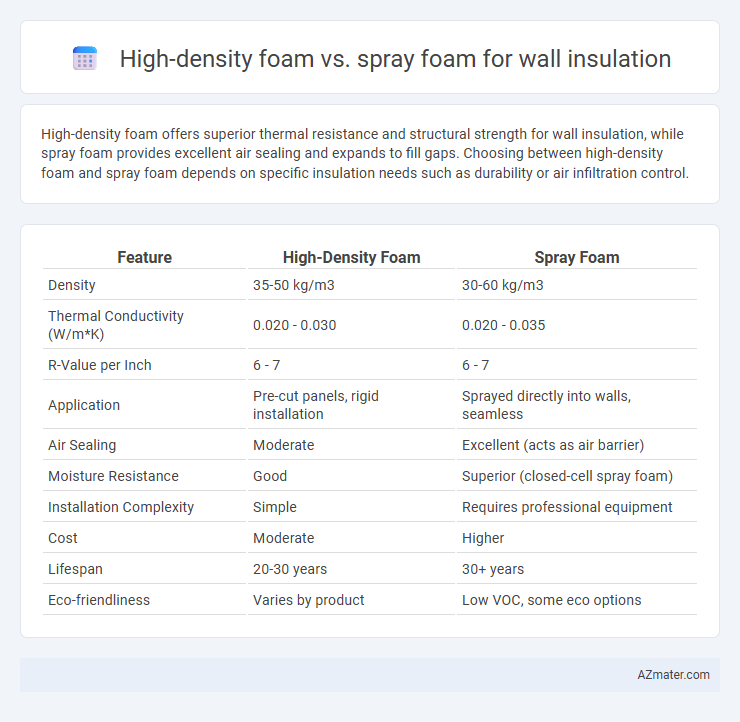
High-density foam offers superior thermal resistance and structural strength for wall insulation, while spray foam provides excellent air sealing and expands to fill gaps. Choosing between high-density foam and spray foam depends on specific insulation needs such as durability or air infiltration control.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High-Density Foam | Spray Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 35-50 kg/m3 | 30-60 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.020 - 0.030 | 0.020 - 0.035 |
| R-Value per Inch | 6 - 7 | 6 - 7 |
| Application | Pre-cut panels, rigid installation | Sprayed directly into walls, seamless |
| Air Sealing | Moderate | Excellent (acts as air barrier) |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Superior (closed-cell spray foam) |
| Installation Complexity | Simple | Requires professional equipment |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Lifespan | 20-30 years | 30+ years |
| Eco-friendliness | Varies by product | Low VOC, some eco options |
Introduction to Wall Insulation Solutions
High-density foam and spray foam are two prominent wall insulation solutions known for their superior thermal resistance and air-sealing properties. High-density foam offers rigidity and enhanced structural support, making it ideal for walls requiring additional strength alongside insulation. Spray foam excels in filling gaps and crevices, providing a seamless barrier that reduces air leakage and improves overall energy efficiency in building envelopes.
What Is High-Density Foam Insulation?
High-density foam insulation is a rigid polyurethane material characterized by its dense cellular structure, typically with a density exceeding 2 pounds per cubic foot. It offers superior thermal resistance and structural strength, making it highly effective for wall insulation by minimizing air infiltration and enhancing energy efficiency. Unlike spray foam, which expands to fill cavities, high-density foam is often installed as pre-formed panels, providing consistent thickness and long-term durability in building envelopes.
Understanding Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation offers superior air sealing by expanding upon application, filling gaps and cracks more effectively than high-density foam panels. It provides a higher R-value per inch, typically ranging from R-6 to R-7, enhancing thermal performance and reducing energy costs. Unlike high-density foam, spray foam also acts as a moisture barrier, preventing mold growth and improving indoor air quality.
Thermal Performance Comparison
High-density foam offers superior thermal performance with an R-value typically around 6 to 7 per inch, providing excellent insulation and air sealing capabilities for walls. Spray foam insulation, particularly closed-cell spray foam, delivers higher R-values, about 6 to 7 per inch, and expands to fill gaps and cracks, enhancing thermal resistance and reducing thermal bridging. Both types significantly improve energy efficiency, but spray foam's expanding property often results in a more effective seal against air infiltration compared to rigid high-density foam panels.
Moisture Resistance and Air Sealing
High-density foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, effectively preventing water infiltration and reducing the risk of mold growth in wall insulation. Spray foam excels in air sealing by expanding to fill gaps and cracks, creating an airtight barrier that minimizes drafts and improves energy efficiency. Combining high-density foam's moisture barrier with spray foam's air-sealing properties results in optimal wall insulation performance in various environmental conditions.
Installation Process and Ease
High-density foam insulation requires precise cutting and fitting, often involving professional installation due to its rigid panels that need to be secured tightly against wall studs, ensuring minimal gaps. Spray foam insulation expands upon application, filling cavities and hard-to-reach areas with ease, making it faster to install and providing superior air sealing properties. Despite requiring protective gear for safe handling, spray foam generally offers a more efficient and flexible installation process compared to the labor-intensive cutting and fitting demanded by high-density foam boards.
Cost Analysis: High-Density Foam vs Spray Foam
High-density foam insulation typically costs between $1.00 and $1.50 per board foot, offering a budget-friendly option for wall insulation with moderate R-values ranging from 6 to 7 per inch. Spray foam insulation, especially closed-cell spray foam, tends to cost between $1.50 and $3.00 per board foot but provides superior air sealing and higher R-values of around 6.5 to 7 per inch. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, high-density foam may reduce upfront expenses, while spray foam's enhanced thermal performance and durability can lead to long-term energy savings.
Longevity and Durability
High-density foam offers superior longevity and structural stability in wall insulation, maintaining its R-value and resisting compression over decades. Spray foam provides excellent air sealing and moisture resistance, but may degrade faster under UV exposure or physical damage. Choosing high-density foam ensures longer-lasting insulation performance with minimal maintenance, while spray foam delivers immediate energy efficiency benefits with moderate durability.
Environmental Impact and Safety
High-density foam offers strong thermal insulation with low global warming potential, containing fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and posing less environmental risk during installation compared to spray foam, which can release harmful isocyanates and blowing agents with high greenhouse gas emissions. Spray foam provides superior air sealing but often uses hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) or other potent greenhouse gases that contribute significantly to climate change. High-density foam's safer chemical profile and reduced off-gassing make it a more environmentally friendly and health-conscious choice for wall insulation.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Walls
High-density foam offers superior R-value per inch and excellent structural reinforcement, making it ideal for walls requiring enhanced thermal resistance and durability. Spray foam expands to fill gaps and irregular spaces, providing an effective air barrier and moisture resistance that prevents drafts and mold growth. Selecting the right foam depends on your insulation goals, budget, and wall configuration, where high-density foam suits consistent thickness applications, and spray foam excels in complex or hard-to-reach areas.
Infographic: High-density foam vs Spray foam for Wall insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com