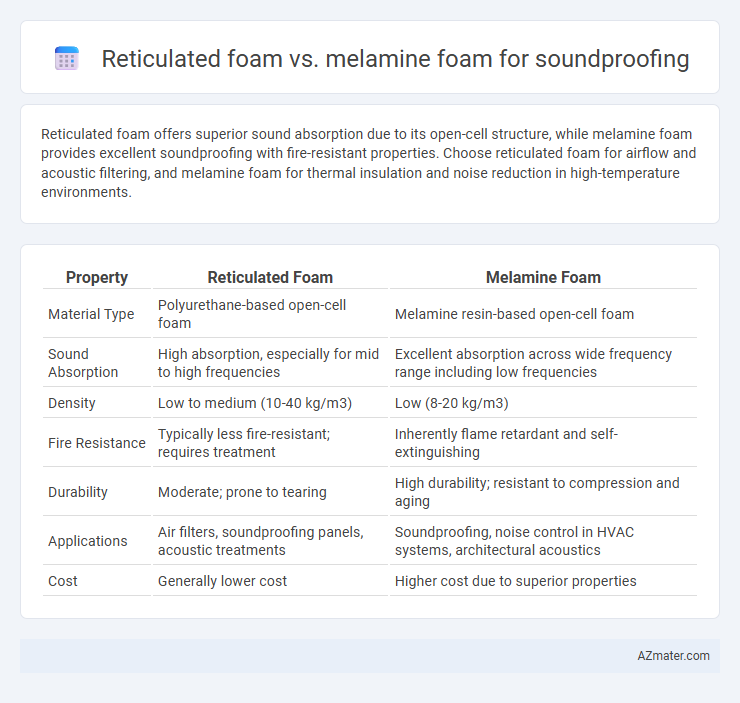
Reticulated foam offers superior sound absorption due to its open-cell structure, while melamine foam provides excellent soundproofing with fire-resistant properties. Choose reticulated foam for airflow and acoustic filtering, and melamine foam for thermal insulation and noise reduction in high-temperature environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reticulated Foam | Melamine Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyurethane-based open-cell foam | Melamine resin-based open-cell foam |
| Sound Absorption | High absorption, especially for mid to high frequencies | Excellent absorption across wide frequency range including low frequencies |
| Density | Low to medium (10-40 kg/m3) | Low (8-20 kg/m3) |
| Fire Resistance | Typically less fire-resistant; requires treatment | Inherently flame retardant and self-extinguishing |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to tearing | High durability; resistant to compression and aging |
| Applications | Air filters, soundproofing panels, acoustic treatments | Soundproofing, noise control in HVAC systems, architectural acoustics |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to superior properties |
Introduction to Acoustic Foams
Reticulated foam and melamine foam are both popular choices for acoustic treatment due to their unique sound absorption properties. Reticulated foam features an open-cell structure that excels in airflow and high-frequency sound absorption, making it highly effective for reducing echo and improving room acoustics. Melamine foam is lightweight, fire-resistant, and offers superior mid to high-frequency sound absorption, often used in professional soundproofing environments for enhanced noise control and thermal insulation.
What is Reticulated Foam?
Reticulated foam is an open-cell material characterized by a network of interconnected pores, making it highly breathable and effective at sound absorption by trapping and dissipating sound waves. It is commonly used in acoustic panels and soundproofing applications where airflow and noise reduction are important, contrasting with melamine foam, which has a more closed-cell structure and is known for its lightweight, fire-resistant, and sound-absorbing properties. Reticulated foam's durability and open structure make it ideal for environments requiring both soundproofing and ventilation.
Understanding Melamine Foam
Melamine foam is a lightweight, open-cell material known for its exceptional sound absorption properties due to its porous structure, which effectively traps and dissipates sound waves. Unlike reticulated foam, melamine foam resists fire and moisture, making it ideal for acoustic treatments in environments requiring safety and durability. Its fine cellular network also provides superior broadband noise reduction, making it a preferred choice for professional soundproofing applications.
Sound Absorption Properties Comparison
Reticulated foam features an open-cell structure with high permeability, offering superior sound absorption for low to mid-frequency noise, making it ideal for environments requiring effective acoustic dampening. Melamine foam, composed of a lightweight, rigid open-cell matrix, excels in absorbing mid to high-frequency sounds due to its fine pore structure and fire-resistant properties. While melamine foam provides better performance in higher frequency ranges, reticulated foam is preferred for applications relying on airflow and sound diffusion in broader frequency spectra.
Durability and Lifespan Differences
Reticulated foam exhibits higher durability and a longer lifespan compared to melamine foam due to its open-cell structure and robust polymer composition, which resists degradation and maintains acoustic performance over time. Melamine foam, while effective for sound absorption, tends to break down more quickly under mechanical stress and environmental factors, leading to reduced longevity in soundproofing applications. Choosing reticulated foam enhances long-term soundproofing effectiveness, especially in high-traffic or industrial environments where durability is critical.
Fire Resistance: Reticulated vs Melamine Foam
Reticulated foam, composed of open-cell polyurethane, generally exhibits lower fire resistance and can ignite more easily compared to melamine foam. Melamine foam is inherently fire-resistant due to its thermoset polymer structure, self-extinguishing properties, and high melting point above 300degC (572degF), making it ideal for soundproofing applications requiring stringent fire safety standards. Choosing melamine foam enhances fire safety compliance while providing effective acoustic insulation in environments with elevated fire risk.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Reticulated foam, characterized by its open-cell structure, offers excellent moisture drainage and resists chemical absorption, making it ideal for humid or chemically exposed environments. Melamine foam exhibits high chemical resistance and is hydrophobic, preventing moisture retention and fungal growth, which enhances durability in soundproofing applications. Both foams provide effective soundproofing, but reticulated foam outperforms in moisture management, while melamine foam excels in chemical resilience.
Installation and Maintenance Ease
Reticulated foam features an open-cell structure that facilitates easy installation by allowing sound waves to pass through while minimizing obstruction, making it suitable for complex surfaces and quick fits. Melamine foam, known for its lightweight and flexible properties, simplifies cutting and fitting around irregular shapes but may require more careful handling to avoid damage during installation. Maintenance of reticulated foam is straightforward due to its durable material and resistance to dust accumulation, whereas melamine foam often needs gentle cleaning to preserve its acoustic performance and prevent surface degradation over time.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Reticulated foam typically costs more upfront than melamine foam but offers greater durability and breathability, enhancing long-term soundproofing performance in industrial and commercial settings. Melamine foam, while cheaper and lightweight, tends to degrade faster, requiring more frequent replacement, which can increase overall costs over time. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, reticulated foam is more cost-effective for applications demanding higher durability and sustained acoustic absorbency.
Choosing the Right Foam for Soundproofing Needs
Reticulated foam features an open-cell structure ideal for sound absorption in environments requiring airflow and moisture resistance, making it suitable for HVAC and industrial applications. Melamine foam offers superior acoustic damping due to its lightweight, rigid, and open-cell properties, excelling in reducing echo and reverberation in studios and offices. Selecting the right foam depends on factors like sound frequency range, environmental conditions, and installation requirements, with melamine foam favored for high-frequency noise control and reticulated foam for ventilation-prioritized soundproofing solutions.
Infographic: Reticulated foam vs Melamine foam for Soundproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com