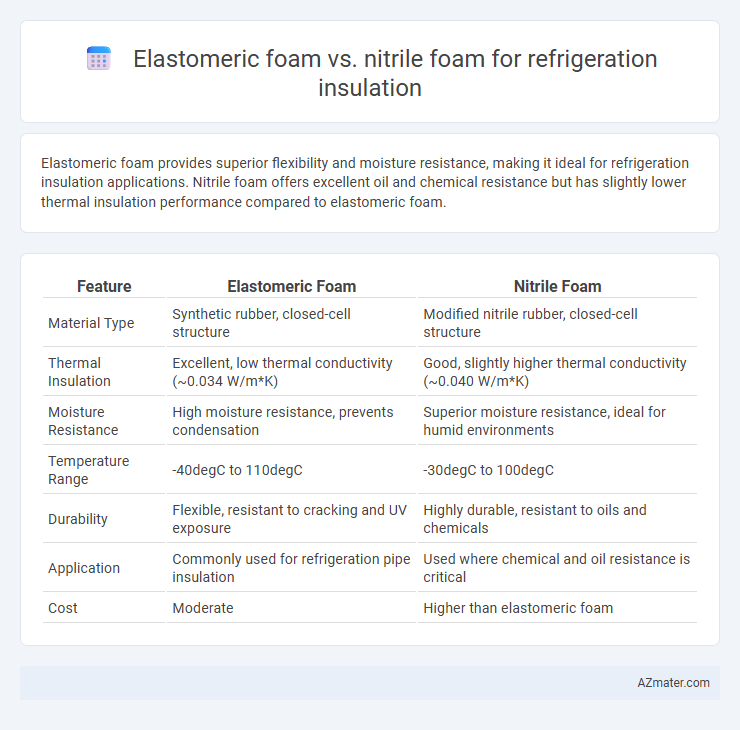
Elastomeric foam provides superior flexibility and moisture resistance, making it ideal for refrigeration insulation applications. Nitrile foam offers excellent oil and chemical resistance but has slightly lower thermal insulation performance compared to elastomeric foam.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elastomeric Foam | Nitrile Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic rubber, closed-cell structure | Modified nitrile rubber, closed-cell structure |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, low thermal conductivity (~0.034 W/m*K) | Good, slightly higher thermal conductivity (~0.040 W/m*K) |
| Moisture Resistance | High moisture resistance, prevents condensation | Superior moisture resistance, ideal for humid environments |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 110degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Durability | Flexible, resistant to cracking and UV exposure | Highly durable, resistant to oils and chemicals |
| Application | Commonly used for refrigeration pipe insulation | Used where chemical and oil resistance is critical |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher than elastomeric foam |
Introduction to Refrigeration Insulation Materials
Refrigeration insulation materials are critical for maintaining thermal efficiency and preventing energy loss in cooling systems. Elastomeric foam offers excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and long-term durability, making it ideal for refrigeration applications. Nitrile foam provides superior chemical and oil resistance, enhancing performance in environments where exposure to oils and refrigerants is common, but it may have less flexibility compared to elastomeric options.
What is Elastomeric Foam?
Elastomeric foam is a flexible, closed-cell insulation material made from synthetic rubber, widely used in refrigeration systems for its excellent thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties. It offers superior durability, compressive strength, and resistance to mold and UV degradation compared to nitrile foam. Elastomeric foam's effective insulation performance and ease of installation make it a preferred choice for minimizing energy loss and preventing condensation in refrigeration applications.
What is Nitrile Foam?
Nitrile foam is a closed-cell elastomeric insulation material known for its excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and fuel, making it ideal for refrigeration systems where durability and performance are crucial. It features high thermal insulation properties with low thermal conductivity, effectively preventing heat transfer and condensation in refrigeration applications. The foam's flexibility and resistance to compression set ensure long-term sealing and energy efficiency in HVAC and refrigeration piping.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Elastomeric foam offers superior thermal insulation with low thermal conductivity values typically around 0.030 to 0.040 W/m*K, making it highly efficient for refrigeration systems. Nitrile foam insulation provides adequate thermal resistance but generally exhibits higher thermal conductivity, often in the range of 0.035 to 0.050 W/m*K, reducing its effectiveness in minimizing heat transfer. The closed-cell structure of elastomeric foam enhances moisture resistance and thermal stability, contributing to better overall performance in refrigeration applications compared to nitrile foam.
Moisture Resistance and Water Vapor Permeability
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior moisture resistance with a closed-cell structure that effectively prevents water ingress, making it ideal for refrigeration insulation where humidity control is critical. Nitrile foam, while offering moderate moisture resistance, generally has higher water vapor permeability, which can allow more moisture transmission and potentially compromise insulation performance over time. For applications requiring stringent moisture barriers and enhanced thermal properties, elastomeric foam is typically preferred due to its lower water vapor permeability and better durability in refrigerated environments.
Fire Resistance and Safety Standards
Elastomeric foam offers superior fire resistance with a low flame spread index and self-extinguishing properties, making it compliant with stringent fire safety standards such as UL 94 and ASTM E84. Nitrile foam, while providing good thermal insulation, typically exhibits lower fire resistance and may require additional treatments to meet similar safety criteria. For refrigeration insulation, elastomeric foam ensures enhanced safety by reducing fire hazards and meeting regulatory requirements critical in commercial and industrial applications.
Durability and Service Life
Elastomeric foam provides superior durability and a longer service life in refrigeration insulation due to its closed-cell structure, which resists moisture absorption and maintains thermal performance over time. Nitrile foam offers good chemical resistance and flexibility but tends to degrade faster in harsh conditions, leading to shorter service life compared to elastomeric foam. The consistent resilience and aging resistance of elastomeric foam make it the preferred choice for long-term refrigeration insulation applications.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and lightweight properties, enabling easier cutting and fitting around complex refrigeration components, which reduces installation time and effort. Nitrile foam provides excellent chemical resistance and durability, requiring less frequent maintenance in harsh environments but can be stiffer, making installation more challenging. Maintenance of elastomeric foam is simplified by its closed-cell structure that resists moisture absorption, while nitrile foam's resilience to oils and solvents ensures long-term performance in industrial refrigeration settings.
Cost Considerations
Elastomeric foam generally offers a higher upfront cost compared to nitrile foam but delivers superior thermal insulation and durability, leading to lower lifecycle expenses in refrigeration applications. Nitrile foam provides a cost-effective initial investment with good resistance to oils and chemicals but may require more frequent replacement due to lower thermal performance and reduced flexibility in low temperatures. Evaluating total cost of ownership, elastomeric foam often proves more economical for long-term refrigeration insulation where energy efficiency and longevity are critical.
Best Applications: Elastomeric vs Nitrile Foam
Elastomeric foam is ideal for refrigeration insulation due to its closed-cell structure, providing superior thermal resistance and moisture vapor control in HVAC systems and chilled water piping. Nitrile foam, with enhanced oil and chemical resistance, is preferred in refrigeration applications involving exposure to lubricants or refrigerants containing hydrocarbons. Choosing elastomeric foam ensures effective condensation control and energy efficiency, while nitrile foam excels in environments requiring robust mechanical and chemical durability.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Nitrile foam for Refrigeration insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com