Latex foam offers superior cushioning and durability compared to expanded polystyrene foam, making it ideal for protecting fragile items during shipping. Expanded polystyrene foam is lightweight and cost-effective but provides less resilience and environmental sustainability than latex foam.
Table of Comparison
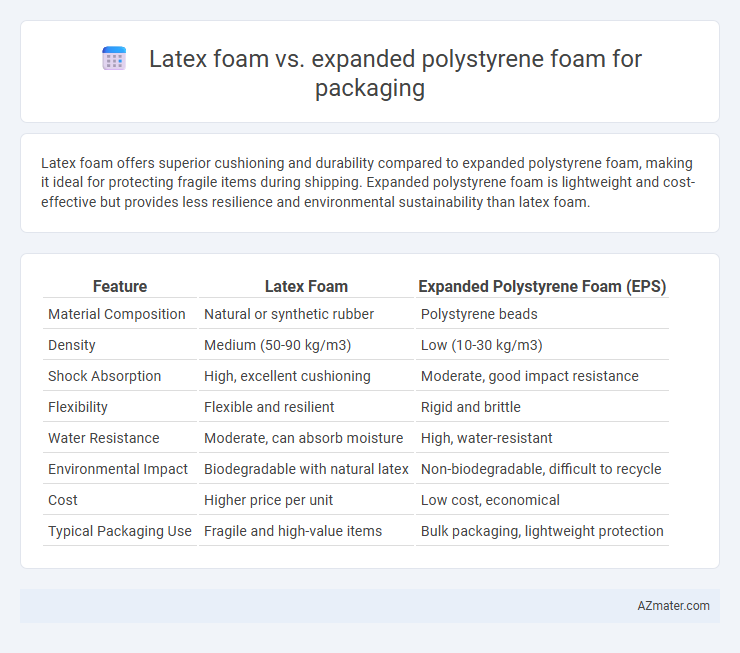
| Feature | Latex Foam | Expanded Polystyrene Foam (EPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural or synthetic rubber | Polystyrene beads |
| Density | Medium (50-90 kg/m3) | Low (10-30 kg/m3) |
| Shock Absorption | High, excellent cushioning | Moderate, good impact resistance |
| Flexibility | Flexible and resilient | Rigid and brittle |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, can absorb moisture | High, water-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable with natural latex | Non-biodegradable, difficult to recycle |
| Cost | Higher price per unit | Low cost, economical |
| Typical Packaging Use | Fragile and high-value items | Bulk packaging, lightweight protection |
Introduction to Latex Foam and Expanded Polystyrene Foam
Latex foam, derived from natural or synthetic latex, offers exceptional resilience, flexibility, and cushioning properties ideal for protective packaging of delicate items. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam, a lightweight, rigid, and shock-absorbing material made from polystyrene beads, provides cost-effective insulation and impact resistance for packaging applications. Both materials are widely used, but latex foam excels in durability and eco-friendliness, whereas EPS foam emphasizes affordability and structural support.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Latex foam consists primarily of natural or synthetic latex derived from rubber trees, created through a whipped froth process that solidifies coconut fibers and other additives, offering high elasticity and resilience. Expanded polystyrene foam (EPS) is composed of polystyrene beads that expand and fuse via steam heating in a mold, producing a rigid, lightweight material with excellent cushioning properties. The natural origin and flexible manufacturing of latex foam result in superior durability and biodegradability, whereas EPS's petroleum-based composition and contour-molding process enable cost-effective mass production and strong impact resistance.
Cushioning Performance and Shock Absorption
Latex foam offers superior cushioning performance due to its high elasticity and ability to conform closely to product shapes, reducing pressure points and enhancing shock absorption during impacts. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam, while lightweight and rigid, provides effective shock absorption through its cellular structure that compresses upon impact, but it lacks the adaptive cushioning resilience of latex. For packaging applications requiring delicate item protection, latex foam's dynamic compression and rebound properties make it preferable over EPS foam's brittle and less adaptive nature.
Durability and Longevity in Packaging Applications
Latex foam exhibits superior durability and resilience in packaging applications due to its elasticity and ability to withstand repeated compressions without permanent deformation, making it ideal for protecting delicate items over extended periods. Expanded polystyrene foam (EPS), while cost-effective and lightweight, tends to be more brittle and prone to cracking or crumbling under prolonged stress, reducing its longevity in packaging environments. The structural integrity of latex foam thus ensures enhanced long-term protection compared to EPS, which may require more frequent replacement or reinforcement.
Moisture Resistance and Protection Capabilities
Latex foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to expanded polystyrene foam, preventing water absorption and maintaining cushioning integrity in humid environments. Its elastic structure provides enhanced shock absorption and impact protection for fragile items during transit. Expanded polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, is more prone to moisture infiltration, which can compromise its protective performance over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Latex foam offers superior biodegradability and is derived from natural rubber, making it a more sustainable option compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. EPS foam contributes significantly to landfill waste and marine pollution due to its slow decomposition and difficulty in recycling. Choosing latex foam over EPS reduces environmental footprint by promoting renewable resource use and enhancing end-of-life composting potential in packaging applications.
Cost Comparison: Latex vs Expanded Polystyrene
Latex foam typically costs more than expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam due to its natural origin and complex manufacturing process, with prices ranging from $4 to $8 per cubic foot compared to EPS's $1 to $3 per cubic foot. EPS is favored in packaging for its low cost, lightweight properties, and high impact resistance, making it ideal for large-scale shipping and protective cushioning. While latex foam offers superior durability and eco-friendliness, EPS remains more economical for budget-sensitive packaging solutions.
Usability and Adaptability for Various Products
Latex foam offers superior cushioning and flexibility, making it ideal for delicate electronics and irregularly shaped items, while expanded polystyrene foam (EPS) excels in lightweight, rigid protection for heavy or bulkier goods. Latex foam's elasticity allows it to conform closely to diverse product contours, enhancing shock absorption and reducing damage during transit. EPS provides robust thermal insulation and moisture resistance, which suits packaging needs for food products and temperature-sensitive materials.
Health and Safety Considerations in Packaging
Latex foam offers superior breathability and hypoallergenic properties, reducing the risk of respiratory irritation during packaging and handling. Expanded polystyrene foam contains styrene, which can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), posing potential health risks in enclosed environments. Proper ventilation and protective gear are essential when using expanded polystyrene to mitigate exposure to harmful substances.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Foam for Packaging Needs
Latex foam offers superior elasticity, resilience, and environmental sustainability, making it ideal for protective packaging of delicate or high-value items. Expanded polystyrene foam, with its lightweight structure and cost-effectiveness, suits large-scale shipping and insulation where budget constraints exist. Selecting the optimal foam depends on specific packaging requirements such as product fragility, environmental considerations, and budget limitations.
Infographic: Latex foam vs Expanded polystyrene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com