Open-cell foam offers excellent cushioning and breathability for packaging fragile items, while closed-cell foam provides superior moisture resistance and higher structural strength. Choosing between them depends on the need for impact absorption versus protection against water and compression.
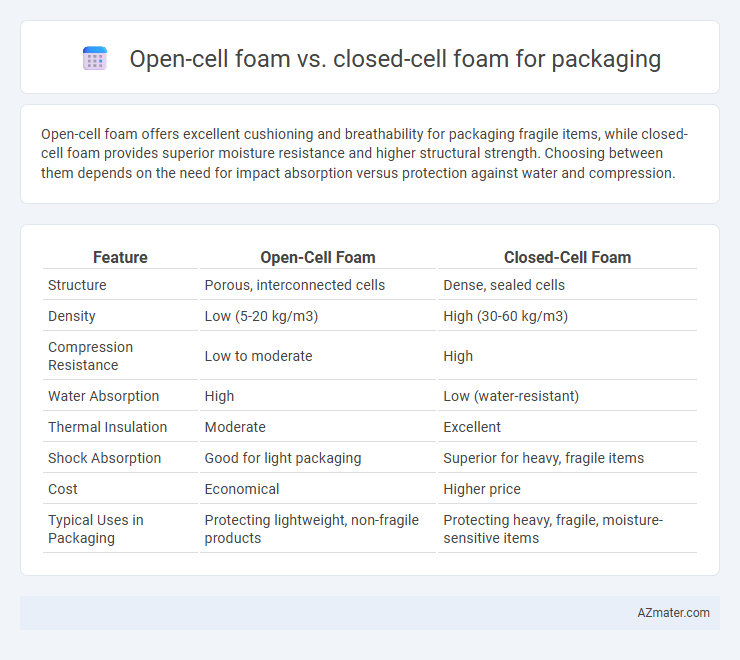
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Open-Cell Foam | Closed-Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Porous, interconnected cells | Dense, sealed cells |
| Density | Low (5-20 kg/m3) | High (30-60 kg/m3) |
| Compression Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
| Water Absorption | High | Low (water-resistant) |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | Excellent |
| Shock Absorption | Good for light packaging | Superior for heavy, fragile items |
| Cost | Economical | Higher price |
| Typical Uses in Packaging | Protecting lightweight, non-fragile products | Protecting heavy, fragile, moisture-sensitive items |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Packaging foams play a critical role in protecting products during shipping and handling, with open-cell and closed-cell foams serving distinct purposes. Open-cell foam features a porous structure that absorbs shocks and provides cushioning by allowing air to pass through, making it ideal for delicate, lightweight items requiring gentle protection. Closed-cell foam offers a dense, rigid composition with superior moisture resistance and high compressive strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty packaging applications where impact absorption and environmental protection are crucial.
What is Open-Cell Foam?
Open-cell foam is a lightweight, porous material where the cells are interconnected, allowing air to flow freely through the structure. Commonly used in packaging, this type of foam provides excellent cushioning and shock absorption for delicate or fragile items due to its breathability and flexibility. Its open-cell design also enhances its ability to conform to irregular shapes, making it ideal for protective packaging applications.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam is a dense material composed of tightly packed cells that are completely sealed, making it highly resistant to water, air, and moisture penetration. This type of foam offers superior insulation, structural rigidity, and impact protection, making it ideal for packaging fragile or sensitive items. Its closed structure prevents absorption, ensuring products remain dry and secure during shipping and storage.
Key Differences Between Open-Cell and Closed-Cell Foams
Open-cell foam features a porous structure allowing air and liquids to pass through, making it lightweight and flexible but less water-resistant, whereas closed-cell foam has tightly packed cells that prevent water absorption and offer higher rigidity and insulation. Closed-cell foam provides superior cushioning and impact resistance, ideal for protecting delicate items during shipping, while open-cell foam is better suited for applications requiring breathability and shock absorption. The density and compressive strength of closed-cell foam surpass those of open-cell foam, leading to enhanced durability in harsh packaging environments.
Cushioning Performance and Protection
Open-cell foam offers superior cushioning performance due to its flexibility and ability to absorb shocks, making it ideal for delicate items that require gentle impact protection. Closed-cell foam provides enhanced protection with its dense, rigid structure that resists moisture, compression, and punctures, ensuring durability in harsh environments. For packaging applications, closed-cell foam is preferred where high impact resistance and moisture barriers are critical, while open-cell foam excels in cushioning fragile goods during transit.
Moisture Resistance and Environmental Factors
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its dense, impermeable structure, making it ideal for packaging sensitive items exposed to humidity or liquids. Open-cell foam, with its porous nature, tends to absorb moisture, reducing its effectiveness in damp or wet environments but often performs better in terms of breathability and cushioning for less moisture-sensitive products. Environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and exposure to corrosive substances significantly impact open-cell foam more than closed-cell foam, which provides enhanced durability and protection in harsh conditions.
Weight and Density Considerations
Open-cell foam is lighter and less dense, offering superior cushioning and breathability for delicate items but may absorb moisture, impacting its protective qualities. Closed-cell foam features higher density and weight, providing enhanced rigidity, moisture resistance, and impact absorption, making it ideal for heavy or fragile goods requiring robust protection. Choosing between the two depends on the balance of weight sensitivity and the level of protection needed in packaging applications.
Cost Comparison: Open-Cell vs Closed-Cell Foam
Open-cell foam is generally more cost-effective than closed-cell foam due to its lower density and simpler manufacturing process, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious packaging applications. Closed-cell foam, while typically more expensive, offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and insulation properties, which can justify the higher upfront cost in protecting high-value or sensitive products. Evaluating total cost of ownership should include not only initial material costs but also potential savings from enhanced protection and reduced damage rates associated with closed-cell foam.
Sustainability and Recycling Options
Open-cell foam, characterized by its porous structure, offers better biodegradability and can be recycled in specialized facilities, making it a more sustainable option for eco-conscious packaging. Closed-cell foam, with its dense and impermeable composition, provides superior moisture resistance but poses challenges for recycling due to limited breakdown processes. Brands prioritizing sustainability often prefer open-cell foam for packaging to reduce environmental impact and enhance circular economy practices.
Choosing the Right Foam for Packaging Needs
Open-cell foam offers excellent cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for packaging delicate, lightweight items that require shock absorption without moisture resistance. Closed-cell foam provides superior water resistance, durability, and higher compressive strength, suitable for packaging heavier, moisture-sensitive goods that need robust protection. Selecting the right foam depends on the product's fragility, exposure to environmental factors, and the level of protection required during shipping and storage.
Infographic: Open-cell foam vs Closed-cell foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com