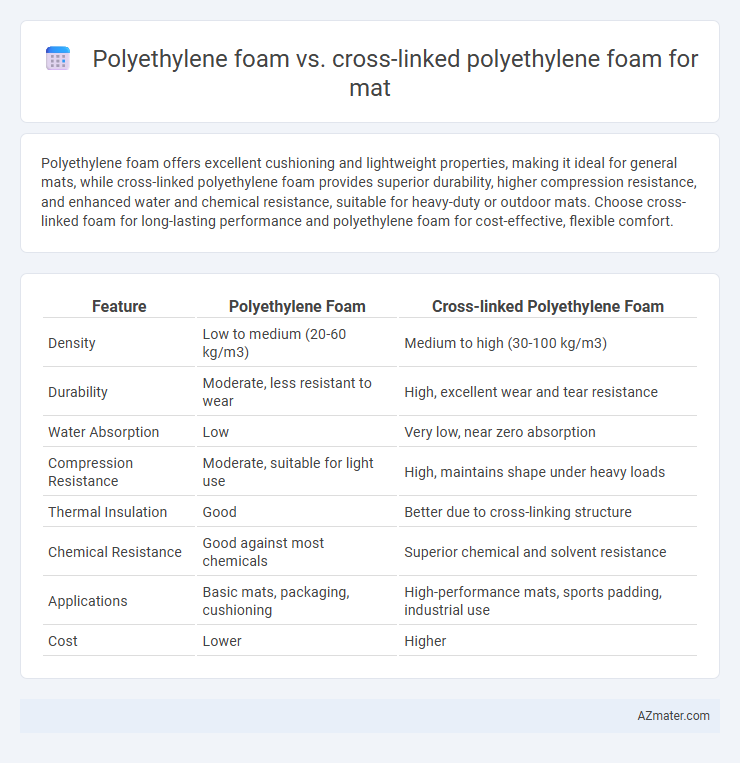
Polyethylene foam offers excellent cushioning and lightweight properties, making it ideal for general mats, while cross-linked polyethylene foam provides superior durability, higher compression resistance, and enhanced water and chemical resistance, suitable for heavy-duty or outdoor mats. Choose cross-linked foam for long-lasting performance and polyethylene foam for cost-effective, flexible comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyethylene Foam | Cross-linked Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium (20-60 kg/m3) | Medium to high (30-100 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to wear | High, excellent wear and tear resistance |
| Water Absorption | Low | Very low, near zero absorption |
| Compression Resistance | Moderate, suitable for light use | High, maintains shape under heavy loads |
| Thermal Insulation | Good | Better due to cross-linking structure |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against most chemicals | Superior chemical and solvent resistance |
| Applications | Basic mats, packaging, cushioning | High-performance mats, sports padding, industrial use |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Polyethylene Foam and Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, flexible material known for its excellent cushioning, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for mats used in sports and packaging. Cross-linked polyethylene foam (XLPE) enhances these qualities through a chemical process that creates a closed-cell structure, resulting in superior durability, higher density, and improved impact absorption. Both materials offer distinct advantages, with polyethylene foam being cost-effective and versatile while XLPE provides enhanced strength and resilience for demanding applications.
Understanding the Chemical Structure Differences
Polyethylene foam consists of a linear polymer structure with loosely connected chains, which provides a softer and more flexible texture ideal for cushioning in mats. Cross-linked polyethylene foam features chemically bonded polymer chains forming a three-dimensional network, enhancing durability, resilience, and resistance to compression under heavy loads. This difference in chemical structure influences the foam's performance in mats, with cross-linked foam offering superior structural integrity and longevity compared to the more pliable standard polyethylene foam.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene foam and cross-linked polyethylene foam differ significantly in physical properties relevant to mat applications. Polyethylene foam typically offers lower density, reduced tensile strength, and higher compressibility, making it suitable for lightweight cushioning. Cross-linked polyethylene foam exhibits higher tensile and compression strength, improved moisture resistance, and better durability, providing superior support and longevity for heavy-duty mat use.
Durability and Longevity of Each Foam Type
Polyethylene foam offers excellent impact resistance and moderate durability, making it suitable for lightweight mats, but it may compress over time with frequent use. Cross-linked polyethylene foam provides superior durability and enhanced longevity due to its closed-cell structure, which resists deformation, moisture, and chemical damage. For applications requiring long-lasting cushioning and resilience, cross-linked polyethylene foam outperforms standard polyethylene foam in maintaining shape and performance over extended periods.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance
Polyethylene foam offers lightweight cushioning with moderate resilience, providing a soft and comfortable surface ideal for general use mats. Cross-linked polyethylene foam enhances comfort through its closed-cell structure, delivering superior durability, higher compression resistance, and excellent shock absorption. The cross-linked variant outperforms standard polyethylene in cushioning stability, making it preferable for high-impact or prolonged-use mat applications.
Water and Moisture Resistance
Polyethylene foam exhibits excellent water and moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, making it highly effective for mat applications in damp environments. Cross-linked polyethylene foam offers superior durability and enhanced moisture resistance, preventing water absorption and maintaining cushioning performance over time. Both materials provide robust protection against water damage, but cross-linked polyethylene foam generally delivers longer-lasting resilience in wet conditions.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Polyethylene foam offers effective thermal insulation with its closed-cell structure that minimizes heat transfer, making it suitable for general-purpose mats. Cross-linked polyethylene foam enhances thermal insulation properties through its more uniform cell structure and greater density, providing superior resistance to heat flow and temperature variations. This makes cross-linked polyethylene foam a preferred choice for mats requiring advanced thermal insulation and durability.
Applications in Mat Production
Polyethylene foam and cross-linked polyethylene foam serve distinct roles in mat production due to their differing properties. Polyethylene foam is commonly used in yoga and exercise mats for its lightweight, cushioning, and cost-effectiveness, providing adequate support for low-impact activities. Cross-linked polyethylene foam, with superior durability, closed-cell structure, and enhanced resistance to water and chemicals, is preferred for industrial, safety, and outdoor mats requiring long-term performance and robust impact absorption.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Polyethylene foam offers a more budget-friendly option for mats due to its lower production cost and widespread availability, making it suitable for large-scale or cost-sensitive projects. Cross-linked polyethylene foam, while more expensive, provides superior durability, resilience, and thermal insulation, which can reduce long-term replacement and maintenance costs. Evaluating the total cost of ownership reveals that initial affordability favors polyethylene foam, but cross-linked foam's enhanced performance may justify the higher upfront investment in demanding environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Mat Needs
Polyethylene foam offers lightweight cushioning and excellent shock absorption, ideal for general-purpose mats, while cross-linked polyethylene foam provides superior durability, chemical resistance, and thermal insulation, making it suitable for heavy-duty or outdoor applications. Cross-linked foam's closed-cell structure prevents water absorption and enhances longevity in demanding environments, whereas polyethylene foam is more cost-effective for lighter use. Evaluating your mat's intended function and environment ensures selecting the optimal foam type that balances performance and budget requirements.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs Cross-linked polyethylene foam for Mat
 azmater.com
azmater.com