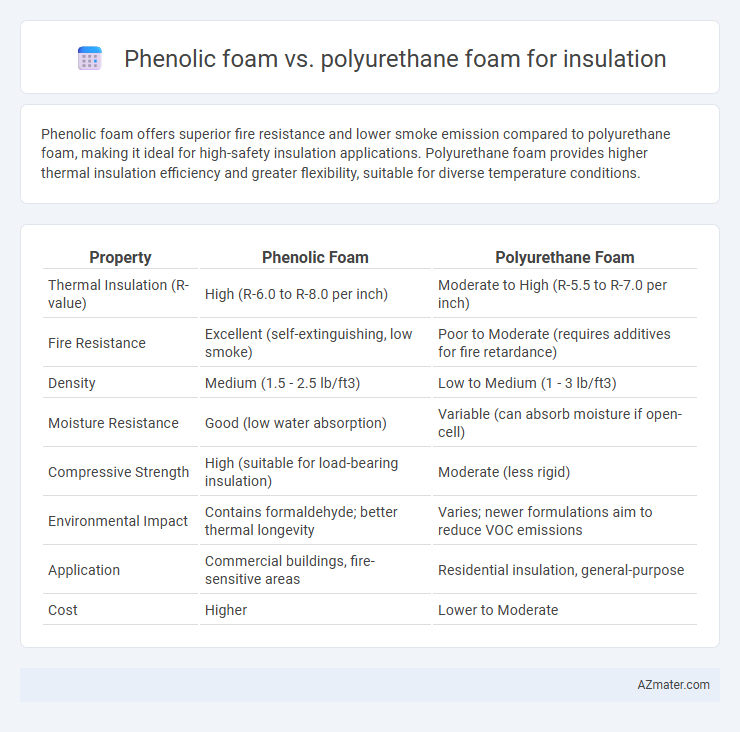
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and lower smoke emission compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for high-safety insulation applications. Polyurethane foam provides higher thermal insulation efficiency and greater flexibility, suitable for diverse temperature conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phenolic Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | High (R-6.0 to R-8.0 per inch) | Moderate to High (R-5.5 to R-7.0 per inch) |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent (self-extinguishing, low smoke) | Poor to Moderate (requires additives for fire retardance) |
| Density | Medium (1.5 - 2.5 lb/ft3) | Low to Medium (1 - 3 lb/ft3) |
| Moisture Resistance | Good (low water absorption) | Variable (can absorb moisture if open-cell) |
| Compressive Strength | High (suitable for load-bearing insulation) | Moderate (less rigid) |
| Environmental Impact | Contains formaldehyde; better thermal longevity | Varies; newer formulations aim to reduce VOC emissions |
| Application | Commercial buildings, fire-sensitive areas | Residential insulation, general-purpose |
| Cost | Higher | Lower to Moderate |
Introduction to Phenolic and Polyurethane Foams
Phenolic foam is a rigid, closed-cell insulation material known for its excellent fire resistance, low smoke emission, and high thermal stability, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced fire safety. Polyurethane foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its low thermal conductivity and high R-value per inch, commonly used in building insulation and refrigeration systems. Both foams serve critical roles in energy efficiency, but phenolic excels in fire performance while polyurethane prioritizes thermal insulation.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Phenolic foam consists primarily of phenol-formaldehyde resin, characterized by a rigid, cross-linked aromatic polymer structure providing excellent fire resistance and low smoke emissions. Polyurethane foam is formed by reacting polyols with isocyanates, resulting in a versatile polymer network with open or closed cells, offering superior thermal insulation and flexibility. The chemical stability and densely cross-linked structure of phenolic foam enhance its dimensional stability, while polyurethane's urethane linkages contribute to its mechanical resilience and moisture resistance.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Phenolic foam offers lower thermal conductivity values, typically around 0.020-0.025 W/m*K, resulting in superior thermal insulation compared to polyurethane foam, which generally ranges from 0.025-0.030 W/m*K. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam enhances its thermal resistance, maintaining stable insulation performance under varying temperature conditions. Polyurethane foam, while effective, tends to exhibit higher thermal bridging and slightly reduced long-term thermal stability in comparison to phenolic foam.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance compared to polyurethane foam, with a higher limiting oxygen index (LOI) and excellent char formation that prevents flame spread and reduces smoke emission. Polyurethane foam is more flammable, releasing toxic gases when burned, making phenolic foam a safer choice in fire-sensitive applications. Fire safety standards such as ASTM E84 favor phenolic foam for insulation where enhanced fire performance is critical.
Moisture and Water Resistance
Phenolic foam offers superior moisture and water resistance due to its closed-cell structure, which significantly reduces water absorption compared to polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam tends to absorb more moisture over time, potentially compromising its insulation efficiency and structural integrity. This makes phenolic foam a preferred choice in environments where consistent moisture exposure is a concern, ensuring long-term thermal performance and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with lower global warming potential due to its formaldehyde-based chemistry, which typically results in less volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam, while highly effective in insulation, often relies on petrochemical-derived isocyanates and blowing agents that can contribute to ozone depletion and higher carbon footprints. Sustainable building practices increasingly favor phenolic foam for its enhanced fire resistance, recyclability, and reduced environmental toxicity throughout its lifecycle.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Phenolic foam exhibits superior mechanical strength and fire resistance compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for applications requiring structural integrity and long-term durability. Polyurethane foam offers excellent thermal insulation but generally has lower compressive strength and is more susceptible to moisture degradation, reducing its lifespan in harsh environments. The inherent chemical stability and closed-cell structure of phenolic foam ensure enhanced durability and mechanical performance under mechanical stress.
Installation Process and Handling
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and dimensional stability, making it easier to handle during installation without significant deformation or off-gassing compared to polyurethane foam. The rigid structure of phenolic foam panels allows for precise cutting and fitting, reducing installation time and minimizing the need for protective measures. Polyurethane foam, while flexible and providing excellent thermal insulation, requires careful handling due to its tendency to emit volatile organic compounds and its sensitivity to moisture during application.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Phenolic foam generally offers a higher initial cost compared to polyurethane foam due to its specialized manufacturing process and superior fire resistance qualities. However, phenolic foam's enhanced thermal performance and longer lifespan can lead to lower lifecycle expenses and greater energy savings, making it economically advantageous for long-term insulation projects. Polyurethane foam, while cheaper upfront, may incur higher maintenance and replacement costs, impacting overall cost-effectiveness in extensive insulation applications.
Applications and Industry Recommendations
Phenolic foam is favored in fire-resistant insulation applications due to its superior fire retardancy and low smoke emission, making it ideal for commercial buildings, marine vessels, and industrial pipelines. Polyurethane foam offers excellent thermal insulation and moisture resistance, widely used in residential construction, refrigeration, and HVAC systems. Industry experts recommend phenolic foam where fire safety regulations are stringent, while polyurethane foam is preferred for cost-effective, versatile insulation solutions.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Polyurethane foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com