Open-cell foam offers superior sound absorption and flexibility, making it ideal for insulation in residential construction, while PVC foam provides higher durability, moisture resistance, and structural strength, suitable for exterior cladding and roofing applications. Choosing between open-cell foam and PVC foam depends on the specific requirements for thermal insulation, moisture control, and mechanical performance in the building project.
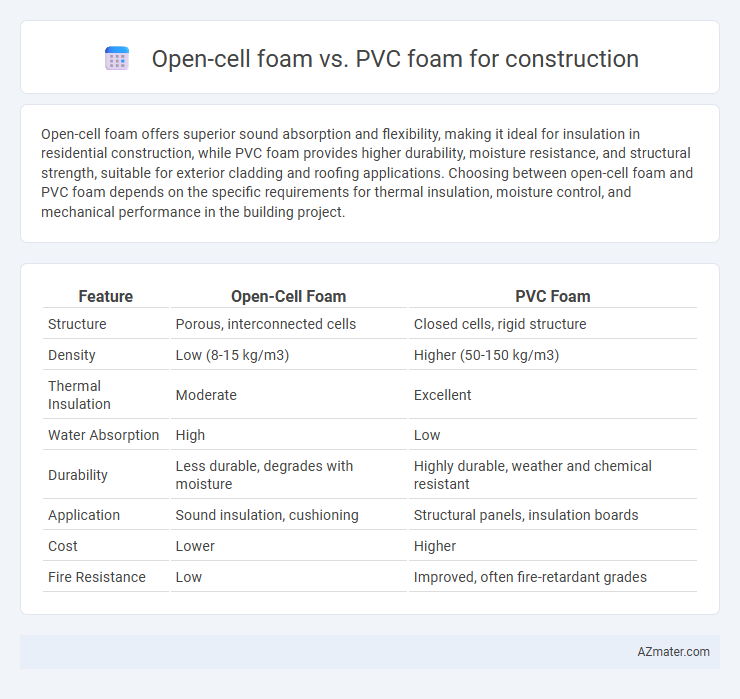
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Open-Cell Foam | PVC Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Porous, interconnected cells | Closed cells, rigid structure |
| Density | Low (8-15 kg/m3) | Higher (50-150 kg/m3) |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | Excellent |
| Water Absorption | High | Low |
| Durability | Less durable, degrades with moisture | Highly durable, weather and chemical resistant |
| Application | Sound insulation, cushioning | Structural panels, insulation boards |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Fire Resistance | Low | Improved, often fire-retardant grades |
Introduction: Comparing Open-Cell Foam and PVC Foam in Construction
Open-cell foam offers high breathability and flexibility, making it ideal for insulation in walls where moisture control is crucial, while PVC foam provides superior rigidity, chemical resistance, and durability suited for structural applications. The lower density and open-cell structure of open-cell foam result in effective sound absorption but reduced water resistance compared to the closed-cell nature of PVC foam. Choosing between open-cell and PVC foam impacts thermal insulation, moisture management, and longevity in building projects.
Material Composition and Structure
Open-cell foam consists of interconnected pores that allow air and moisture to pass through, providing excellent insulation and sound absorption but lower density and strength compared to PVC foam. PVC foam features a closed-cell structure made from polyvinyl chloride resin, resulting in a dense, rigid, and water-resistant material ideal for load-bearing applications and enhanced durability in construction. The open-cell foam's porous nature makes it lighter and more flexible, while PVC foam's compact structure offers superior resistance to chemical exposure and environmental degradation.
Insulation Properties and Thermal Performance
Open-cell foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its low density and higher R-value per inch, effectively reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. PVC foam, while less insulating than open-cell foam, provides better moisture resistance and structural rigidity, making it suitable for environments prone to humidity or mechanical stress. Choosing between open-cell foam and PVC foam depends on balancing insulation performance with durability requirements in construction projects.
Soundproofing Capabilities
Open-cell foam offers superior sound absorption due to its porous structure, effectively reducing airborne noise and echo in construction applications. PVC foam, with its denser and closed-cell composition, provides better sound insulation by blocking sound transmission through walls and partitions. Choosing between open-cell foam and PVC foam depends on whether the primary goal is sound absorption or sound blocking in architectural soundproofing design.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Open-cell foam demonstrates high water absorption due to its porous structure, making it less suitable for moisture-resistant construction applications compared to PVC foam. PVC foam exhibits superior moisture resistance, characterized by its closed-cell structure that effectively prevents water infiltration and maintains structural integrity in damp environments. This moisture-resistant property of PVC foam enhances its durability and longevity in construction projects exposed to humidity and water exposure.
Durability and Lifespan in Construction Applications
Open-cell foam offers excellent flexibility and sound absorption but generally exhibits lower durability and a shorter lifespan in construction compared to PVC foam, which is highly resistant to moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure. PVC foam's rigid structure and superior resistance to environmental stressors make it ideal for long-term structural components, ensuring extended service life in harsh conditions. For applications demanding robustness and longevity, PVC foam outperforms open-cell foam by maintaining integrity and performance over decades in diverse construction environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Open-cell foam, derived from polyurethane, offers better breathability and biodegradability compared to PVC foam, which is made from polyvinyl chloride and contains additives that can release toxic chemicals during manufacturing and disposal. PVC foam has a higher environmental impact due to its non-biodegradable nature and the presence of chlorine, which can generate harmful dioxins when burned or improperly discarded. Sustainable construction benefits from using open-cell foam because it reduces long-term ecological damage and supports improved indoor air quality by minimizing off-gassing and chemical emissions.
Installation Process and Workability
Open-cell foam offers superior flexibility and conformability, making it easier to cut and shape on-site, which speeds up the installation process in complex building geometries. PVC foam, characterized by its rigidity and higher density, requires precise measurements and specialized cutting tools to ensure proper fitting, impacting installation time but providing enhanced structural stability. Workability favors open-cell foam for rapid application and seamless sealing, whereas PVC foam excels in durability and resistance to moisture, ideal for load-bearing or exterior applications.
Cost Comparison and Value for Money
Open-cell foam generally costs less than PVC foam, making it a budget-friendly option for insulation in construction projects. While PVC foam offers enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and fire retardancy, its higher price reflects these added benefits and long-term savings. For cost-conscious builders, open-cell foam provides excellent thermal performance at a lower upfront cost, but PVC foam delivers greater value for money in applications demanding longevity and robust environmental resistance.
Best Use Cases for Open-Cell Foam vs. PVC Foam
Open-cell foam excels in insulation and soundproofing applications within construction due to its flexible, breathable structure and superior energy efficiency, making it ideal for residential walls and ceilings where moisture management is crucial. PVC foam, characterized by its rigid, dense composition and chemical resistance, suits exterior applications such as signage, cladding, and structural panels that require durability and weather resistance. Choosing between open-cell foam and PVC foam depends on project-specific factors like desired insulation properties, exposure to elements, and mechanical strength requirements.
Infographic: Open-cell foam vs PVC foam for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com