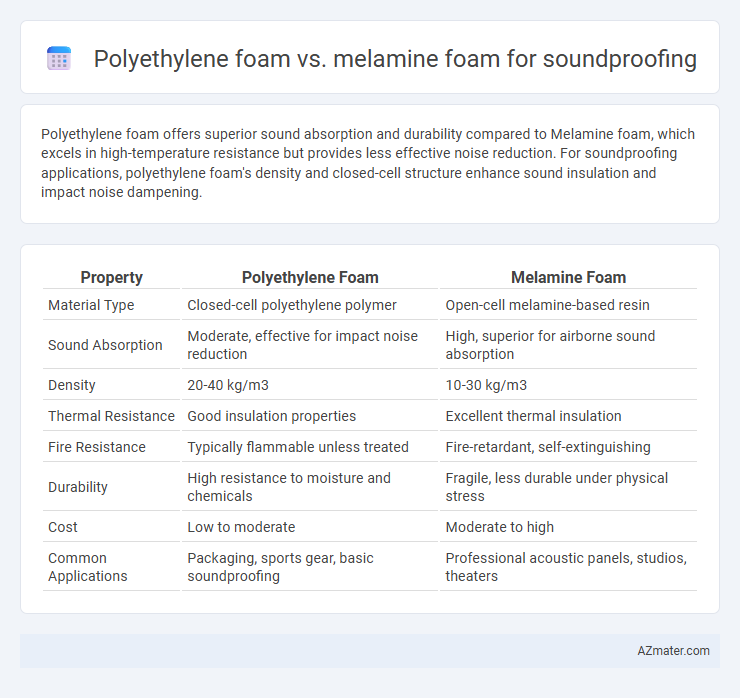
Polyethylene foam offers superior sound absorption and durability compared to Melamine foam, which excels in high-temperature resistance but provides less effective noise reduction. For soundproofing applications, polyethylene foam's density and closed-cell structure enhance sound insulation and impact noise dampening.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Foam | Melamine Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Closed-cell polyethylene polymer | Open-cell melamine-based resin |
| Sound Absorption | Moderate, effective for impact noise reduction | High, superior for airborne sound absorption |
| Density | 20-40 kg/m3 | 10-30 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Resistance | Good insulation properties | Excellent thermal insulation |
| Fire Resistance | Typically flammable unless treated | Fire-retardant, self-extinguishing |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture and chemicals | Fragile, less durable under physical stress |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Common Applications | Packaging, sports gear, basic soundproofing | Professional acoustic panels, studios, theaters |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Melamine Foam
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material known for its excellent impact resistance and moisture resistance, making it ideal for soundproofing applications where durability and insulation are critical. Melamine foam is an open-cell structure with high sound absorption properties, effective in reducing mid to high-frequency noise due to its porous and soft nature. Both foams serve distinct acoustic purposes: polyethylene foam provides thermal and sound insulation with structural strength, while melamine foam excels at dampening sound reflections and reverberations in interior environments.
How Soundproofing Works: Key Principles
Soundproofing works by reducing sound transmission through materials that absorb, reflect, or dampen sound waves. Polyethylene foam, with its closed-cell structure, primarily blocks noise by reflecting and isolating sound energy, making it effective against airborne noise. Melamine foam, characterized by its open-cell, porous nature, excels in absorbing sound waves, reducing echoes and reverberations by converting acoustic energy into heat.
Material Composition: Polyethylene vs Melamine Foam
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell material made primarily from polyethylene polymers, providing excellent moisture resistance and durability, making it suitable for impact absorption and thermal insulation. Melamine foam, composed of a melamine-formaldehyde resin, features an open-cell structure with high porosity, delivering superior sound absorption and fire resistance due to its lightweight and rigid composition. The fundamental difference in material composition results in polyethylene foam excelling in moisture and shock resistance, while melamine foam offers enhanced acoustic performance and flame retardancy for soundproofing applications.
Acoustic Performance Comparison
Polyethylene foam offers effective sound absorption primarily in low to mid frequencies due to its closed-cell structure, making it suitable for impact noise reduction and vibration damping. Melamine foam excels in high-frequency sound attenuation with its open-cell, porous architecture, providing superior acoustic treatment in environments requiring echo reduction and speech clarity. While polyethylene foam is durable and moisture-resistant, melamine foam delivers enhanced overall acoustic performance for comprehensive soundproofing solutions.
Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) Ratings
Polyethylene foam typically features an NRC rating ranging from 0.20 to 0.40, making it moderately effective for sound absorption in lower frequency ranges. Melamine foam, on the other hand, demonstrates superior acoustic performance with NRC ratings between 0.60 and 1.00, excelling in high-frequency noise reduction. The higher NRC of melamine foam indicates its enhanced capability to absorb sound waves, rendering it a preferred choice for applications requiring efficient noise control and soundproofing.
Durability and Longevity
Polyethylene foam offers superior durability and longevity compared to melamine foam due to its resilience against compression and moisture, making it ideal for long-term soundproofing applications. Melamine foam, while effective in absorbing sound, tends to degrade faster under mechanical stress and environmental exposure. For projects requiring sustained performance and durability, polyethylene foam is the preferred choice in soundproofing materials.
Installation Methods and Flexibility
Polyethylene foam offers easy installation with adhesive backing and can be cut into various shapes, making it highly adaptable for irregular surfaces in soundproofing applications. Melamine foam, while lightweight and fire-resistant, requires mechanical fasteners or specialized adhesives due to its brittle structure, limiting flexibility during installation. Polyethylene's flexibility allows for seamless coverage around corners and curves, whereas melamine foam is better suited for flat surfaces because of its rigid form.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Polyethylene foam generally offers a lower cost per square foot compared to melamine foam, making it a more budget-friendly option for large-scale soundproofing projects. Melamine foam, while more expensive, provides superior acoustic performance and fire resistance, potentially reducing long-term expenses related to safety compliance and sound quality. Budget considerations should weigh initial material costs against performance benefits and project scale to determine the most cost-effective choice.
Fire Resistance and Safety Aspects
Polyethylene foam offers limited fire resistance and can release toxic fumes when exposed to high temperatures, posing safety concerns in soundproofing applications. Melamine foam exhibits excellent fire resistance, meeting stringent fire safety standards with low smoke emission and self-extinguishing properties, making it a safer choice for acoustic insulation. Prioritizing fire safety, melamine foam provides superior performance in environments where flame retardancy and reduced toxicity are critical.
Best Use Cases: Which Foam to Choose?
Polyethylene foam excels in soundproofing for impact noise and vibration control, making it ideal for flooring underlays and packaging applications. Melamine foam offers superior absorption of mid to high-frequency sound waves, perfect for acoustic panels in studios and office environments. Choose polyethylene foam for durability and insulation in industrial settings, while melamine foam is best for precise acoustic treatment and noise reduction in enclosed spaces.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs Melamine foam for Soundproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com