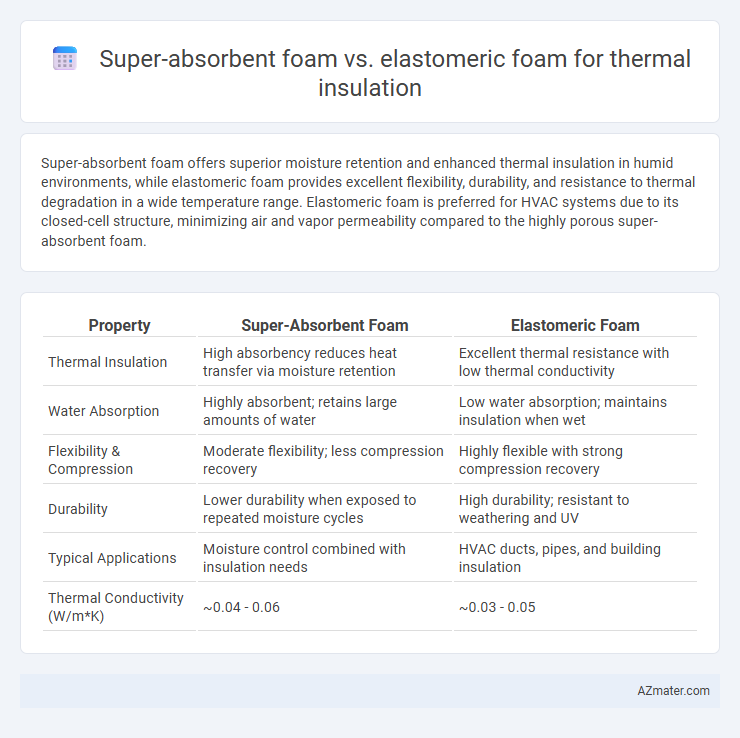
Super-absorbent foam offers superior moisture retention and enhanced thermal insulation in humid environments, while elastomeric foam provides excellent flexibility, durability, and resistance to thermal degradation in a wide temperature range. Elastomeric foam is preferred for HVAC systems due to its closed-cell structure, minimizing air and vapor permeability compared to the highly porous super-absorbent foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Super-Absorbent Foam | Elastomeric Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High absorbency reduces heat transfer via moisture retention | Excellent thermal resistance with low thermal conductivity |
| Water Absorption | Highly absorbent; retains large amounts of water | Low water absorption; maintains insulation when wet |
| Flexibility & Compression | Moderate flexibility; less compression recovery | Highly flexible with strong compression recovery |
| Durability | Lower durability when exposed to repeated moisture cycles | High durability; resistant to weathering and UV |
| Typical Applications | Moisture control combined with insulation needs | HVAC ducts, pipes, and building insulation |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | ~0.04 - 0.06 | ~0.03 - 0.05 |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Materials
Super-absorbent foam and elastomeric foam both serve as effective thermal insulation materials but differ fundamentally in their properties and applications. Super-absorbent foam excels in moisture absorption, making it ideal for environments requiring both insulation and moisture management, while elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility, durability, and resistance to temperature fluctuations, commonly used in HVAC systems and pipe insulation. Selecting between these foams depends on the specific insulation needs, including thermal conductivity, moisture control, and mechanical resilience.
What is Super-Absorbent Foam?
Super-absorbent foam is a specialized material designed to absorb and retain large amounts of liquid relative to its own weight, primarily used in applications requiring moisture management and thermal insulation. Its unique porous structure enables superior water absorption while maintaining thermal resistance, making it effective in preventing heat transfer in humid environments. Compared to elastomeric foam, super-absorbent foam offers enhanced moisture control without compromising insulating properties, ideal for safeguarding building envelopes and HVAC systems against condensation and heat loss.
