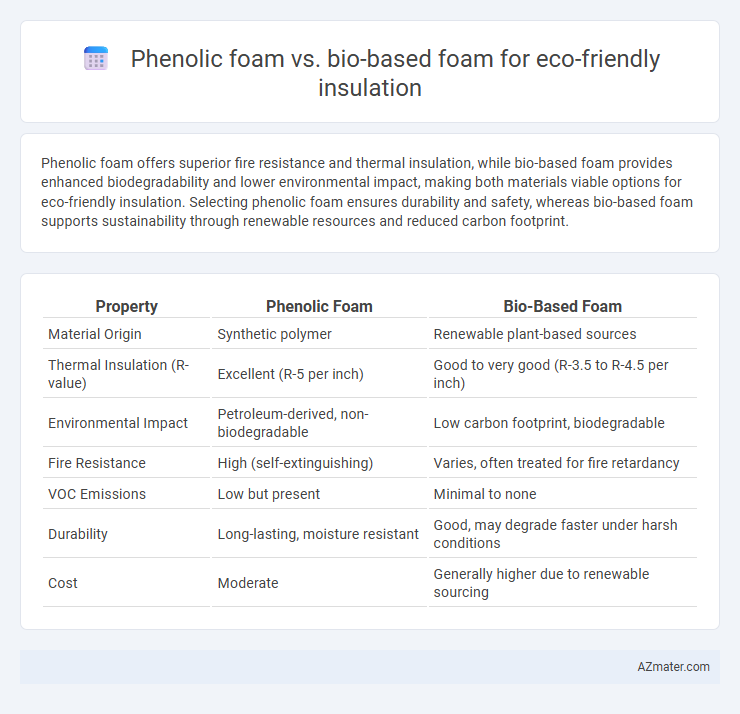
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and thermal insulation, while bio-based foam provides enhanced biodegradability and lower environmental impact, making both materials viable options for eco-friendly insulation. Selecting phenolic foam ensures durability and safety, whereas bio-based foam supports sustainability through renewable resources and reduced carbon footprint.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phenolic Foam | Bio-Based Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Synthetic polymer | Renewable plant-based sources |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | Excellent (R-5 per inch) | Good to very good (R-3.5 to R-4.5 per inch) |
| Environmental Impact | Petroleum-derived, non-biodegradable | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable |
| Fire Resistance | High (self-extinguishing) | Varies, often treated for fire retardancy |
| VOC Emissions | Low but present | Minimal to none |
| Durability | Long-lasting, moisture resistant | Good, may degrade faster under harsh conditions |
| Cost | Moderate | Generally higher due to renewable sourcing |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Insulation Materials
Phenolic foam offers excellent thermal performance and fire resistance, making it a popular choice for eco-friendly insulation in commercial and industrial applications. Bio-based foams, derived from natural materials such as soy or cellulose, provide sustainable alternatives with lower environmental impact and enhanced biodegradability. Both types contribute to energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprints, but bio-based foams prioritize renewable resources and circular economy principles.
What is Phenolic Foam?
Phenolic foam is a rigid, high-performance insulation material known for its excellent fire resistance, low smoke emissions, and thermal efficiency, commonly used in building and industrial applications. Its cellular structure provides superior thermal insulation while maintaining dimensional stability and resistance to moisture and chemicals. Compared to bio-based foams, phenolic foam is petrochemical-based but offers enhanced durability and fire retardancy, making it a preferred option for environments requiring stringent fire safety standards.
What is Bio-Based Foam?
Bio-based foam is an eco-friendly insulation material derived from renewable natural resources such as plant oils, starches, or agricultural waste, significantly reducing reliance on petroleum-based chemicals. Unlike phenolic foam, which is synthesized from petrochemical phenol and formaldehyde, bio-based foam offers improved sustainability by lowering carbon footprint and enhancing biodegradability. This type of foam provides effective thermal insulation while aligning with green building standards and environmental certifications.
Environmental Impact: Phenolic vs Bio-Based Foam
Phenolic foam offers low thermal conductivity and excellent fire resistance but is derived from petroleum-based chemicals, resulting in higher carbon emissions and limited biodegradability. Bio-based foam, composed of renewable materials like plant fibers or algae, significantly reduces carbon footprint and enhances biodegradability while maintaining effective insulation performance. Life cycle assessments reveal bio-based foam's superior environmental benefits, including reduced fossil fuel dependence and improved sustainability metrics compared to traditional phenolic foams.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with an R-value typically ranging from 5.5 to 7.0 per inch, outperforming most bio-based foams whose R-values generally fall between 3.5 and 5.0 per inch. Bio-based foams, derived from renewable resources like soy or castor oil, often exhibit lower thermal conductivity but can vary significantly depending on formulation and density. The higher closed-cell content in phenolic foam contributes to its enhanced thermal resistance and fire retardancy, making it a preferred choice for high-performance eco-friendly insulation applications.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance with a low flame spread index, excellent smoke suppression, and self-extinguishing properties, making it a top choice for fire-safe insulation. Bio-based foams, such as those made from soy or cellulose, provide eco-friendly alternatives but generally exhibit lower fire resistance and may require chemical additives to meet stringent safety standards. Prioritizing phenolic foam ensures enhanced safety in building applications where fire performance is critical, while bio-based foams promote sustainability with moderate fire protection.
Moisture and Mold Resistance
Phenolic foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, effectively preventing water absorption and reducing mold growth risk. Bio-based foams, while eco-friendly, often have higher permeability and may require additional treatments to enhance moisture barriers and mold resistance. Selecting phenolic foam ensures long-lasting insulation performance in humid environments, minimizing potential health hazards linked to mold.
Health and Indoor Air Quality
Phenolic foam offers excellent fire resistance and low thermal conductivity but can release formaldehyde and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs), potentially affecting indoor air quality. Bio-based foam insulation, derived from renewable materials such as soy or cellulose, typically emits fewer harmful VOCs and contributes to healthier indoor environments by reducing exposure to toxic chemicals. Both materials provide energy efficiency benefits, but bio-based foam is often favored for eco-friendly insulation due to its lower impact on occupant health and improved air quality.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Phenolic foam generally presents higher upfront costs compared to bio-based foam, but its superior fire resistance and thermal performance can lead to long-term savings in commercial applications. Bio-based foam, derived from renewable resources like soy or cellulose, tends to be more cost-effective and widely available in residential and small-scale projects due to growing demand for sustainable materials. Market availability for phenolic foam remains limited as production is specialized, while bio-based foams benefit from increasing investment and broader distribution networks in the eco-friendly insulation sector.
Choosing the Best Eco-Friendly Foam for Insulation
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and low thermal conductivity, making it an effective choice for eco-friendly insulation in commercial buildings. Bio-based foam, derived from renewable resources like soy or algae, provides a sustainable alternative with lower embodied carbon and excellent moisture resistance. Selecting the best eco-friendly foam depends on balancing insulation performance, environmental impact, and application-specific requirements such as fire safety and vapor permeability.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Bio-based foam for Eco-friendly insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com