance Capabilities
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for insulation panels in high-humidity environments. Its closed-cell structure effectively prevents water absorption and vapor transmission, enhancing durability and thermal performance. Polyurethane foam, while offering good insulation properties, is more susceptible to moisture infiltration and potential degradation over time.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Elastomeric foam offers superior fire resistance compared to polyurethane foam, with enhanced self-extinguishing properties and lower smoke emission during combustion. Polyurethane foam, while highly effective for thermal insulation, is more combustible and produces toxic gases, posing greater safety risks in fire scenarios. Selecting elastomeric foam for insulation panels improves overall fire safety and compliance with strict building fire codes.
Installation and Application Differences
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and resilience, making it ideal for applications requiring vibration dampening and thermal insulation in HVAC systems, whereas polyurethane foam provides higher rigidity and greater thermal resistance, suitable for structural panel insulation. Installation of elastomeric foam involves simple cutting and compressive fitting around pipes and ducts without adhesives, while polyurethane foam panels typically require precise cutting, adhesive bonding, and sometimes mechanical fastening due to their rigid nature. Elastomeric foam's closed-cell structure reduces moisture ingress, enhancing durability in moist environments, contrasting with polyurethane foam's susceptibility to moisture when not properly sealed, affecting long-term insulation performance.
Longevity and Durability
Elastomeric foam offers superior longevity and durability for insulation panels due to its high resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and microbial growth, maintaining flexibility and performance over time. Polyurethane foam, while providing excellent thermal insulation, tends to degrade faster under moisture and UV exposure, potentially leading to reduced lifespan and structural integrity. For long-term durability in various environments, elastomeric foam insulation panels ensure sustained protection and energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior environmental sustainability due to its long lifespan, excellent thermal insulation reducing energy consumption, and recyclability compared to polyurethane foam, which often contains toxic flame retardants and produces more greenhouse gases during manufacturing. Polyurethane foam insulation panels contribute to higher volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and are less biodegradable, posing challenges for end-of-life disposal and environmental pollution. Increasing demand for eco-friendly building materials favors elastomeric foam, which also supports LEED certification and enhanced indoor air quality through its low toxicity profile.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Elastomeric foam insulation panels generally command higher upfront costs due to superior flexibility and durability, while polyurethane foam panels offer a more cost-effective solution with efficient thermal insulation properties. Market availability favors polyurethane foam, widely produced and distributed globally, making it more accessible for large-scale insulation projects. Cost analysis highlights elastomeric foam's value in long-term savings through enhanced weather resistance and reduced maintenance, despite its higher initial investment.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Polyurethane foam for Insulation panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com