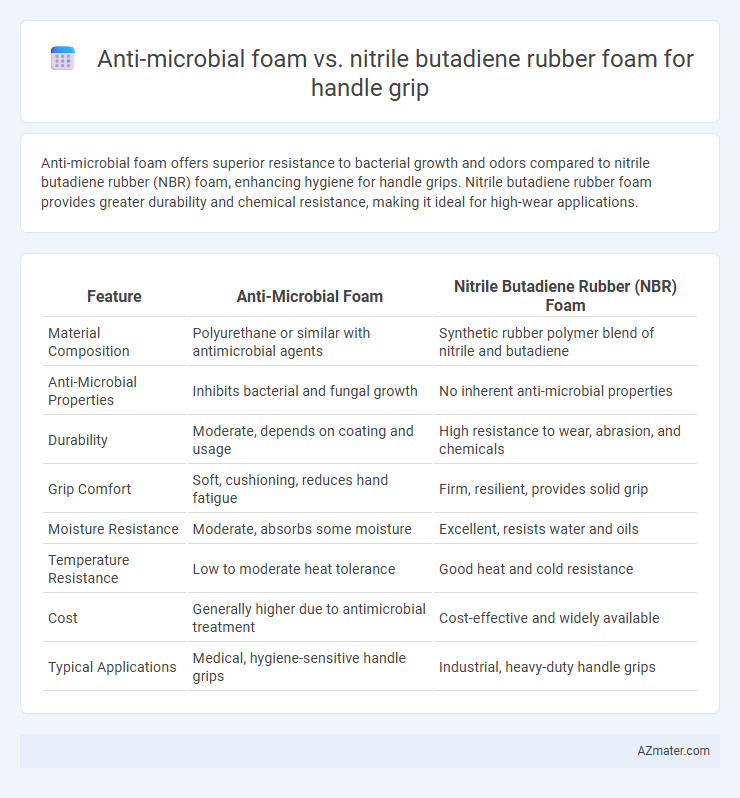
Anti-microbial foam offers superior resistance to bacterial growth and odors compared to nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam, enhancing hygiene for handle grips. Nitrile butadiene rubber foam provides greater durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-wear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Microbial Foam | Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyurethane or similar with antimicrobial agents | Synthetic rubber polymer blend of nitrile and butadiene |
| Anti-Microbial Properties | Inhibits bacterial and fungal growth | No inherent anti-microbial properties |
| Durability | Moderate, depends on coating and usage | High resistance to wear, abrasion, and chemicals |
| Grip Comfort | Soft, cushioning, reduces hand fatigue | Firm, resilient, provides solid grip |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, absorbs some moisture | Excellent, resists water and oils |
| Temperature Resistance | Low to moderate heat tolerance | Good heat and cold resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to antimicrobial treatment | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Typical Applications | Medical, hygiene-sensitive handle grips | Industrial, heavy-duty handle grips |
Introduction to Handle Grip Materials
Anti-microbial foam and nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam are popular materials for handle grips due to their unique properties. Anti-microbial foam inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi, enhancing hygiene and durability in high-contact applications. NBR foam offers excellent resistance to oils, abrasion, and impact, making it ideal for heavy-duty grips requiring robustness and long-lasting performance.
Overview of Anti-Microbial Foam
Anti-microbial foam used in handle grips offers superior resistance to bacterial and fungal growth, enhancing hygiene and longevity in high-contact applications. This material incorporates antimicrobial agents that actively inhibit microorganism proliferation, reducing odors and surface degradation. Compared to nitrile butadiene rubber foam, anti-microbial foam provides improved cleanliness and maintenance benefits, making it ideal for medical, sports, and public equipment handles.
Key Features of Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Foam
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) foam offers exceptional resistance to oils, chemicals, and abrasion, making it highly durable for handle grips in demanding environments. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and moisture resistance, enhancing user comfort and grip stability. Compared to anti-microbial foam, NBR foam excels in mechanical strength and longevity, although it lacks inherent antimicrobial properties unless specially treated.
Anti-Microbial Properties and Health Benefits
Anti-microbial foam handle grips inhibit bacterial growth through embedded silver ions or other biocides, reducing the risk of contamination and infections in high-touch environments. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam offers durability and chemical resistance but lacks inherent anti-microbial properties, making it less effective in preventing microbial proliferation. Using anti-microbial foam for handle grips enhances hygiene and promotes health by minimizing pathogen transmission on frequently handled surfaces.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Anti-microbial foam handle grips offer enhanced resistance to bacterial growth, reducing wear from microbial contamination and extending hygiene-related durability compared to Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) foam, which excels in abrasion resistance and chemical stability. NBR foam typically provides a longer lifespan under mechanical stress due to its superior elasticity and resistance to oils and chemicals, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. However, anti-microbial foam's capacity to maintain structural integrity while inhibiting microbial degradation can result in improved longevity in environments prone to sweat and moisture exposure.
Comfort and Ergonomics for Users
Anti-microbial foam offers superior moisture-wicking properties and prevents bacterial growth, enhancing hygiene and comfort for handle grips during prolonged use. Nitrile butadiene rubber foam provides excellent cushioning and durability, supporting ergonomic design by reducing hand fatigue and improving grip stability. Both materials contribute to user comfort, but anti-microbial foam excels in maintaining a cleaner, odor-free surface while nitrile butadiene rubber foam emphasizes impact resistance and long-term resilience.
Slip Resistance and Grip Performance
Anti-microbial foam offers superior slip resistance by inhibiting bacterial buildup that can cause surface slipperiness, enhancing grip performance in wet or sweaty conditions. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides excellent mechanical grip due to its higher friction coefficient and durability under repeated stress, making it suitable for heavy-duty handle grips. Both materials enhance grip performance, but anti-microbial foam excels in maintaining hygiene and consistent traction, while NBR foam delivers long-lasting, robust slip resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Anti-microbial foam handles offer enhanced hygienic benefits but often rely on synthetic polymers with limited biodegradability, contributing to environmental persistence and microplastic pollution. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam, while also synthetic, can be engineered for improved durability, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation, yet its production involves petrochemical processes with a significant carbon footprint. Selecting eco-friendly additives or incorporating recycled content in both materials can improve sustainability profiles, but overall, neither foam currently matches the environmental advantages of natural or bio-based alternatives.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Anti-microbial foam handle grips generally incur higher production costs due to their specialized additives that inhibit microbial growth, making them pricier than standard nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam grips. NBR foam offers cost-effective manufacturing, broad availability, and consistent performance, contributing to its dominance in the market for industrial and consumer applications. Market analysis shows that while anti-microbial foam demand is rising in healthcare and fitness sectors, NBR foam remains the preferred choice for cost-sensitive markets due to its widespread distribution and lower price point.
Choosing the Best Foam for Handle Grips
Anti-microbial foam offers superior resistance to bacterial growth and odor, making it ideal for handle grips in hygienic or high-contact environments. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides excellent durability, chemical resistance, and cushioning, enhancing grip comfort and longevity under heavy use. Selecting the best foam depends on prioritizing antimicrobial protection or mechanical durability to meet specific application needs.
Infographic: Anti-microbial foam vs Nitrile butadiene rubber foam for Handle grip
 azmater.com
azmater.com