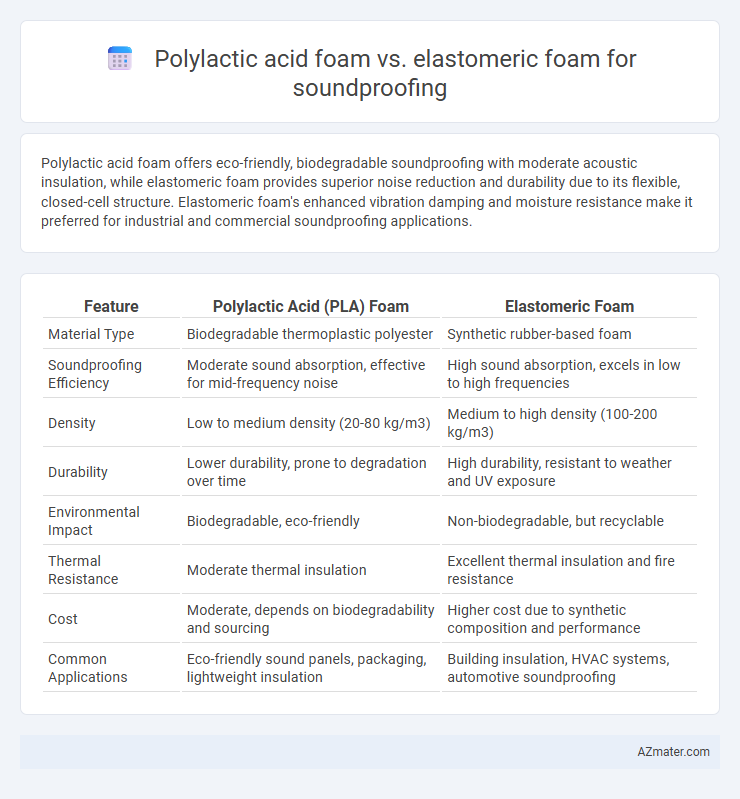
Polylactic acid foam offers eco-friendly, biodegradable soundproofing with moderate acoustic insulation, while elastomeric foam provides superior noise reduction and durability due to its flexible, closed-cell structure. Elastomeric foam's enhanced vibration damping and moisture resistance make it preferred for industrial and commercial soundproofing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polylactic Acid (PLA) Foam | Elastomeric Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable thermoplastic polyester | Synthetic rubber-based foam |
| Soundproofing Efficiency | Moderate sound absorption, effective for mid-frequency noise | High sound absorption, excels in low to high frequencies |
| Density | Low to medium density (20-80 kg/m3) | Medium to high density (100-200 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Lower durability, prone to degradation over time | High durability, resistant to weather and UV exposure |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, but recyclable |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate thermal insulation | Excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on biodegradability and sourcing | Higher cost due to synthetic composition and performance |
| Common Applications | Eco-friendly sound panels, packaging, lightweight insulation | Building insulation, HVAC systems, automotive soundproofing |
Introduction to Soundproofing Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam and elastomeric foam are widely used soundproofing materials, each offering distinct acoustic properties. PLA foam, derived from biodegradable polymers, provides effective noise absorption with sustainable benefits and a lightweight structure. Elastomeric foam, known for its flexibility and durability, excels in vibration damping and impact noise reduction, making it ideal for both commercial and industrial soundproofing applications.
Overview of Polylactic Acid (PLA) Foam
Polylactic Acid (PLA) foam is a biodegradable, eco-friendly soundproofing material derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional foams. It exhibits excellent acoustic absorption properties due to its cellular structure, effectively reducing noise transmission in residential and commercial applications. Compared to elastomeric foam, PLA foam provides a lightweight solution with competitive thermal insulation and sound dampening performance while emphasizing environmental benefits.
Overview of Elastomeric Foam
Elastomeric foam is a flexible, closed-cell material commonly used in soundproofing for its excellent noise absorption and thermal insulation properties. Its cellular structure effectively reduces airborne noise and vibrations, making it ideal for HVAC ducts, walls, and ceilings. Compared to polylactic acid foam, elastomeric foam offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and long-term performance in diverse environmental conditions.
Acoustic Properties: PLA Foam vs Elastomeric Foam
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam offers moderate sound absorption with its lightweight, biodegradable structure, making it suitable for eco-friendly soundproofing applications where environmental impact is a priority. Elastomeric foam exhibits superior acoustic properties due to its flexible, closed-cell structure, providing excellent sound dampening and vibration isolation across a wide frequency range. The density and tensile strength of elastomeric foam contribute to enhanced noise reduction compared to the more rigid and less elastic PLA foam.
Sound Absorption Efficiency Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam exhibits moderate sound absorption efficiency, particularly effective in mid to high-frequency ranges due to its rigid cellular structure. Elastomeric foam demonstrates superior soundproofing performance across a broader frequency spectrum, especially excelling in low-frequency sound attenuation because of its flexible, porous matrix. Comparative studies reveal elastomeric foam's noise reduction coefficient (NRC) often surpasses PLA foam, making it more efficient for comprehensive acoustic insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam demonstrates superior environmental benefits compared to elastomeric foam due to its biodegradable and compostable nature, derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. Elastomeric foam, typically made from non-renewable petrochemicals, poses challenges in disposal and contributes to long-term environmental pollution. PLA foam's closed-loop lifecycle and reduced carbon footprint make it a more sustainable choice in soundproofing applications focused on ecological impact.
Installation and Application Differences
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam offers lightweight, biodegradable soundproofing ideal for temporary or eco-friendly installations, whereas elastomeric foam provides superior durability and flexibility suited for permanent applications and harsh environments. PLA foam typically requires less specialized tools for cutting and fitting, making it easier for quick setups, while elastomeric foam demands precise handling due to its dense structure and adhesive compatibility for long-term sealing. The application of elastomeric foam excels in industrial and HVAC soundproofing due to its resistance to moisture and temperature fluctuations, contrasted with PLA foam's preference for residential or low-impact acoustic damping.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam offers moderate durability with biodegradability, requiring less chemical maintenance but is prone to degradation under prolonged moisture exposure. Elastomeric foam exhibits superior durability with high resistance to moisture, UV, and temperature variations, reducing upkeep and extending lifespan in soundproofing applications. Maintenance for elastomeric foam is generally minimal, involving occasional cleaning, whereas PLA foam may need more frequent inspections and replacements in humid environments.
Cost Analysis: PLA vs Elastomeric Foam
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam generally offers a lower material cost compared to elastomeric foam, making it a budget-friendly option for soundproofing applications. Elastomeric foam, however, often incurs higher initial costs due to its superior acoustic performance and durability, potentially reducing long-term expenses through less frequent replacement. Evaluating the total cost of ownership requires considering factors such as installation, lifespan, and acoustic efficiency alongside material price.
Choosing the Right Foam for Soundproofing Needs
Polylactic acid foam offers excellent biodegradability and moderate sound absorption, making it suitable for eco-friendly acoustic solutions with lower-frequency noise control. Elastomeric foam provides superior flexibility, durability, and high noise-reduction coefficients, ideal for industrial or commercial soundproofing requiring long-term performance and resistance to environmental factors. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing environmental impact, sound absorption efficiency, and application-specific durability requirements.
Infographic: Polylactic acid foam vs Elastomeric foam for Soundproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com