Polyethylene foam offers superior flexibility, impact resistance, and moisture resistance compared to PVC foam, making it ideal for delicate packaging applications. PVC foam provides higher rigidity and better chemical resistance, suited for protective packaging requiring structural support.
Table of Comparison
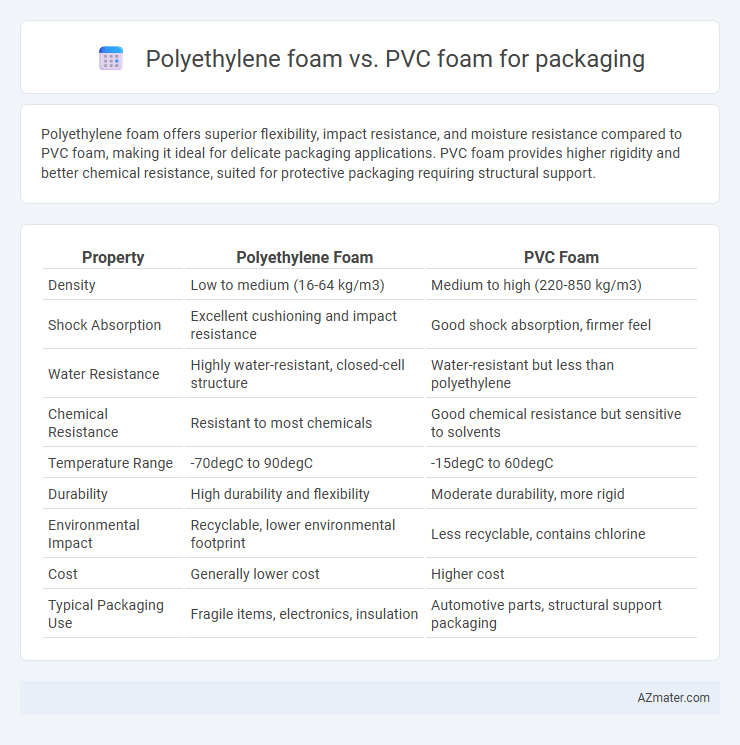
| Property | Polyethylene Foam | PVC Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium (16-64 kg/m3) | Medium to high (220-850 kg/m3) |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent cushioning and impact resistance | Good shock absorption, firmer feel |
| Water Resistance | Highly water-resistant, closed-cell structure | Water-resistant but less than polyethylene |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most chemicals | Good chemical resistance but sensitive to solvents |
| Temperature Range | -70degC to 90degC | -15degC to 60degC |
| Durability | High durability and flexibility | Moderate durability, more rigid |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, lower environmental footprint | Less recyclable, contains chlorine |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Packaging Use | Fragile items, electronics, insulation | Automotive parts, structural support packaging |
Introduction to Polyethylene Foam and PVC Foam
Polyethylene foam, known for its lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing properties, is widely used in packaging to protect delicate items from impact and vibration. PVC foam, characterized by its rigidity, high density, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, offers robust structural support and cushioning in packaging applications. Both materials provide effective protection, with polyethylene foam excelling in cushioning and PVC foam delivering durable, moisture-resistant packaging solutions.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Polyethylene foam consists primarily of ethylene polymers offering excellent flexibility and impact absorption, while PVC foam is made from polyvinyl chloride, providing higher rigidity and chemical resistance. Polyethylene foam is typically produced through extrusion or bead expansion methods, resulting in a closed-cell structure that enhances cushioning properties. PVC foam manufacturing involves polymerization followed by foaming with chemical blowing agents, creating a denser and more durable foam suitable for heavy-duty packaging applications.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene foam exhibits superior cushioning and impact absorption with a density range of 18 to 60 kg/m3 and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for delicate packaging. PVC foam presents higher rigidity and dimensional stability, featuring a density between 200 and 600 kg/m3, which enhances structural support and resistance to compression. Both materials offer moisture resistance, but polyethylene foam excels in vibration dampening, while PVC foam provides better thermal insulation and chemical resistance for specific packaging needs.
Cushioning Performance and Shock Absorption
Polyethylene foam offers superior cushioning performance and shock absorption due to its closed-cell structure, which provides excellent resilience and energy absorption. PVC foam, while denser, provides good cushioning but is less effective in dissipating shock impact compared to polyethylene. Polyethylene foam's lightweight and flexible nature make it ideal for protecting fragile items during shipping by minimizing damage from vibrations and drops.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polyethylene foam exhibits superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, effectively preventing water absorption and providing excellent cushioning in damp environments. PVC foam offers enhanced chemical resistance, particularly against oils, acids, and solvents, making it suitable for packaging sensitive or reactive materials. Choosing between polyethylene and PVC foam depends on specific packaging needs, with polyethylene favored for high moisture exposure and PVC preferred for chemical protection.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Polyethylene foam is significantly lighter than PVC foam, making it ideal for applications requiring reduced shipping costs and easier handling. Its higher flexibility allows it to absorb shocks and conform to irregular shapes more effectively than the stiffer, denser PVC foam. PVC foam offers greater rigidity and durability but at the expense of increased weight and reduced pliability compared to polyethylene foam.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene foam offers superior recyclability due to its lightweight, non-toxic composition and widespread acceptance in recycling programs, reducing environmental impact by minimizing landfill waste. PVC foam, while durable and resistant, poses greater environmental concerns because it releases harmful dioxins during production and disposal and is less commonly recycled. Choosing polyethylene foam for packaging supports sustainability efforts by enabling easier recycling and lowering ecological footprints compared to PVC foam.
Cost Efficiency for Packaging Applications
Polyethylene foam offers superior cost efficiency for packaging applications due to its lower material cost and excellent cushioning properties that reduce product damage during transit. PVC foam, while providing higher rigidity and chemical resistance, incurs higher production expenses, making it less economical for mass packaging needs. Selecting polyethylene foam can significantly lower overall packaging costs while maintaining adequate protection for a wide range of products.
Common Packaging Use Cases
Polyethylene foam is widely used in packaging for its excellent shock absorption and cushioning properties, making it ideal for protecting fragile electronics and delicate machinery. PVC foam offers superior rigidity and chemical resistance, commonly employed for packaging industrial components requiring structural support and moisture protection. Both materials provide lightweight solutions, with polyethylene foam favored for impact protection and PVC foam chosen for durability in harsh environments.
Selecting the Right Foam for Packaging Needs
Polyethylene foam offers excellent cushioning, impact absorption, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for protecting delicate electronics and fragile items during shipping. PVC foam provides superior rigidity, chemical resistance, and durability, suitable for packaging heavier or more industrial products. Selecting the right foam depends on factors such as product weight, fragility, environmental exposure, and cost, ensuring optimal protection and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs PVC foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com