Understanding Elastomeric Foam
Elastomeric foam, a flexible and closed-cell material, excels in thermal insulation by providing superior resistance to moisture, air infiltration, and heat transfer, making it ideal for HVAC systems and building envelopes. Its durability and ability to maintain insulation performance at extreme temperatures enhance energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Compared to super-absorbent foam, elastomeric foam offers long-term stability without absorbing water, thereby preventing mold growth and structural damage.
Key Thermal Performance Comparison
Super-absorbent foam exhibits superior moisture retention properties, significantly reducing thermal conductivity by maintaining consistent insulation even in humid conditions, whereas elastomeric foam primarily relies on its closed-cell structure to provide effective thermal resistance and flexibility. The thermal conductivity of super-absorbent foam typically ranges from 0.030 to 0.035 W/m*K, benefiting applications requiring moisture management, while elastomeric foam offers values around 0.035 to 0.040 W/m*K, excelling in vibration damping and long-term durability. Selection between the two foams depends on specific environmental challenges and thermal performance requirements, with super-absorbent foams favored for damp environments and elastomeric foams preferred for applications needing elastomeric resilience.
Moisture Resistance and Absorption
Super-absorbent foam excels in moisture absorption due to its high porosity and ability to retain large quantities of water, making it ideal for applications requiring moisture control. Elastomeric foam offers superior moisture resistance with its closed-cell structure that prevents water penetration and maintains thermal insulation efficiency in humid environments. Choosing between these materials depends on whether moisture absorption or resistance is critical for optimizing thermal insulation performance.
Durability and Longevity
Super-absorbent foam generally exhibits lower durability and longevity compared to elastomeric foam due to its tendency to degrade under prolonged exposure to moisture and temperature fluctuations. Elastomeric foam maintains structural integrity and thermal insulation properties over extended periods, resisting cracking, crumbling, and UV damage. Industry studies show elastomeric foam's lifespan exceeds 20 years in harsh thermal environments, while super-absorbent foam often requires more frequent replacement.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Super-absorbent foam for thermal insulation requires careful moisture management during installation to prevent degradation, necessitating precise handling and specialized sealing techniques. Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility, allowing for easier cutting and fitting around complex shapes, which simplifies on-site installation and reduces labor time. The inherent elasticity of elastomeric foam enhances thermal performance by maintaining a tight seal despite building movement or thermal expansion.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Super-absorbent foam typically contains synthetic polymers that can pose challenges in biodegradability and recycling, potentially contributing to long-term environmental waste. Elastomeric foam, often made from flexible, durable materials like nitrile rubber or neoprene, generally offers better sustainability through its longevity and reusability, reducing the frequency of replacement and overall material consumption. Energy-efficient manufacturing processes and lower chemical emissions further enhance the environmental performance of elastomeric foam compared to super-absorbent foam in thermal insulation applications.
Cost Analysis: Super-Absorbent vs Elastomeric Foam
Super-absorbent foam generally incurs higher initial costs due to advanced material composition and manufacturing processes compared to elastomeric foam, which offers economical pricing with adequate thermal insulation performance. Elastomeric foam's cost-effectiveness is enhanced by lower installation expenses and longer service life, reducing total ownership costs in typical HVAC applications. Life cycle cost analysis highlights elastomeric foam as preferable for budget-sensitive projects, while super-absorbent foam justifies its expense in specialized environments requiring superior moisture management.
Best Applications and Industry Recommendations
Super-absorbent foam excels in moisture management and is ideal for applications requiring high water retention and thermal insulation, such as in HVAC systems and industrial refrigeration. Elastomeric foam offers superior durability, flexibility, and resistance to temperature extremes, making it the preferred choice for automotive, aerospace, and construction industries focused on energy efficiency. Industry recommendations favor elastomeric foam for long-term insulation solutions due to its closed-cell structure and resistance to mold and chemicals, while super-absorbent foam is suited for environments with significant moisture exposure.
Infographic: Super-absorbent foam vs Elastomeric foam for Thermal insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com