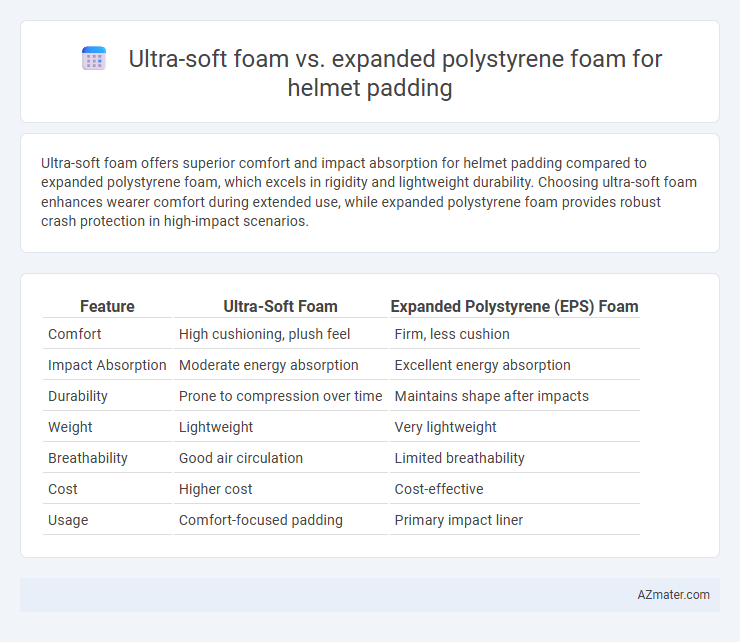
Ultra-soft foam offers superior comfort and impact absorption for helmet padding compared to expanded polystyrene foam, which excels in rigidity and lightweight durability. Choosing ultra-soft foam enhances wearer comfort during extended use, while expanded polystyrene foam provides robust crash protection in high-impact scenarios.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Soft Foam | Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Comfort | High cushioning, plush feel | Firm, less cushion |
| Impact Absorption | Moderate energy absorption | Excellent energy absorption |
| Durability | Prone to compression over time | Maintains shape after impacts |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Breathability | Good air circulation | Limited breathability |
| Cost | Higher cost | Cost-effective |
| Usage | Comfort-focused padding | Primary impact liner |
Introduction to Helmet Padding Materials
Helmet padding materials significantly impact comfort and safety, with ultra-soft foam and expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam being two primary options. Ultra-soft foam offers superior cushioning and comfort by conforming closely to the head, reducing pressure points during impact. EPS foam excels in energy absorption, effectively dissipating impact forces to protect against head injuries, making it a critical component in helmet safety design.
What is Ultra-Soft Foam?
Ultra-soft foam is a highly cushioned, flexible material designed to absorb impact and provide superior comfort in helmet padding, featuring low density and high resilience for effective shock absorption. Unlike expanded polystyrene foam (EPS), which is rigid and designed primarily for energy dispersion during impacts, ultra-soft foam offers enhanced conformability to the wearer's head, improving fit and reducing pressure points. Its advanced cell structure and viscoelastic properties make ultra-soft foam ideal for multi-impact absorption, extending helmet durability and safety performance.
What is Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Foam?
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam is a lightweight, rigid cellular plastic material commonly used in helmet padding for its excellent impact absorption properties. EPS foam consists of small beads fused together, creating a structure that efficiently disperses energy upon impact to protect the head. Compared to ultra-soft foam, EPS provides superior shock absorption and durability, making it the industry standard in safety helmets.
Key Differences in Foam Structure
Ultra-soft foam used in helmet padding features an open-cell structure, allowing for superior energy absorption and enhanced comfort by conforming closely to the head's shape. Expanded polystyrene foam (EPS) consists of a closed-cell, rigid structure that offers excellent impact resistance through energy dispersion but lacks the same cushioning softness. The difference in cell structure directly affects the performance, with ultra-soft foam prioritizing comfort and EPS focusing on impact protection and durability.
Impact Absorption Capabilities
Ultra-soft foam offers superior comfort but provides less impact absorption compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam, which excels at dissipating energy during high-force collisions. EPS foam's rigid cellular structure crushes upon impact, effectively reducing the force transmitted to the skull and minimizing concussion risk. Helmet padding combining both materials can optimize comfort while maintaining critical impact protection standards.
Comfort and Fit Considerations
Ultra-soft foam offers superior cushioning and conforms better to the head's shape, enhancing overall comfort and reducing pressure points compared to expanded polystyrene foam. Expanded polystyrene foam, while excellent for impact absorption, tends to be firmer and less adaptive, which can compromise fit and long-term comfort during extended wear. Choosing ultra-soft foam padding improves helmet fit by providing a snug, personalized feel, critical for both safety and user satisfaction.
Durability and Longevity
Ultra-soft foam offers superior comfort but tends to compress and degrade faster under repeated impact, reducing its durability and lifespan in helmet padding. Expanded polystyrene foam (EPS) provides excellent energy absorption and maintains structural integrity over time, ensuring longer-lasting protection in helmets. EPS's rigid cellular structure resists permanent deformation, making it the preferred choice for durable and long-lasting helmet padding solutions.
Safety Standards and Certifications
Ultra-soft foam and expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam are both widely used in helmet padding, with EPS foam meeting rigorous safety standards such as DOT, ECE, and Snell certifications due to its superior energy absorption and impact resistance. Ultra-soft foam offers enhanced comfort and shock absorption but typically lacks the same level of certified impact protection required for high-impact safety certifications. EPS foam's ability to crush and dissipate impact forces efficiently aligns with stringent safety regulations, making it the preferred choice for certified protective helmets.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ultra-soft foam used in helmet padding offers improved biodegradability compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam, which is notorious for its persistence in landfills and marine environments due to its non-biodegradable nature. The production of ultra-soft foam typically involves fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint relative to EPS foam manufacturing. Choosing ultra-soft foam enhances sustainability in helmet design by facilitating easier recycling and minimizing environmental pollution throughout the product lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Helmet
Ultra-soft foam provides superior comfort and impact absorption, making it ideal for helmet padding where prolonged wear occurs. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam excels in energy dispersion during high-impact collisions, offering enhanced protection against trauma. Selecting the right foam involves balancing comfort needs with safety requirements, prioritizing EPS for impact resistance and ultra-soft foam for cushioning and fit.
Infographic: Ultra-soft foam vs Expanded polystyrene foam for Helmet padding
 azmater.com
azmater.com