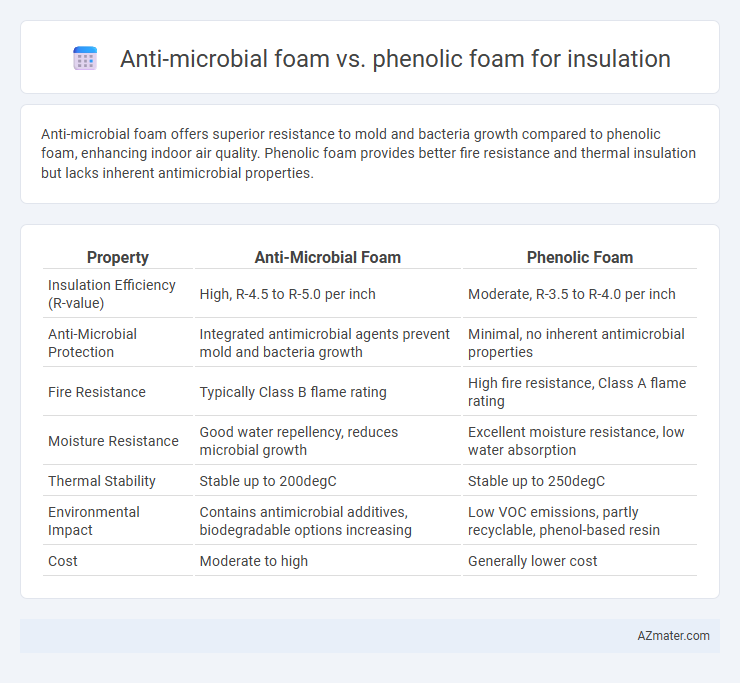
Anti-microbial foam offers superior resistance to mold and bacteria growth compared to phenolic foam, enhancing indoor air quality. Phenolic foam provides better fire resistance and thermal insulation but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Anti-Microbial Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Efficiency (R-value) | High, R-4.5 to R-5.0 per inch | Moderate, R-3.5 to R-4.0 per inch |
| Anti-Microbial Protection | Integrated antimicrobial agents prevent mold and bacteria growth | Minimal, no inherent antimicrobial properties |
| Fire Resistance | Typically Class B flame rating | High fire resistance, Class A flame rating |
| Moisture Resistance | Good water repellency, reduces microbial growth | Excellent moisture resistance, low water absorption |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 200degC | Stable up to 250degC |
| Environmental Impact | Contains antimicrobial additives, biodegradable options increasing | Low VOC emissions, partly recyclable, phenol-based resin |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Anti-microbial foam insulation resists mold, mildew, and bacterial growth, enhancing indoor air quality and durability in humid environments. Phenolic foam insulation offers superior thermal resistance and fire retardancy, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings requiring strict fire safety standards. Both materials provide effective insulation but differ significantly in moisture resistance and flame performance.
What is Anti-Microbial Foam?
Anti-microbial foam is an insulation material treated with agents that inhibit the growth of bacteria, mold, and mildew, enhancing indoor air quality and durability. Phenolic foam, known for its high thermal resistance and fire retardancy, lacks inherent anti-microbial properties without additional treatments. Choosing anti-microbial foam offers improved hygiene and longevity in environments prone to moisture and microbial contamination.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a rigid insulation material known for its excellent fire resistance, low smoke emission, and high thermal performance with R-values typically ranging from 4.2 to 4.4 per inch. Its closed-cell structure provides superior moisture resistance and dimensional stability compared to other insulation types, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and long-term efficiency. Phenolic foam is commonly used in building envelopes, refrigerated storage, and industrial equipment, offering a sustainable option with low environmental impact due to its formaldehyde-free formulations.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Anti-microbial foam insulation typically offers a thermal conductivity range of 0.020 to 0.030 W/m*K, providing effective resistance to heat transfer while inhibiting microbial growth. Phenolic foam insulation exhibits superior thermal performance with a lower thermal conductivity value, often between 0.018 to 0.022 W/m*K, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency and improved insulation effectiveness. The denser cell structure of phenolic foam contributes to its lower thermal conductivity, making it a preferred choice for high-performance insulation applications.
Moisture and Mold Resistance
Anti-microbial foam offers superior moisture resistance by inhibiting microbial growth within the insulation material, effectively reducing the risk of mold development. Phenolic foam exhibits excellent moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, which prevents water absorption and limits mold formation. Both foams provide effective solutions for mold prevention, but anti-microbial foam specifically targets microbial activity, enhancing long-term durability in damp environments.
Fire Safety and Chemical Stability
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced resistance to microbial growth but typically exhibits lower fire resistance compared to phenolic foam, which is known for its excellent fire-retardant properties and minimal smoke emission. Phenolic foam maintains superior chemical stability under high temperatures, ensuring consistent insulation performance during fire exposure, whereas anti-microbial foam may degrade or release toxic compounds when exposed to extreme heat. In fire safety applications, phenolic foam is preferred due to its low flame spread, low heat release rate, and robust chemical stability, making it a safer choice for building insulation.
Applications in Building Insulation
Anti-microbial foam offers superior resistance to mold and bacteria, making it ideal for humid building environments such as bathrooms and basements, while phenolic foam excels in fire resistance and thermal insulation, suitable for exterior walls and roofing applications. The low smoke emission and high fire retardance of phenolic foam comply with stringent building codes in commercial constructions, whereas anti-microbial foam enhances indoor air quality in residential and healthcare facilities. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing moisture control and hygiene versus fire safety and energy efficiency in building insulation projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Anti-microbial foam typically contains chemicals that inhibit microbial growth but may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production and disposal, impacting indoor air quality and environmental health. Phenolic foam offers a more sustainable option with lower embodied carbon and excellent thermal insulation, contributing to energy efficiency and reduced greenhouse gas emissions over its lifecycle. Both foams should be evaluated for recyclability and potential environmental toxins to ensure sustainable building practices.
Cost Analysis: Anti-Microbial vs Phenolic Foam
Anti-microbial foam typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to phenolic foam due to specialized additives that prevent microbial growth, contributing to increased durability in moisture-prone environments. Phenolic foam offers a more cost-effective solution with strong thermal insulation properties and fire resistance, making it a preferred choice for large-scale commercial projects seeking budget efficiency. When evaluating lifecycle costs, anti-microbial foam may reduce maintenance and replacement expenses in settings vulnerable to mold and bacteria, potentially offsetting the initial price difference over time.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Insulation Needs
Anti-microbial foam offers superior resistance to mold, bacteria, and fungi, making it ideal for environments prone to moisture and biological growth, while phenolic foam excels in fire resistance and thermal insulation with low smoke emissions. Selecting the right foam depends on specific insulation requirements such as moisture control, fire safety standards, and thermal performance levels. Understanding the distinct properties of anti-microbial versus phenolic foam ensures optimized insulation longevity and indoor air quality tailored to your building's environmental conditions.
Infographic: Anti-microbial foam vs Phenolic foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com