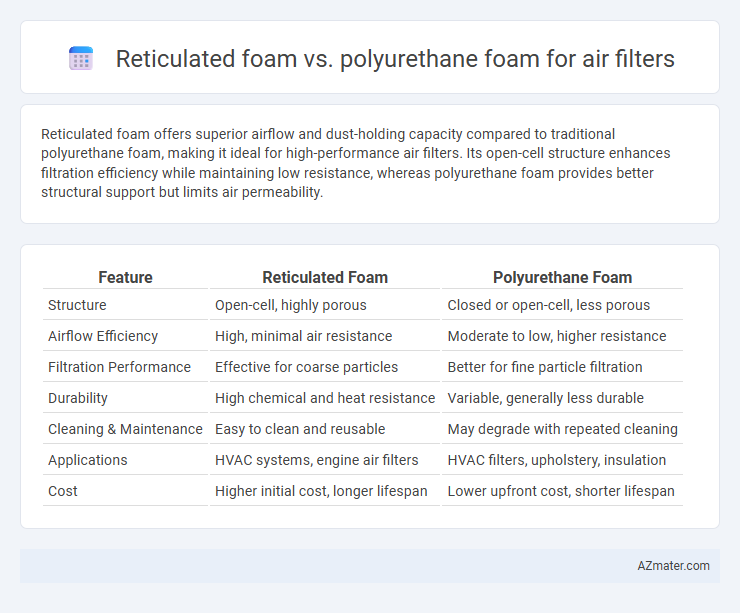
Reticulated foam offers superior airflow and dust-holding capacity compared to traditional polyurethane foam, making it ideal for high-performance air filters. Its open-cell structure enhances filtration efficiency while maintaining low resistance, whereas polyurethane foam provides better structural support but limits air permeability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reticulated Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Open-cell, highly porous | Closed or open-cell, less porous |
| Airflow Efficiency | High, minimal air resistance | Moderate to low, higher resistance |
| Filtration Performance | Effective for coarse particles | Better for fine particle filtration |
| Durability | High chemical and heat resistance | Variable, generally less durable |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy to clean and reusable | May degrade with repeated cleaning |
| Applications | HVAC systems, engine air filters | HVAC filters, upholstery, insulation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, longer lifespan | Lower upfront cost, shorter lifespan |
Introduction to Reticulated and Polyurethane Foams
Reticulated foam features a highly porous, open-cell structure that allows efficient airflow and particle capture, making it ideal for air filtration applications. Polyurethane foam, typically denser with closed or semi-open cells, offers robust mechanical strength and excellent filtration for larger contaminants. Selecting between reticulated and polyurethane foams depends on specific filtration needs regarding airflow resistance, particle size, and durability.
Composition and Structure Differences
Reticulated foam consists of an open-cell network formed by removing cell faces, creating highly porous structures ideal for air filtration due to superior airflow and particle capture. Polyurethane foam features closed-cell or semi-open-cell structures with a denser composition, resulting in lower porosity and reduced permeability compared to reticulated foam. These structural differences impact filtration efficiency, with reticulated foam providing enhanced air permeability and polyurethane foam offering greater mechanical strength and durability.
Porosity and Airflow Efficiency
Reticulated foam features a highly porous structure with interconnected open cells, maximizing airflow efficiency and dust capture in air filters. Polyurethane foam typically has a closed-cell or less open structure, resulting in lower porosity and reduced airflow compared to reticulated foam. Enhanced porosity in reticulated foam improves filtration performance by balancing particle retention with minimal pressure drop.
Filtration Capabilities and Performance
Reticulated foam offers superior airflow and particle capture due to its open-cell structure, making it highly effective in trapping airborne contaminants in air filters. Polyurethane foam provides enhanced durability and higher filtration efficiency for larger particles but may reduce airflow because of its denser composition. For optimal air filter performance, selecting reticulated foam ensures better dust holding capacity and pressure drop characteristics compared to traditional polyurethane foam.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Reticulated foam exhibits superior durability compared to polyurethane foam due to its open-cell structure, which resists clogging and maintains airflow over extended use. Polyurethane foam tends to degrade faster under continuous exposure to dust and moisture, reducing filter lifespan significantly. The inherent resilience of reticulated foam results in longer-lasting air filters with consistent performance in demanding environments.
Applications in Air Filtration Systems
Reticulated foam offers superior airflow and particle retention, making it ideal for high-efficiency air filtration systems in HVAC units, automotive cabin filters, and industrial air purifiers. Polyurethane foam provides excellent cushioning and sound absorption but generally exhibits lower porosity, which limits its effectiveness in fine particle air filtration applications. In air filtration systems requiring both durability and efficient particulate capture, reticulated foam is often preferred due to its open-cell structure and enhanced contaminant trapping capabilities.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Reticulated foam offers superior air filtration due to its open-cell structure, allowing easier removal of trapped particles during maintenance compared to polyurethane foam's denser cellular composition. Cleaning reticulated foam typically involves simple rinsing and air drying, preserving its filtration efficiency without requiring harsh chemicals or extensive drying times. Polyurethane foam, by contrast, tends to retain contaminants more stubbornly, necessitating more frequent replacement or deeper cleaning methods that can degrade its material over time.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Reticulated foam offers superior air filtration efficiency and durability but comes at a higher initial cost compared to polyurethane foam, which is more affordable but less effective in particle retention. Polyurethane foam requires more frequent replacement due to its lower durability, increasing long-term maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, reticulated foam often proves more cost-effective in high-performance applications where filtration quality and lifespan reduce operational costs.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Reticulated foam offers a more environmentally friendly option compared to traditional polyurethane foam due to its open-cell structure, which facilitates easier cleaning and longer lifespan, reducing waste production. Polyurethane foam, while widely used for air filters, often faces challenges in recyclability because it contains mixed polymer components and additives that complicate processing. Choosing reticulated foam enhances sustainability by promoting higher recyclability rates and lowering the environmental footprint associated with filter disposal.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Air Filter Needs
Reticulated foam offers superior airflow and efficient particulate trapping due to its open-cell structure, making it ideal for high-performance air filters requiring maximum ventilation. Polyurethane foam provides enhanced durability and sound absorption, suitable for applications where filtration and noise reduction are both priorities. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing airflow demands with filtration efficiency and environmental conditions specific to your air filter requirements.
Infographic: Reticulated foam vs Polyurethane foam for Air filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com