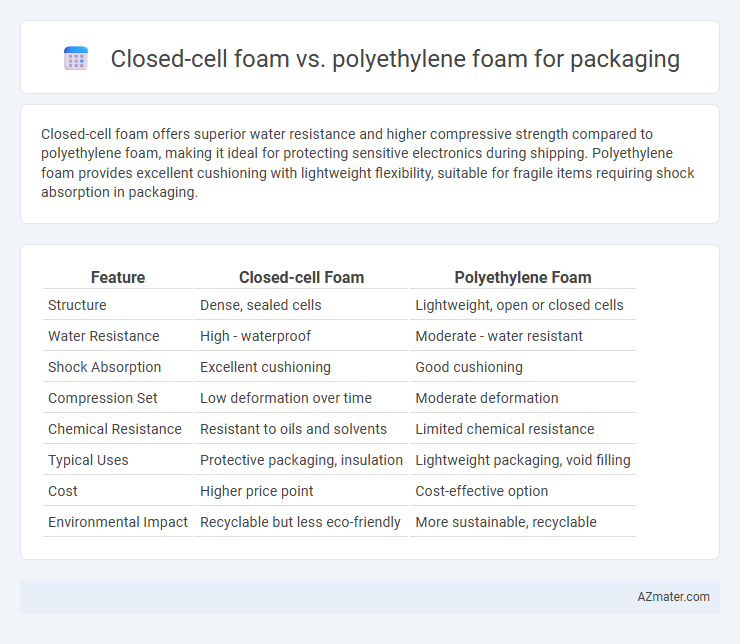
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and higher compressive strength compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for protecting sensitive electronics during shipping. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning with lightweight flexibility, suitable for fragile items requiring shock absorption in packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-cell Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Dense, sealed cells | Lightweight, open or closed cells |
| Water Resistance | High - waterproof | Moderate - water resistant |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent cushioning | Good cushioning |
| Compression Set | Low deformation over time | Moderate deformation |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and solvents | Limited chemical resistance |
| Typical Uses | Protective packaging, insulation | Lightweight packaging, void filling |
| Cost | Higher price point | Cost-effective option |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but less eco-friendly | More sustainable, recyclable |
Introduction to Foam Packaging Materials
Closed-cell foam offers superior rigidity and moisture resistance compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for protective packaging of sensitive electronics and medical devices. Polyethylene foam, known for its lightweight flexibility and excellent cushioning properties, provides effective shock absorption and is widely used for packaging fragile items during shipping. Both materials contribute to enhanced product safety, with closed-cell foam excelling in durability and polyethylene foam favored for cost-efficiency and versatility.
Overview of Closed-Cell Foam
Closed-cell foam, characterized by its dense, non-permeable structure, offers superior impact resistance and moisture barrier properties compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for protecting sensitive goods during shipping. Its closed cells trap gas, providing excellent insulation and buoyancy, which enhances cushioning performance in packaging applications. Typical materials include ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and vinyl nitrile, offering durability and chemical resistance for long-term product protection.
What is Polyethylene (PE) Foam?
Polyethylene (PE) foam is a closed-cell foam known for its excellent cushioning and impact resistance, making it ideal for protective packaging applications. Its lightweight, water-resistant, and chemical-resistant properties enhance durability and prevent damage during shipping and storage. Compared to other closed-cell foams, PE foam offers superior flexibility and compression recovery, ensuring better shield and reusable packaging solutions.
Key Differences Between Closed-Cell and Polyethylene Foam
Closed-cell foam offers higher rigidity, water resistance, and better compression strength compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for protecting delicate items in moisture-prone environments. Polyethylene foam is more flexible, lightweight, and provides excellent cushioning with superior shock absorption, suited for fragile, irregularly shaped products. Key differences include density, durability, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation properties, impacting their specific packaging applications.
Cushioning Performance and Shock Absorption
Closed-cell foam offers superior cushioning performance due to its dense structure, effectively distributing impact forces and minimizing damage during transportation. Polyethylene foam provides excellent shock absorption with its lightweight, flexible nature, making it ideal for protecting fragile items in packaging applications. Both materials deliver reliable protection, but closed-cell foam excels in environments requiring higher durability and resistance to compression.
Moisture Resistance and Durability Comparison
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its dense, non-porous structure that prevents water absorption, making it ideal for packaging sensitive electronics or food products. Polyethylene foam, while lightweight and cushioning, has a more open-cell structure that can absorb moisture over time, reducing its effectiveness in damp environments. In terms of durability, closed-cell foam provides enhanced compression resistance and long-term performance, whereas polyethylene foam is more susceptible to deformation under heavy loads or prolonged use.
Weight, Flexibility, and Handling
Closed-cell foam is typically denser and heavier than polyethylene foam, offering superior rigidity and excellent impact resistance, ideal for protecting delicate items during shipping. Polyethylene foam is lighter and more flexible, providing easy handling and cushioning for irregular or lightweight products. While closed-cell foam excels in structural support, polyethylene foam adapts better to dynamic packaging needs requiring bending and compressibility.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Closed-cell foam typically has a lower environmental impact due to its greater durability and resistance to moisture, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation. Polyethylene foam offers better recyclability as it is widely accepted by recycling programs and can be reprocessed into new products, contributing to a circular economy. Both materials vary in biodegradability, with polyethylene foam being more favorable for eco-friendly disposal and closed-cell foam requiring specialized recycling methods to minimize landfill accumulation.
Cost Analysis and Value for Packaging
Closed-cell foam generally offers superior cushioning and moisture resistance compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for protecting high-value or fragile items. Although closed-cell foam tends to have a higher initial cost, its durability and enhanced protective properties often result in lower overall expenses through reduced product damage and returns. Polyethylene foam provides a cost-effective solution for lightweight or less fragile goods, balancing affordability with adequate protection for budget-conscious packaging needs.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and higher impact protection, making it ideal for packaging sensitive electronics or moisture-sensitive items. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning and is lightweight, suitable for bulkier, less fragile products requiring shock absorption during transit. Selecting the right foam depends on product fragility, exposure to moisture, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring optimal protection and shipping efficiency.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com