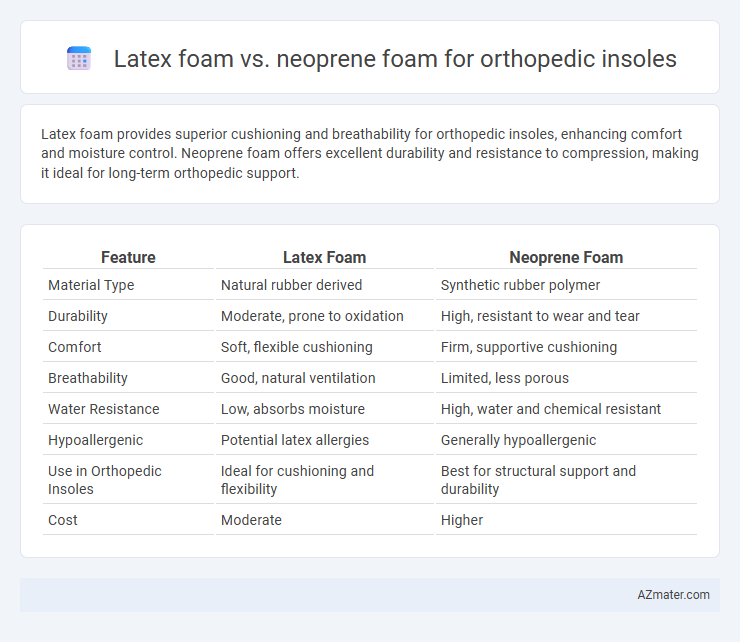
Latex foam provides superior cushioning and breathability for orthopedic insoles, enhancing comfort and moisture control. Neoprene foam offers excellent durability and resistance to compression, making it ideal for long-term orthopedic support.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Latex Foam | Neoprene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural rubber derived | Synthetic rubber polymer |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to oxidation | High, resistant to wear and tear |
| Comfort | Soft, flexible cushioning | Firm, supportive cushioning |
| Breathability | Good, natural ventilation | Limited, less porous |
| Water Resistance | Low, absorbs moisture | High, water and chemical resistant |
| Hypoallergenic | Potential latex allergies | Generally hypoallergenic |
| Use in Orthopedic Insoles | Ideal for cushioning and flexibility | Best for structural support and durability |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Orthopedic Insole Materials
Latex foam offers excellent cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for enhancing comfort in orthopedic insoles while providing natural resistance to microbial growth. Neoprene foam provides superior durability, water resistance, and consistent support, which helps maintain structural integrity in orthopedic applications. Both materials are chosen for their unique properties that address the specific needs of foot support, pressure distribution, and long-term wear in orthopedic insoles.
What is Latex Foam?
Latex foam is a natural material derived from the sap of rubber trees, valued for its excellent elasticity, breathability, and durability in orthopedic insoles. Its open-cell structure allows for superior air circulation and moisture wicking, reducing foot odor and enhancing comfort during extended wear. Latex foam provides responsive cushioning that adapts to foot contours, offering enhanced pressure distribution and support for orthopedic applications.
What is Neoprene Foam?
Neoprene foam is a synthetic rubber material known for its excellent durability, flexibility, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for orthopedic insoles that require cushioning and support. It offers superior shock absorption and insulation, helping to reduce foot fatigue and provide comfort during prolonged use. Unlike latex foam, neoprene foam maintains its structural integrity over time, making it a preferred choice for orthopedic applications where long-lasting support is essential.
Comfort and Cushioning Comparison
Latex foam offers superior breathability and resilience, providing enhanced comfort and long-lasting cushioning for orthopedic insoles. Neoprene foam excels in moisture resistance and shock absorption, making it ideal for high-impact support but may retain heat during extended wear. The choice between latex and neoprene foam depends on the user's need for temperature regulation and cushioning durability in orthopedic applications.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Latex foam offers excellent elasticity and resilience, making it durable for orthopedic insoles but prone to degradation over time due to moisture and sweat absorption. Neoprene foam provides superior resistance to wear, moisture, and chemical breakdown, resulting in longer-lasting orthopedic insoles with stable cushioning properties. In durability and longevity analysis, neoprene foam generally outperforms latex foam, maintaining structural integrity and support in demanding environments.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Latex foam offers superior breathability and moisture management due to its open-cell structure that promotes air circulation and helps wick away sweat, keeping feet dry and comfortable. Neoprene foam, while durable and cushioning, has a closed-cell composition that limits airflow and traps moisture, potentially leading to increased heat and discomfort during extended wear. Orthopedic insoles made with latex foam are thus preferred for enhanced ventilation and moisture control, reducing the risk of odor and skin irritation.
Support and Shock Absorption
Latex foam offers superior shock absorption due to its natural elasticity and resilience, effectively reducing impact forces on joints. Neoprene foam provides excellent support with its durable, dense structure, maintaining stability during prolonged wear. For orthopedic insoles, latex foam enhances cushioning comfort while neoprene foam ensures consistent support and pressure distribution.
Allergy Concerns and Skin Sensitivity
Latex foam, derived from natural rubber, often triggers allergic reactions in sensitive individuals due to its proteins, making it less suitable for those with latex allergies or sensitive skin. Neoprene foam is a synthetic material hypoallergenic by nature, thereby reducing the risk of irritation and allergic responses in orthopedic insoles. Choosing neoprene foam improves comfort and safety for patients prone to dermatitis or inflammatory skin conditions.
Cost and Availability
Latex foam offers moderate affordability and is widely available due to its natural latex origins and common use in orthopedic insoles. Neoprene foam tends to be more expensive because of its synthetic production process but is also readily accessible through specialized suppliers. The choice between latex and neoprene foams depends largely on budget constraints and sourcing preferences within the orthopedic insole market.
Which Foam Is Best for Orthopedic Insoles?
Latex foam offers superior cushioning and resilience for orthopedic insoles, providing excellent shock absorption and natural breathability, which helps prevent moisture build-up and foot discomfort. Neoprene foam excels in durability and water resistance, making it ideal for insoles requiring long-term support and protection in moist environments. Choosing the best foam depends on the specific orthopedic needs, with latex foam favored for comfort and flexibility, while neoprene is preferred for structural support and durability.
Infographic: Latex foam vs Neoprene foam for Orthopedic insole
 azmater.com
azmater.com