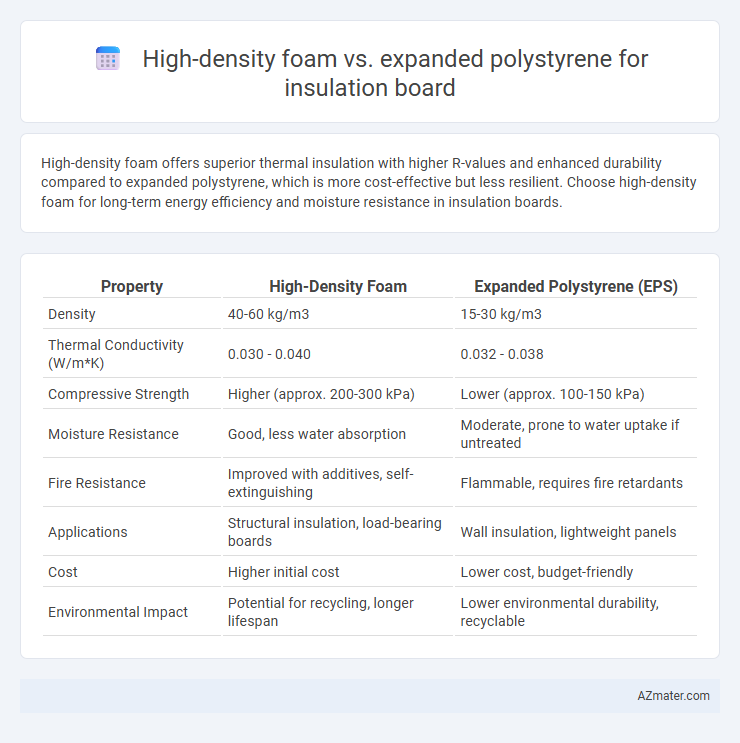
High-density foam offers superior thermal insulation with higher R-values and enhanced durability compared to expanded polystyrene, which is more cost-effective but less resilient. Choose high-density foam for long-term energy efficiency and moisture resistance in insulation boards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Density Foam | Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 40-60 kg/m3 | 15-30 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.030 - 0.040 | 0.032 - 0.038 |
| Compressive Strength | Higher (approx. 200-300 kPa) | Lower (approx. 100-150 kPa) |
| Moisture Resistance | Good, less water absorption | Moderate, prone to water uptake if untreated |
| Fire Resistance | Improved with additives, self-extinguishing | Flammable, requires fire retardants |
| Applications | Structural insulation, load-bearing boards | Wall insulation, lightweight panels |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Environmental Impact | Potential for recycling, longer lifespan | Lower environmental durability, recyclable |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
High-density foam and expanded polystyrene (EPS) are widely used insulation board materials, each offering distinct thermal resistance and durability characteristics. High-density foam provides superior R-values per inch, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum insulation efficiency in limited space. EPS is valued for its cost-effectiveness and moisture resistance, often used in wall cavities and beneath slabs to prevent heat loss and enhance energy savings.
What is High-Density Foam?
High-density foam is a rigid insulation material characterized by its compact cellular structure and increased thermal resistance, typically made from polyurethane or polyisocyanurate. It provides superior compressive strength and moisture resistance compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS), making it ideal for applications requiring durability and long-term performance. This type of foam also offers enhanced energy efficiency due to its low thermal conductivity and excellent air barrier properties.
Understanding Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a lightweight, rigid foam insulation material known for its excellent thermal resistance and moisture permeability, making it suitable for various construction applications. It consists of pre-expanded beads that are molded into boards, delivering consistent R-values typically around 3.6 to 4.2 per inch while maintaining structural integrity and durability. Compared to high-density foam, EPS provides superior breathability and is cost-effective, although it has lower compressive strength and may require protective facings in load-bearing scenarios.
Thermal Performance Comparison
High-density foam insulation boards generally exhibit superior thermal performance compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS) due to their lower thermal conductivity values, often ranging between 0.020 to 0.030 W/m*K, whereas EPS typically ranges from 0.032 to 0.038 W/m*K. This difference means high-density foam provides better resistance to heat flow, resulting in improved energy efficiency for buildings. The enhanced thermal insulation of high-density foam is particularly beneficial in applications requiring stringent temperature control and longer-term thermal stability.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
High-density foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS), reducing the risk of water absorption and mold growth in insulation boards. Its closed-cell structure enhances durability, enabling better performance under compression and longer lifespan in humid environments. EPS, while lightweight and cost-effective, tends to absorb moisture more readily, which can compromise both insulation efficiency and structural integrity over time.
Installation and Application Differences
High-density foam insulation boards offer superior compressive strength and moisture resistance, making them ideal for use in load-bearing applications such as under concrete slabs and roofing systems. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) boards are lighter and easier to cut, facilitating quicker installation in wall cavities and residential insulation projects where high structural strength is not critical. While high-density foam provides enhanced thermal performance in demanding environments, EPS offers cost-effective versatility for moderate insulation needs with simpler fastening and trimming.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
High-density foam insulation boards often have a higher embodied carbon footprint compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS) due to their energy-intensive manufacturing processes and use of hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) blowing agents, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. EPS insulation is more environmentally favorable, being lightweight, recyclable, and composed of around 98% air, which reduces raw material consumption and landfill waste. Sustainable building projects prefer EPS for its lower environmental impact, recyclability, and potential for reuse, aligning with green construction and LEED certification goals.
Cost Analysis: High-Density Foam vs EPS
High-density foam insulation boards typically cost more upfront than expanded polystyrene (EPS) due to higher material density and enhanced thermal performance. EPS offers a lower price per board and decent R-value, making it a budget-friendly choice for large-scale or less demanding insulation projects. Long-term energy savings from high-density foam's superior R-value can offset initial costs, but initial budget constraints often make EPS the preferred option.
Fire Safety Considerations
High-density foam insulation boards offer superior fire resistance compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS), as they typically have higher ignition temperatures and slower flame spread rates. EPS, while cost-effective and lightweight, is more combustible, requiring additional fire-retardant treatments to meet building code standards. Building regulations often favor high-density foam for critical applications due to its enhanced fire safety performance and reduced smoke toxicity during combustion.
Choosing the Right Insulation Board
High-density foam insulation boards offer superior thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 6 to 7 per inch, making them ideal for tight spaces requiring maximum insulation efficiency. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) boards provide cost-effective insulation with an R-value around 3.6 to 4.2 per inch, suitable for larger surface areas and applications where moisture resistance is essential. Selecting the right insulation board depends on evaluating project-specific needs such as thermal performance, budget constraints, moisture exposure, and installation environment to ensure long-lasting energy efficiency.
Infographic: High-density foam vs Expanded polystyrene for Insulation board
 azmater.com
azmater.com